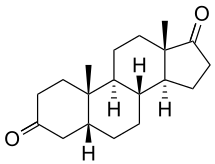
Etiocholanedione
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3aS,3bR,5aR,9aS,9bS,11aS)-9a,11a-Dimethyltetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-1,7(3bH)-dione | |
| Other names
Etiocholane-3,17-dione; 5β-Androstanedione; 5β-Androstane-3,17-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C19H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 288.431 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Etiocholanedione, also known as 5β-androstanedione or as etiocholane-3,17-dione, is a naturally occurring etiocholane (5β-androstane) steroid and an endogenous metabolite of androgens like testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and androstenedione.[1] It is the C5 epimer of androstanedione (5α-androstanedione).[1] Although devoid of androgenic activity like other 5β-reduced steroids, etiocholanedione has some biological activity of its own.[2][3] The compound has been found to possess potent haematopoietic effects in a variety of models.[2] In addition, it has been found to promote weight loss in animals and in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study in humans conducted in 1993.[3][4] These effects are said to be similar to those of DHEA.[5] Unlike DHEA however, etiocholanedione cannot be metabolized further into steroid hormones like androgens and estrogens.[5]
References
- 1 2 "Human Metabolome Database: Showing metabocard for Etiocholanedione (HMDB0003769)". hmdb.ca. Retrieved 2018-07-13.
- 1 2 Bradlow HL, Murphy J, Byrne JJ (June 1999). "Immunological properties of dehydroepiandrosterone, its conjugates, and metabolites". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 876: 91–101. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07627.x. PMID 10415598.
- 1 2 Douglas McKeag; James L. Moeller (2007). ACSM's Primary Care Sports Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 616–. ISBN 978-0-7817-7028-6.
- ↑ James M. Rippe (15 March 2013). Lifestyle Medicine, Second Edition. CRC Press. pp. 559–. ISBN 978-1-4398-4544-8.
- 1 2 Clore JN (November 1995). "Dehydroepiandrosterone and body fat". Obes. Res. 3 Suppl 4: 613S–616S. doi:10.1002/j.1550-8528.1995.tb00234.x. PMID 8697065.
External links