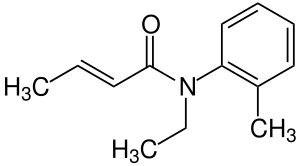
Crotamiton
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Main uses | Scabies, lice, itching[1] |
| Side effects | Rash, allergic reactions[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H17NO |
| Molar mass | 203.285 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Crotamiton, sold under the brand name Eurax among others, is a used to treat scabies, lice, and itching.[1] For scabies it appear to work less well compared to permethrin.[1] It is applied to the skin.[2]
Common side effects include rash and allergic reactions.[1] Safety in pregnancy is unclear.[2] Its mechanism of action is unknown.[1]
Crotamiton has been approved in the United States for medical use since at least 1949.[1] In the United Kingdom 100 grams of cream costs the NHS about £4.[2] In the United States 60 grams costs about 500 USD.[3]
Medical use
For treating scabies, crotamiton should be applied to the whole body rather than a localized area. It is applied two or three times, with a 24-hour delay between applications, and the patient is asked to take a shower no sooner than after 48 hours. For children under 3 years, it is applied once daily. It can also be used to treat itching stemming from other causes, e.g. insect bites, in which case it is applied to the itching areas only, and repeated if necessary after 4 to 8 hours. Use near the eyes, or breaks in the skin, should be avoided.
Side effects
The most common side effect of crotamiton is skin irritation.
Pharmacology
Crotamiton is toxic to the scabies mite,[4] The mechanism of action of crotamiton as a general antipruritic was reported, in which crotamiton inhibits TRPV4 (transient receptor potential vanilloid 4) channel that is expressed in the skin, primary sensory neurons, and so on.[5]
Pharmacokinetics
After topical application, crotamiton is absorbed systemically. It has an elimination half-life of 30.9 hours and 4.8-8.8% is excreted in the urine.[6]
Trade name
Crotamiton is marketed under the trade names Eurax, which is manufactured by Ranbaxy Laboratories in the United States, and GlaxoSmithKline in the United Kingdom, and Euracin, which is manufactured by Green Cross in South Korea. In Germany, it is marketed under the brand name Crotamitex. In India, it is sold as Eurax by Ranbaxy Laboratories.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Crotamiton Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 30 June 2019. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 1309. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ "Crotamiton Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ↑ "Crotamiton: mechanism of action". Medscape Drug Information. Archived from the original on 2019-12-16. Retrieved 2020-06-19.
- ↑ Kittaka H, Yamanoi Y, Tominaga M (October 2017). "Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) channel as a target of crotamiton and its bimodal effects". Pflugers Archiv. 469 (10): 1313–1323. doi:10.1007/s00424-017-1998-7. PMID 28612138. S2CID 4059914.
- ↑ "Crotamiton: pharmacokinetics". Medscape Drug Information. Archived from the original on 2020-04-14. Retrieved 2020-06-19.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|