Native American disease and epidemics
| Part of a series on |
| Native Americans |
|---|
Although a variety of infectious diseases existed in the Americas in pre-Columbian times,[1] the limited size of the populations, smaller number of domesticated animals with zoonotic diseases, and limited interactions between those populations (as compared to areas of Europe and Asia) hampered the transmission of communicable diseases. One notable infectious disease of American origin is syphilis.[1] Aside from that, most of the major infectious diseases known today originated in the Old World (Africa, Asia, and Europe). The American era of limited infectious disease ended with the arrival of Europeans in the Americas and the Columbian exchange of microorganisms, including those that cause human diseases. Eurasian infections and epidemics had major effects on Native American life in the colonial period and nineteenth century, especially.
Europe was a crossroads among many distant, different peoples separated by hundreds, if not thousands, of miles. But repeated warfare by invading populations spread infectious disease throughout the continent, as did trade, including the Silk Road. For more than 1,000 years travelers brought goods and infectious diseases from the East, where some of the latter had jumped from animals to humans. As a result of chronic exposure, many infections became endemic within their societies over time, so that surviving Europeans gradually developed some acquired immunity, although they were still subject to pandemics and epidemics. Europeans carried such endemic diseases when they migrated and explored the New World.
Native Americans often contracted infectious disease through trading and exploration contacts with Europeans, and these were transmitted far from the sources and colonial settlements, through exclusively Native American trading transactions. Warfare and enslavement also contributed to disease transmission. Because their populations had not been previously exposed to most of these infectious diseases, the indigenous people rarely had individual or population acquired immunity and consequently suffered very high mortality. The numerous deaths disrupted Native American societies. This phenomenon is known as the virgin soil effect.[2]
European contact


The arrival and settlement of Europeans in the Americas resulted in what is known as the Columbian exchange. During this period European settlers brought many different technologies, animals, plants, and lifestyles with them, some of which benefited the indigenous peoples. Europeans also took plants and goods back to the Old World. Potatoes and tomatoes from the Americas became integral to European and Asian cuisines, for instance.[3]
But Europeans also unintentionally brought new infectious diseases, including smallpox, bubonic plague, chickenpox, cholera, the common cold, diphtheria, influenza, malaria, measles, scarlet fever, sexually transmitted diseases (with the possible exception of syphilis), typhoid, typhus, tuberculosis (although a form of this infection existed in South America prior to contact),[4] and pertussis.[5][6][7] Each of these resulted in sweeping epidemics among Native Americans, who suffered disability, illness, and a high mortality rate.[7] The Europeans infected with such diseases typically carried them in a dormant state, were actively infected but asymptomatic, or had only mild symptoms, because Europe had been subject for centuries to a selective process by these diseases. The explorers and colonists often unknowingly passed the diseases to natives.[3] The introduction of African slaves and the use of commercial trade routes contributed to the spread of disease.[8][9]
The infections brought by Europeans are not easily tracked, since there were numerous outbreaks and all were not equally recorded. Historical accounts of epidemics are often vague or contradictory in describing how victims were affected. A rash accompanied by a fever might be smallpox, measles, scarlet fever, or varicella, and many epidemics overlapped with multiple infections striking the same population at once, therefore it is often impossible to know the exact causes of mortality (although ancient DNA studies can often determine the presence of certain microbes).[10] Smallpox was the disease brought by Europeans that was most destructive to the Native Americans, both in terms of morbidity and mortality. The first well-documented smallpox epidemic in the Americas began in Hispaniola in late 1518 and soon spread to Mexico.[3] Estimates of mortality range from one-quarter to one-half of the population of central Mexico.[11]
Native Americans initially believed that illness primarily resulted from being out of balance, in relation to their religious beliefs. Typically, Native Americans held that disease was caused by either a lack of magical protection, the intrusion of an object into the body by means of sorcery, or the absence of the free soul from the body. Disease was understood to enter the body as a natural occurrence if a person was not protected by spirits, or less commonly as a result of malign human or supernatural intervention.[12] For example, Cherokee spiritual beliefs attribute disease to revenge imposed by animals for killing them.[13] In some cases, disease was seen as a punishment for disregarding tribal traditions or disobeying tribal rituals.[14] Spiritual powers were called on to cure diseases through the practice of shamanism.[15] Most Native American tribes also used a wide variety of medicinal plants and other substances in the treatment of disease.[16]
Smallpox
Smallpox was lethal to many Native Americans, resulting in sweeping epidemics and repeatedly affecting the same tribes. After its introduction to Mexico in 1519, the disease spread across South America, devastating indigenous populations in what are now Colombia, Peru and Chile during the sixteenth century. The disease was slow to spread northward due to the sparse population of the northern Mexico desert region. It was introduced to eastern North America separately by colonists arriving in 1633 to Plymouth, Massachusetts, and local Native American communities were soon struck by the virus. It reached the Mohawk nation in 1634,[17] the Lake Ontario area in 1636, and the lands of other Iroquois tribes by 1679.[18] Between 1613 and 1690 the Iroquois tribes living in Quebec suffered twenty-four epidemics, almost all of them caused by smallpox.[19] By 1698 the virus had crossed the Mississippi, causing an epidemic that nearly obliterated the Quapaw Indians of Arkansas.[14]
The disease was often spread during war. John McCullough, a Delaware captive since July 1756, who was then 15 years old, wrote that the Lenape people, under the leadership of Shamokin Daniel, "committed several depredations along the Juniata; it happened to be at a time when the smallpox was in the settlement where they were murdering, the consequence was, a number of them got infected, and some died before they got home, others shortly after; those who took it after their return, were immediately moved out of the town, and put under the care of one who had the disease before."[20][21][22][23]
By the mid-eighteenth century the disease was affecting populations severely enough to interrupt trade and negotiations. Thomas Hutchins, in his August 1762 journal entry while at Ohio's Fort Miami, named for the Mineamie people, wrote:
The 20th, The above Indians met, and the Ouiatanon Chief spoke in behalf of his and the Kickaupoo Nations as follows: "Brother, We are very thankful to Sir William Johnson for sending you to enquire into the State of the Indians. We assure you we are Rendered very miserable at Present on Account of a Severe Sickness that has seiz'd almost all our People, many of which have died lately, and many more likely to Die..." The 30th, Set out for the Lower Shawneese Town and arriv'd 8th of September in the afternoon. I could not have a meeting with the Shawneese the 12th, as their People were Sick and Dying every day.[24]
On June 24, 1763, during the siege of Fort Pitt, as recorded in his journal by fur trader and militia captain William Trent, dignitaries from the Delaware tribe met with Fort Pitt officials, warned them of "great numbers of Indians" coming to attack the fort, and pleaded with them to leave the fort while there was still time. The commander of the fort refused to abandon the fort. Instead, the British gave as gifts two blankets, one silk handkerchief and one linen from the smallpox hospital, to the two Delaware emissaries Turtleheart and Mamaltee, allegedly in the hope of spreading the deadly disease to nearby tribes, as attested in Trent's journal.[25][26][27][28][29] The dignitaries were met again later and they seemingly hadn't contracted smallpox.[30] A relatively small outbreak of smallpox had begun spreading earlier that spring, with a hundred dying from it among Native American tribes in the Ohio Valley and Great Lakes area through 1763 and 1764.[30] The effectiveness of the biological warfare itself remains unknown, and the method used is inefficient compared to airborne transmission.[31][32]
21st-century scientists such as V. Barras and G. Greub have examined such reports. They say that smallpox is spread by respiratory droplets in personal interaction, not by contact with fomites, such objects as were described by Trent. The results of such attempts to spread the disease through objects are difficult to differentiate from naturally occurring epidemics.[33][34]
Gershom Hicks, held captive by the Ohio Country Shawnee and Delaware between May 1763 and April 1764, reported to Captain William Grant of the 42nd Regiment "that the Small pox has been very general & raging amongst the Indians since last spring and that 30 or 40 Mingoes, as many Delawares and some Shawneese Died all of the Small pox since that time, that it still continues amongst them".[35]
In the mid to late nineteenth century, at a time of increasing European-American travel and settlement in the West, at least four different epidemics broke out among the Plains tribes between 1837 and 1870.[5] When the Plains tribes began to learn of the "white man’s diseases", many intentionally avoided contact with them and their trade goods. But the lure of trade goods such as metal pots, skillets, and knives sometimes proved too strong. The Indians traded with the white newcomers anyway and inadvertently spread disease to their villages.[36] In the late 19th century, the Lakota Indians of the Plains called the disease the "rotting face sickness".[14][36]
The 1862 Pacific Northwest smallpox epidemic, which was brought from San Francisco to Victoria, devastated the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, with a death rate of over 50% for the entire coast from Puget Sound to Southeast Alaska.[37] In some areas the native population fell by as much as 90%.[38][39] That the Colony of Vancouver Island and the Colony of British Columbia could have prevented the epidemic but chose not to, and in some ways facilitated the epidemic, has caused some historians to describe the epidemic as an example of deliberate genocide.[38][40]
Effect on population numbers
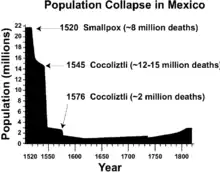
Many Native American tribes suffered high mortality and depopulation, averaging 25–50% of the tribes' members lost to disease. Additionally, some smaller tribes neared extinction after facing a severely destructive spread of disease.[5]
A specific example was what followed Cortés' invasion of Mexico. Before his arrival, the Mexican population is estimated to have been around 25 to 30 million. Fifty years later, the Mexican population was reduced to 3 million, mainly by infectious disease. A 2018 study by Koch, Brierley, Maslin and Lewis concluded that an estimated "55 million indigenous people died following the European conquest of the Americas beginning in 1492."[41] By 1700, fewer than 5,000 Native Americans remained in the southeastern coastal region of the United States.[7] In Florida alone, an estimated 700,000 Native Americans lived there in 1520, but by 1700 the number was around 2,000.[7]
Some 21st-century climate scientists have suggested that a severe reduction of the indigenous population in the Americas and the accompanying reduction in cultivated lands during the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries may have contributed to a global cooling event known as the Little Ice Age.[41][42]
The loss of the population was so high that it was partially responsible for the myth of the Americas as "virgin wilderness". By the time significant European colonization was underway, native populations had already been reduced by 90%. This resulted in settlements vanishing and cultivated fields being abandoned. Since forests were recovering, the colonists had an impression of a land that was an untamed wilderness.[43]
Disease had both direct and indirect effects on deaths. High mortality meant that there were fewer people to plant crops, hunt game, and otherwise support the group. Loss of cultural knowledge transfer also affected the community as vital agricultural and food-gathering skills were not passed on to survivors. Missing the right time to hunt or plant crops affected the food supply, thus further weakening the community and making it more vulnerable to the next epidemic. Communities under such crisis were often unable to care for the disabled, elderly, or young.[7]
In summer 1639, a smallpox epidemic struck the Huron natives in the St. Lawrence and Great Lakes regions. The disease had reached the Huron tribes through French colonial traders from Québec who remained in the region throughout the winter. When the epidemic was over, the Huron population had been reduced to roughly 9000 people, about half of what it had been before 1634.[44] The Iroquois people, generally south of the Great Lakes, faced similar losses after encounters with French, Dutch and English colonists.[7]
During the 1770s, smallpox killed at least 30% of the West Coast Native Americans.[45] The smallpox epidemic of 1780–1782 brought devastation and drastic depopulation among the Plains Indians.[46]
By 1832, the federal government of the United States established a smallpox vaccination program for Native Americans.[47] The Commissioner of Indian Affairs in 1839 reported on the casualties of the 1837 Great Plains smallpox epidemic: "No attempt has been made to count the victims, nor is it possible to reckon them in any of these tribes with accuracy; it is believed that if [the number 17,200 for the upper Missouri River Indians] was doubled, the aggregate would not be too large for those who have fallen east of the Rocky Mountains."[48]
Historian David Stannard asserts that by "focusing almost entirely on disease ... contemporary authors increasingly have created the impression that the eradication of those tens of millions of people was inadvertent—a sad, but both inevitable and 'unintended consequence' of human migration and progress." He says that their destruction "was neither inadvertent nor inevitable", but the result of microbial pestilence and purposeful genocide working in tandem.[49] Historian Andrés Reséndez says that evidence suggests "among these human factors, slavery has emerged as a major killer" of the indigenous populations of the Caribbean between 1492 and 1550, rather than diseases such as smallpox, influenza and malaria.[50]
Disability
Epidemics killed a high portion of people with disabilities and also resulted in numerous people with disabilities. The material and societal realities of disability for Native American communities were tangible.[7] Scarlet fever could result in blindness or deafness, and sometimes both.[7] Smallpox epidemics led to blindness and depigmented scars. Many Native American tribes prided themselves in their appearance, and the resulting skin disfigurement of smallpox deeply affected them psychologically. Unable to cope with this condition, tribe members were said to have committed suicide.[51]
See also
- Little Ice Age
- New World Syndrome
- Alcohol and Native Americans
- Native American health
- Environmental racism
- Impact of Old World diseases on the Maya
- History of smallpox in Mexico
- 1918 Spanish flu pandemic
- COVID-19 pandemic in the Navajo Nation
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on Native American tribes and tribal communities
General:
- Native Americans in the United States
- Population history of indigenous peoples of the Americas
References
- 1 2 Martin, Debra L; Goodman, Alan H (January 2002). "Health conditions before Columbus: paleopathology of native North Americans". Western Journal of Medicine. 176 (1): 65–68. doi:10.1136/ewjm.176.1.65. ISSN 0093-0415. PMC 1071659. PMID 11788545.
- ↑ Crosby, Alfred W. (1976), "Virgin Soil Epidemics as a Factor in the Aboriginal Depopulation in America", The William and Mary Quarterly, Omohundro Institute of Early American History and Culture, 33 (2): 289–299, doi:10.2307/1922166, JSTOR 1922166, PMID 11633588
- 1 2 3 Francis, John M. (2005). Iberia and the Americas culture, politics, and history: A Multidisciplinary Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO.
- ↑ Bos, Kirsten I.; Harkins, Kelly M.; Herbig, Alexander; Coscolla, Mireia; et al. (20 August 2014). "Pre-Columbian mycobacterial genomes reveal seals as a source of New World human tuberculosis". Nature. 514 (7523): 494–7. Bibcode:2014Natur.514..494B. doi:10.1038/nature13591. PMC 4550673. PMID 25141181.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|last1= - 1 2 3 Waldman, Carl (2009). Atlas of the North American Indian. New York: Checkmark Books. p. 206.
- ↑ Rossi, Ann (2006). Two Cultures Meet: Native American and European. National Geographic Society. pp. 31–32. ISBN 978-0-7922-8679-0.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Nielsen, K.E. (2012). A Disability History of the United States. Beacon Press. ISBN 978-0-8070-2204-7.
- ↑ Rodrigo Barquera, Johannes Krause, AJ Zeilstra, Petra Mader, "Slavery entailed the spread of epidemics," Max-Planck-Gesellschaft, May 09, 2020
- ↑ Tine Huyse, "The Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade and the Introduction of Human Diseases: The Case of Schistosomiasis," Africa Atlanta 2014 Publications, Ivan Allen College of Liberal Arts, Georgia Institute of Technology, May 2014
- ↑ Austin Alchon, Suzanne (2003). A Pest in the Land: New World Epidemics in a Global Perspective. University of New Mexico Press. p. 62. ISBN 978-0-8263-2871-7. Retrieved 2019-03-09.
- ↑ Hays, J. N.. Epidemics and Pandemics: Their Impacts on Human History. United Kingdom: ABC-CLIO, 2005.
- ↑ Vogel, Virgil J. American Indian Medicine. University of Oklahoma Press, 1970.
- ↑ John Phillip. A law of blood; the primitive law of the Cherokee nation. New York: Northern Illinois University Press, 1970.
- 1 2 3 Robertson, R. G. Rotting Face: Smallpox and the American Indian. Caxton Press, 2001.ISBN 0870044974
- ↑ Lyon, William S. (1998). Encyclopedia of Native American Healing. W. W. Norton and Company. ISBN 978-0-393-31735-0.
- ↑ Daniel E. Moerman, Native American Ethnobotany, Timber Press, 1998 ISBN 0881924539
- ↑ Dutch Children's Disease Kills Thousands of Mohawks Archived 2007-12-17 at the Wayback Machine. Paulkeeslerbooks.com
- ↑ Duffy, John (1951). "Smallpox and the Indians in the American Colonies". Bulletin of the History of Medicine. 25 (4): 324–341. PMID 14859018.
- ↑ Ramenofsky, Ann Felice. Vectors of Death: The Archaeology of European Contact. University of New Mexico Press, 1987.
- ↑ McCullough, John: The Captivity of John McCullough/ Personally written after eight years of captivity. Archived 2014-04-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Ecuyer, Simeon: Fort Pitt and letters from the frontier (1892)Journal of Captain Simeon Ecuyer, Entry June 2, 1763
- ↑ McCullough, John: http://The Captivity of John McCullough Personally written after eight years of captivity. Archived 2014-04-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Dixon, David, Never Come to Peace Again: Pontiac's Uprising and the Fate of the British Empire in North America (pg. 155)
- ↑ Hanna, Charles A.: The wilderness trail: or, the ventures and adventures of the Pennsylvania traders on the Allegheny path, with some new annals of the old West, and the records of some strong men and some bad ones (1911) pg.366
- ↑ Ewald, Paul W. (2000). Plague Time: How Stealth Infections Cause Cancer, Heart Disease, and Other Deadly Ailments. New York: Free. ISBN 978-0-684-86900-1.
- ↑ Ecuyer, Simeon: Fort Pitt and letters from the frontier (1892). Captain Simeon Ecuyer's Journal: Entry of June 24,1763
- ↑ Fenn, Elizabeth A. Biological Warfare in Eighteenth-Century North America: Beyond Jeffery Amherst Archived 2015-04-03 at the Wayback Machine; The Journal of American History, Vol. 86, No. 4, March, 2000
- ↑ "BBC – History – Silent Weapon: Smallpox and Biological Warfare". Retrieved 2008-01-02.
- ↑ Elizabeth A. Fenn. "Biological Warfare in Eighteenth-Century North America: Beyond Jeffery Amherst," The Journal of American History, Vol. 86, No. 4 (Mar., 2000), pp. 1552–1580
- 1 2 Ranlet, P (2000). "The British, the Indians, and smallpox: what actually happened at Fort Pitt in 1763?". Pennsylvania History. 67 (3): 427–441. PMID 17216901.
- ↑ Barras, V.; Greub, G. (June 2014). "History of biological warfare and bioterrorism". Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 20 (6): 497–502. doi:10.1111/1469-0691.12706. PMID 24894605.
- ↑ King, J. C. H. (2016). Blood and Land: The Story of Native North America. Penguin UK. p. 73. ISBN 978-1-84614-808-8.
- ↑ Barras, V.; Greub, G. (June 2014). "History of biological warfare and bioterrorism" (PDF). Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 20 (6): 497–502. doi:10.1111/1469-0691.12706. PMID 24894605.
However, in the light of contemporary knowledge, it remains doubtful whether his hopes were fulfilled, given the fact that the transmission of smallpox through this kind of vector is much less efficient than respiratory transmission, and that Native Americans had been in contact with smallpox >200 years before Ecuyer's trickery, notably during Pizarro's conquest of South America in the 16th century. As a whole, the analysis of the various 'pre-micro-biological' attempts at BW illustrate the difficulty of differentiating attempted biological attack from naturally occurring epidemics.
- ↑ Medical Aspects of Biological Warfare. Government Printing Office. 2007. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-16-087238-9.
In retrospect, it is difficult to evaluate the tactical success of Captain Ecuyer's biological attack because smallpox may have been transmitted after other contacts with colonists, as had previously happened in New England and the South. Although scabs from smallpox patients are thought to be of low infectivity as a result of binding of the virus in fibrin metric, and transmission by fomites has been considered inefficient compared with respiratory droplet transmission.
- ↑ Burke, James P., Pioneers of Second Fork (pgs. 19–22)
- 1 2 Marshall, Joseph (2005) [2004]. The Journey of Crazy Horse, A Lakota History. Penguin Books.
- ↑ Lange, Greg. "Smallpox Epidemic of 1862 among Northwest Coast and Puget Sound Indians". HistoryLink. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- 1 2 Ostroff, Joshua (August 2017). "How a smallpox epidemic forged modern British Columbia". Maclean's. Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ↑ Boyd, Robert; Boyd, Robert Thomas (1999). "A final disaster: the 1862 smallpox epidemic in coastal British Columbia". The Coming of the Spirit of Pestilence: Introduced Infectious Diseases and Population Decline Among Northwest Coast Indians, 1774–1874. University of British Columbia Press. pp. 172–201. ISBN 978-0-295-97837-6. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ↑ Swanky, Tom (2013). The True Story of Canada's "War" of Extermination on the Pacific – Plus the Tsilhqot'in and other First Nations Resistance. Dragon Heart Enterprises. pp. 617–619. ISBN 978-1-105-71164-0.
- 1 2 Koch, Alexander; Brierley, Chris; Maslin, Mark M.; Lewis, Simon L. (2019). "Earth system impacts of the European arrival and Great Dying in the Americas after 1492". Quaternary Science Reviews. 207: 13–36. Bibcode:2019QSRv..207...13K. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.12.004.
- ↑ Degroot, Dagomar (2019). "Did Colonialism Cause Global Cooling? Revisiting an Old Controversy". Historical Climatology.
- ↑ Denevan, William M. "The pristine myth: the landscape of the Americas in 1492." Annals of the Association of American Geographers 82, no. 3 (1992): 369-385.
- ↑ Bruce Trigger. Natives and Newcomers: Canada’s “Heroic Age” Reconsidered. (Kingston: McGill-Queen’s University Press, 1985), 588–589.
- ↑ Smallpox, The Canadian Encyclopedia
- ↑ Houston CS, Houston S (2000). "The first smallpox epidemic on the Canadian Plains: In the fur-traders' words". Can J Infect Dis. 11 (2): 112–5. doi:10.1155/2000/782978. PMC 2094753. PMID 18159275.
- ↑ Lewis Cass and the Politics of Disease: The Indian Vaccination Act of 1832. Muse.jhu.edu. Retrieved on 2011-12-06.(registration required)
- ↑ The Effect of Smallpox on the Destiny of the Amerindian; Esther Wagner Stearn, Allen Edwin Stearn; University of Minnesota; 1945; Pgs. 13-20, 73-94, 97
- ↑ David E. Stannard (1993-11-18). American Holocaust: The Conquest of the New World. Oxford University Press, USA. p. xii. ISBN 978-0-19-508557-0.
- ↑ Reséndez, Andrés (2016). The Other Slavery: The Uncovered Story of Indian Enslavement in America. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-547-64098-3.
- ↑ Watts, Sheldon (1999). Epidemics and History: Disease, Power and Imperialism. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-08087-2.