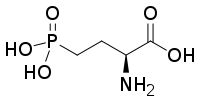
L-AP4
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | L-2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.384 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C4H10NO5P |
| Molar mass | 183.100 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
L-AP4 (L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid) is a drug used in scientific research, which acts as a group-selective agonist for the group III metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR4/6/7/8). It was the first ligand found to act as an agonist selective for this group of mGlu receptors,[1] but does not show selectivity between the different mGluR Group III subtypes. It is widely used in the study of this receptor family and their various functions.[2][3][4][5]
References
- ↑ Thomsen C (August 1997). "The L-AP4 receptor". General Pharmacology. 29 (2): 151–8. doi:10.1016/S0306-3623(96)00417-X. PMID 9251893.
- ↑ Lopez S, Turle-Lorenzo N, Acher F, De Leonibus E, Mele A, Amalric M (June 2007). "Targeting group III metabotropic glutamate receptors produces complex behavioral effects in rodent models of Parkinson's disease". The Journal of Neuroscience. 27 (25): 6701–11. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0299-07.2007. PMC 6672706. PMID 17581957.
- ↑ Macinnes N, Duty S (February 2008). "Group III metabotropic glutamate receptors act as hetero-receptors modulating evoked GABA release in the globus pallidus in vivo". European Journal of Pharmacology. 580 (1–2): 95–9. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.10.030. PMID 18035348.
- ↑ Zhang HM, Chen SR, Pan HL (January 2009). "Effects of activation of group III metabotropic glutamate receptors on spinal synaptic transmission in a rat model of neuropathic pain". Neuroscience. 158 (2): 875–84. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.10.042. PMC 2649787. PMID 19017536.
- ↑ Maciejak P, Szyndler J, Turzyńska D, Sobolewska A, Taracha E, Skórzewska A, et al. (July 2009). "The effects of group III mGluR ligands on pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling of seizures and hippocampal amino acids concentration". Brain Research. 1282: 20–7. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.05.049. PMID 19481536. S2CID 20844494.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.