GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant
| GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Hexosaminidase activator deficiency[1] | |
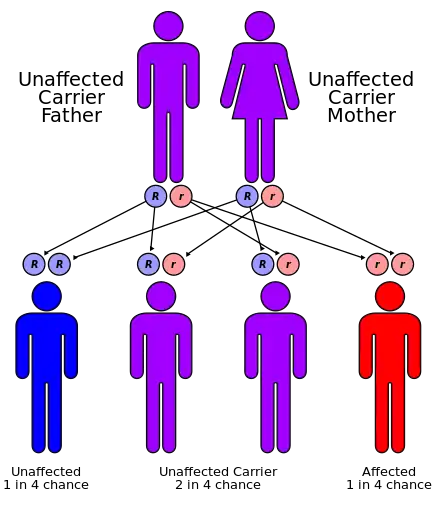 | |
| GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. | |
GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant is a rare, autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that causes progressive destruction of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. It has a similar pathology to Sandhoff disease and Tay–Sachs disease. The three diseases are classified together as the GM2 gangliosidoses, because each disease represents a distinct molecular point of failure in the activation of the same enzyme, beta-hexosaminidase. AB variant is caused by a failure in the gene that makes an enzyme cofactor for beta-hexosaminidase, called the GM2 activator.[2][3]
Symptoms and signs
Signs and symptoms of GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant are identical with those of infantile Tay–Sachs disease, except that enzyme assay testing shows normal levels of hexosaminidase A.[2] Infantile Sandhoff disease has similar symptoms and prognosis, except that there is deficiency of both hexosaminidase A and hexosaminidase B. Infants with this disorder typically appear normal until the age of 3 to 6 months, when development slows and muscles used for movement weaken. Affected infants lose motor skills such as turning over, sitting, and crawling. As the disease progresses, infants develop seizures, vision and hearing loss, mental retardation, and paralysis.[4]
An ophthalmological abnormality called a cherry-red spot, which can be identified with an eye examination, is characteristic of this disorder. This cherry-red spot is the same finding that Warren Tay first reported in 1881, when he identified a case of Tay–Sachs disease, and it has the same etiology.[5]
The prognosis for AB variant is the same as for infantile Tay–Sachs disease. Children with AB variant die in infancy or early childhood.
Cause
Mutations in the GM2A gene cause GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant. This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
The GM2A gene provides instructions for making a protein called the GM2 activator. This protein is required for the normal function of beta-hexosaminidase A, a critical enzyme in the nervous system that breaks down a lipid called GM2 ganglioside. If mutations in both alleles at this locus disrupt the activity of the GM2 activator, beta-hexosaminidase A cannot perform its normal function. As a result, gangliosides accumulate in the central nervous system until they interfere with normal biological processes. Progressive damage caused by buildup of gangliosides leads to the destruction of nerve cells.[2][3]
GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant is extremely rare. In contrast with both Tay–Sachs disease and Sandhoff disease, in which many mutant polymorphic alleles have been discovered, including pseudodeficiency alleles, very few GM2A mutations have been reported. When AB variant is reported, in often occurs with consanguineous parents or in genetically isolated populations.[2]
GM2A is expressed in many tissues, and the GM2 activator protein has been reported to have other cellular functions. Because AB variant is so rarely diagnosed, it is likely that most mutations of GM2A are fatal at the embryonic or fetal stage of development in homozygotes and genetic compounds, and thus are never observed clinically.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant is based on, but not limited to the following:[6]
- Medical history
- Physical exam
Treatment
There are no therapies for the treatment of the GM2 Gangliosidosis.[7]
History
AB variant was first observed clinically shortly after the biochemical characterization of Tay–Sachs disease in 1969. The disease was initially thought to be caused by variant alleles of the HEXA gene, and Konrad Sandhoff designated it as AB variant in 1971.[8] Enzyme assay tests of TSD patients revealed a few unusual false negative cases, patients who developed the disease, yet had normal enzyme activity. In other cases, parents who had not tested as carriers for TSD had children who nevertheless became ill with the symptoms of classic infantile TSD.[9]
It was eventually determined that GM2 gangliosidosis could be caused by mutations on three distinct genes, one of which was an activator protein. Disease caused by a mutation that disables this protein was termed AB variant.[10] In 1992, the GM2A gene itself was localized to chromosome 5,[11] and the precise locus was determined the following year.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: GM2 gangliosidosis, AB variant". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 30 April 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man". United States National Institute of Health. Archived from the original on 2009-05-28. Retrieved 2009-04-21.
- 1 2 Mahuran, Dj (Oct 1999). "Biochemical consequences of mutations causing the GM2 gangliosidoses". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 1455 (2–3): 105–38. doi:10.1016/S0925-4439(99)00074-5. ISSN 0006-3002. PMID 10571007.
- ↑ "Sandhoff disease". NCBI MedGen. NCBI. Archived from the original on 2 May 2021. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ↑ Aragao, Ricardo E. M. (August 2009). ""Cherry red spot" in a patient with Tay-Sachs disease: Case report". Arquivos Brasileiros de Oftalmologia. 72 (4): 537–9. doi:10.1590/S0004-27492009000400019. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ↑ "GM2-gangliosidosis, B, B1, AB variant - Diagnosis & Treatment - Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Retrieved 18 June 2022.
- ↑ Patterson, Marc C. (2013-01-01), Dulac, Olivier; Lassonde, Maryse; Sarnat, Harvey B. (eds.), "Chapter 174 - Gangliosidoses", Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Pediatric Neurology Part III, Elsevier, vol. 113, pp. 1707–1708, archived from the original on 2019-08-01, retrieved 2019-08-01
- ↑ Sandhoff K, Harzer K, Wassle W, Jatzkewitz H (Nov 1971). "Enzyme alterations and lipid storage in three variants of Tay–Sachs disease". Journal of Neurochemistry. 18 (12): 2469–2489. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00204.x. PMID 5135907. S2CID 28107036.
- ↑ O'Brien JS, Tennant L, Veath ML, Scott CR, Bucknall WE (Nov 1978). "Characterization of unusual hexosaminidase A (HEX A) deficient human mutants". American Journal of Human Genetics. 30 (6): 602–608. PMC 1685872. PMID 747188.
- ↑ O'Brien JS (1983). "The Gangliosidoses". In Stanbury JB; et al. (eds.). The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. New York: McGraw Hill. pp. 945–969. ISBN 0-07-060726-5.
- ↑ Xie b, M. B.; McInnes, B.; Neote, K.; Lamhonwah, A. M.; Mahuran, D. (Jun 1991). "Isolation and expression of a full-length cDNA encoding the human GM2 activator protein". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 177 (3): 1217–1223. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(91)90671-S. ISSN 0006-291X. PMID 2059210.
External links
| Classification |
|
|---|---|
| External resources |