Sodium azide
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Sodium trinitride Smite Azium | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.043.487 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1687 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
NaN3 |
| Molar mass | 65.0099 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless to white solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.846 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 275 °C (527 °F; 548 K) violent decomposition |
Solubility in water |
38.9 g/100 mL (0 °C) 40.8 g/100 mL (20 °C) 55.3 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
| Solubility | very soluble in ammonia slightly soluble in benzene insoluble in ether, acetone, hexane, chloroform |
| Solubility in methanol | 2.48 g/100 mL (25 °C) |
| Solubility in ethanol | 0.22 g/100 mL (0 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.8 |
| Structure | |
Crystal structure |
Hexagonal, hR12[1] |
Space group |
R-3m, No. 166 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
76.6 J/(mol·K) |
Std molar entropy (S |
70.5 J/(mol·K) |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
21.3 kJ/mol |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚) |
99.4 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
Pictograms |
    |
Signal word |
Danger |
Hazard statements |
H300, H310, H410 |
Precautionary statements |
P260, P280, P301+P310, P501 [2] |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
27 mg/kg (oral, rats/mice)[1] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
none[3] |
REL (Recommended) |
C 0.1 ppm (as HN3) [skin] C 0.3 mg/m3 (as NaN3) [skin][3] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[3] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0950 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Sodium cyanide |
Other cations |
Potassium azide Ammonium azide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sodium azide is the inorganic compound with the formula NaN3. This colorless salt is the gas-forming component in legacy car airbag systems. It is used for the preparation of other azide compounds. It is an ionic substance, is highly soluble in water and is very acutely poisonous.[5]
Structure
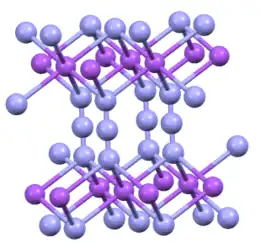
Sodium azide is an ionic solid. Two crystalline forms are known, rhombohedral and hexagonal.[1][6] Both adopt layered structures. The azide anion is very similar in each form, being centrosymmetric with N–N distances of 1.18 Å. The Na+ ion has an octahedral geometry. Each azide is linked to six Na+ centers, with three Na-N bonds to each terminal nitrogen center.[7]
Preparation
The common synthesis method is the "Wislicenus process", which proceeds in two steps in liquid ammonia. In the first step, ammonia is converted to sodium amide by metallic sodium:
- 2 Na + 2 NH3 → 2 NaNH2 + H2
It is a redox reaction in which metallic sodium gives an electron to a proton of ammonia which is reduced in hydrogen gas. Sodium easily dissolves in liquid ammonia to produce hydrated electrons responsible of the blue color of the resulting liquid. The Na+ and NH2– ions are produced by this reaction.
The sodium amide is subsequently combined with nitrous oxide:
- 2 NaNH2 + N2O → NaN3 + NaOH + NH3
These reactions are the basis of the industrial route, which produced about 250 tons per year in 2004, with production increasing owing to the popularization of airbags.[5]
Laboratory methods
Curtius and Thiele developed another production process, where a nitrite ester is converted to sodium azide using hydrazine. This method is suited for laboratory preparation of sodium azide:
- 2 NaNO2 + 2 C2H5OH + H2SO4 → 2 C2H5ONO + Na2SO4 + 2 H2O
- C2H5ONO + N2H4 · H2O + NaOH → NaN3 + C2H5OH + 3 H2O
Alternatively the salt can be obtained by the reaction of sodium nitrate with sodium amide.[8]
Chemical reactions
Treatment of sodium azide with strong acids gives hydrazoic acid, which is also extremely toxic:
- H+
+ N−
3 → HN
3
Aqueous solutions contain minute amounts of hydrogen azide, the formation of which is described by the following equilibrium:
- N−
3 + H
2O ⇌ HN
3 + OH−
(K = 10−4.6
)
Sodium azide can be destroyed by treatment with nitrous acid solution:[9]
- 2 NaN3 + 2 HNO2 → 3 N2 + 2 NO + 2 NaOH
Applications
Automobile airbags and aircraft evacuation slides
Older airbag formulations contained mixtures of oxidizers and sodium azide and other agents including ignitors and accelerants. An electronic controller detonates this mixture during an automobile crash:
- 2 NaN3 → 2 Na + 3 N2
The same reaction occurs upon heating the salt to approximately 300 °C. The sodium that is formed is a potential hazard alone and, in automobile airbags, it is converted by reaction with other ingredients, such as potassium nitrate and silica. In the latter case, innocuous sodium silicates are generated.[10] While sodium azide is still used in evacuation slides on modern aircraft, newer-generation automotive air bags contain less sensitive explosives such as nitroguanidine or guanidine nitrate.
Organic and inorganic synthesis
Due to its explosion hazard, sodium azide is of only limited value in industrial-scale organic chemistry. In the laboratory, it is used in organic synthesis to introduce the azide functional group by displacement of halides. The azide functional group can thereafter be converted to an amine by reduction with either SnCl2 in ethanol or lithium aluminium hydride or a tertiary phosphine, such as triphenylphosphine in the Staudinger reaction, with Raney nickel or with hydrogen sulfide in pyridine.
Sodium azide is a versatile precursor to other inorganic azide compounds, e.g., lead azide and silver azide, which are used in explosives.
Biochemistry and biomedical uses
Sodium azide is a useful probe reagent and a preservative.
In hospitals and laboratories, it is a biocide; it is especially important in bulk reagents and stock solutions which may otherwise support bacterial growth where the sodium azide acts as a bacteriostatic by inhibiting cytochrome oxidase in gram-negative bacteria; however, some gram-positive bacteria (streptococci, pneumococci, lactobacilli) are intrinsically resistant.[11]
Agricultural uses
It is used in agriculture for pest control of soil-borne pathogens such as Meloidogyne incognita or Helicotylenchus dihystera.[12]
It is also used as a mutagen for crop selection of plants such as rice,[13] barley[14] or oats.[15]
Safety considerations
Sodium azide has caused deaths for decades,[16] and even minute amounts can cause symptoms. The toxicity of this compound is comparable to that of soluble alkali cyanides,[17] although no toxicity has been reported from spent airbags.[18]
It produces extrapyramidal symptoms with necrosis of the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. Toxicity may also include hypotension,[19] blindness and hepatic necrosis. Sodium azide increases cyclic GMP levels in the brain and liver by activation of guanylate cyclase.[20]
Sodium azide solutions react with metallic ions to precipitate metal azides, which can be shock sensitive and explosive. This should be considered for choosing a non-metallic transport container for sodium azide solutions in the laboratory. This can also create potentially dangerous situations if azide solutions should be directly disposed down the drain into a sanitary sewer system. Metal in the plumbing system could react, forming highly sensitive metal azide crystals which could accumulate over years. Adequate precautions are necessary for the safe and environmentally responsible disposal of azide solution residues.[21]
References
- 1 2 3 Stevens E. D.; Hope H. (1977). "A Study of the Electron-Density Distribution in Sodium Azide, NaN
3". Acta Crystallographica A. 33 (5): 723–729. doi:10.1107/S0567739477001855. - ↑ "Sodium azide".
- 1 2 3 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0560". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "Material Safety Data Sheet" (PDF). Sciencelab.com. November 6, 2008. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- 1 2 Jobelius, Horst H.; Scharff, Hans-Dieter (2000). "Hydrazoic Acid and Azides". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_193. ISBN 9783527306732.
- ↑ Wells, A. F. (1984), Structural Inorganic Chemistry (5th ed.), Oxford: Clarendon Press, ISBN 0-19-855370-6
- ↑ Pringle, G. E.; Noakes, D. E. (1968-02-15). "The crystal structures of lithium, sodium and strontium azides". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 24 (2): 262–269. doi:10.1107/s0567740868002062.
- ↑ Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ↑ Committee on Prudent Practices for Handling, Storage, and Disposal of Chemicals in Laboratories, Board on Chemical Sciences and Technology, Commission on Physical Sciences, Mathematics, and Applications, National Research Council (1995). "Disposal of Waste". Prudent Practices in the Laboratory: Handling and Disposal of Chemicals. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-309-05229-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Betterton, E. A. (2003). "Environmental Fate of Sodium Azide Derived from Automobile Airbags". Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology. 33 (4): 423–458. doi:10.1080/10643380390245002. S2CID 96404307.
- ↑ Lichstein, H. C.; Soule, M. H. (1943). "Studies of the Effect of Sodium Azide on Microbic Growth and Respiration: I. The Action of Sodium Azide on Microbic Growth". Journal of Bacteriology. 47 (3): 221–230. doi:10.1128/JB.47.3.221-230.1944. PMC 373901. PMID 16560767.
- ↑ Applications of sodium azide for control of soilborne pathogens in potatoes. Rodriguez-Kabana, R., Backman, P. A. and King, P.S., Plant Disease Reporter, 1975, Vol. 59, No. 6, pp. 528-532 (link)
- ↑ Awan, M. Afsar; Konzak, C. F.; Rutger, J. N.; Nilan, R. A. (2000-01-01). "Mutagenic Effects of Sodium Azide in Rice1". Crop Science. 20 (5): 663–668. doi:10.2135/cropsci1980.0011183x002000050030x.
- ↑ Cheng, Xiongying; Gao, Mingwei (1988). "Biological and genetic effects of combined treatments of sodium azide, gamma rays and EMS in barley". Environmental and Experimental Botany. 28 (4): 281–288. doi:10.1016/0098-8472(88)90051-2.
- ↑ Rines, H. W. (1985-02-01). "Sodium azide mutagenesis in diploid and hexaploid oats and comparison with ethyl methanesulfonate treatments". Environmental and Experimental Botany. 25 (1): 7–16. doi:10.1016/0098-8472(85)90043-7.
- ↑ Chang, Soju; Lamm, Steven H. (2003-05-01). "Human Health Effects of Sodium Azide Exposure: A Literature Review and Analysis". International Journal of Toxicology. 22 (3): 175–186. doi:10.1080/10915810305109. ISSN 1091-5818. PMID 12851150. S2CID 38664824.
- ↑ "MSDS: sodium azide". Mallinckrodt Baker. 2008-11-21. MSDS S2906.
- ↑ Olson, Kent; Anderson, Ilene B. (18 September 2006). Poisoning & Drug Overdose, 5th Edition. McGraw-Hill Companies,Incorporated. pp. 123–. ISBN 978-0-07-144333-3.
- ↑ Gordon, Steven M.; Drachman, Jonathan; Bland, Lee A.; Reid, Marie H.; Favero, Martin; Jarvis, William R. (1990-01-01). "Kidney International - Abstract of article: Epidemic hypotension in a dialysis center caused by sodium azide". Kidney Int. 37 (1): 110–115. doi:10.1038/ki.1990.15. ISSN 0085-2538. PMID 2299796.
- ↑ Kimura, Hiroshi; Mittal, Chandra K.; Murad, Ferid (1975-10-23). "Increases in cyclic GMP levels in brain and liver with sodium azide an activator of guanylate cyclase". Nature. 257 (5528): 700–702. Bibcode:1975Natur.257..700K. doi:10.1038/257700a0. PMID 241939. S2CID 115294.
- ↑ "Sodium Azide | Environmental Health & Safety | Northeastern University".
