This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff. Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards.
There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 98% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 72,290 times.
Learn more...
Lipedema (sometimes called painful fat syndrome) is a disorder that causes fat to build up in the lower half of the body. This disease typically only occurs in women, though in a few rare cases it has been found in men. A person suffering from lipedema may find it nearly impossible to lose weight in the lower half of the body, even if they are able to lose fat from the upper part of the body. The legs may bruise easily and feel tender to the touch.
Steps
Getting Diagnosed
-
1Visit your doctor. The only way to have lipedema diagnosed is to visit your doctor. If your normal doctor is not trained in this area, they may refer you to a specialist who will examine your condition to determine if it is lipedema or another similar fat disorder.[1]
- The symptoms of this disorder make some people feel embarrassed to discuss the matter with their doctor. Try to remember that there is nothing to be embarrassed about, and if it is lipedema, the earlier you catch the disorder, the more treatable it will be.
-
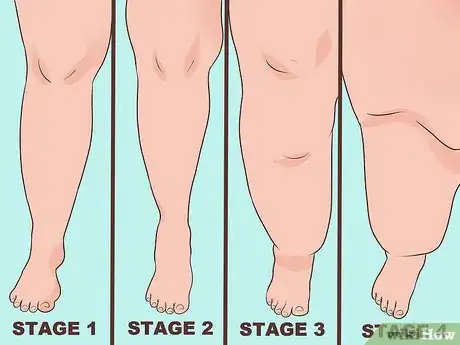
2Understand the stages of lipedema. As with many disorders and diseases, lipedema is often more treatable in the earlier stages than in the later stages. There are four stages of lipedema.[2] [3]
- In stage 1, the skin will still be smooth, and swelling may increase during the day, but disappear with rest. During this stage, the disorder responds well to treatment.
- In stage 2, there may be indentations in the skin, and lipomas (fatty lumps) may develop. You may experience eczema or skin infections known as erysipelas. Swelling may still appear during the day, but likely doesn’t go away completely, even with rest and elevation of the legs. At this stage, your body may still respond well to treatment.
- During stage 3, you may experience a hardening of the connective tissues. At this stage, the swelling is unlikely to go down regardless of whether you are resting or elevating your legs. You might also experience overhanging skin. It is still possible to treat the disorder, but you may be less responsive to various treatments.
- In stage 4 you will likely experience a worsening of the symptoms present in stage 3. At this stage, the disorder is referred to by some experts as lipo-lymphedema. As with stage 3, treatment is still worth trying, but you may not respond to some treatments.
Advertisement -
3Understanding what the doctor will look for. The best way to diagnose the disorder is through visual inspection of the affected area. The doctor may feel the area to check for nodules that characterize this disorder. Additionally, your doctor will likely ask you about whether or not you are experiencing any pain, and to describe when/if the swelling increases or decreases.[4]
- Currently, there is no blood test that will allow a doctor to determine if you have lipedema.
Understanding the Symptoms
-
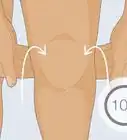
1Look for swelling in the legs. This is the most common and obvious symptom of the disorder. The swelling will typically be in both legs and may include the hips and buttocks. The swelling may be gradual or you may have a very distinct difference between your upper half and your lower half.[5]
- For example, some people suffering from lipedema are very thin above the waist but appear disproportionately large below the waste.
-
2Note that the feet often remain a “normal” size. The swelling may be isolated to the legs and stop just at the ankles. This gives your legs a column-like appearance.[6]
- Note that the symptoms are not always exactly the same. Your entire leg may not be swollen or you may have swelling from the tops of the ankles all the way to the hips. Some people experience only a small pocket of fat just above each ankle.
-
3Realize that the upper arms may also be affected. Though most people experience symptoms in the lower half of the body, it is possible to experience the same symptoms in the upper arms. Fat in the arms will be similar to in the legs. This means that you might experience an accumulation of fat that occurs equally in both arms.[7]
- The fat may create a column appearance that stops abruptly at the elbows or the wrists.
-
4Check whether or not the skin feels cold to the touch. People suffering from lipedema report that the skin of the affected area feels cold when they touch it. The skin might also feel soft and dough-like.[8]
- Additionally, it may be painful to the touch, and you may find that the affected area bruises very easily.[9]
Understanding the Causes
-
1Be aware that the causes are not well understood. Though there are some suspects, doctors still aren’t sure what exactly causes lipedema. Unfortunately, not knowing the cause can make this disorder difficult to treat.[10]
- Providing your doctor with as much information about your health and genetic history as possible will aid your doctor in determining possible causes and treatments.
-
2Learn about potential genetic links. In many cases, there appears to be a genetic component to this disorder. This is because a person suffering from lipedema sometimes has family members who are also dealing with the disorder themselves.[11]
- For example, if you are suffering from lipedema it is not unlikely that one of your parents is also suffering from the disorder.[12]
-
3Consider hormonal changes. Many doctors believe that lipedema may have a link with hormones. This is because the disorder occurs almost exclusively in women, and is often found to occur during times of hormonal change such as puberty, during pregnancy, or menopause.[13]
- Though the cause of the disorder may not seem important, it could be helpful for your doctor when deciding upon good treatment option.
Warnings
- It is important to understand that lipedema is not the same thing as being obese. If you are suffering from lipedema remember that you have not done anything wrong. It is not your fault.[15]⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.wikihow.com/Diagnose-Lipedema
- ↑ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25586162/
- ↑ https://www.lipedema.org/staging
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK552156/
- ↑ http://www.lipoedema.co.uk/about-lipoedema/symptoms/
- ↑ https://www.lipedema.net/am-i-overweight-or-do-i-have-lipedema.html
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17175-lipedema
- ↑ https://www.aspirephysiobunbury.com.au/lipoedema/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5055019/
- ↑ https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/ddg.12024
- ↑ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20358611/
- ↑ http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/lipoedema/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- ↑ https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/75320
- ↑ http://www.lipoedema.co.uk/about-lipoedema/symptoms/
- ↑ https://health.clevelandclinic.org/heres-what-you-should-know-about-lipedema-a-condition-that-causes-excess-fat-in-the-legs/
About This Article
Lipedema is a disorder that causes fat to build up in the lower half of your body, and it typically only occurs in women. Early signs of Lipedema include swelling in the legs, hips, and buttocks, fatty lumps, and eczema or skin infections. Signs of later stage Lipedema include swelling that doesn’t go away, overhanging skin, and hardened connective tissue. If you have any of these symptoms, see your doctor so they can diagnose you and provide treatment. Your doctor will likely examine the areas on your body that have been affected and ask you to describe your symptoms. To learn more about the causes of Lipedema, read more from our Medical co-author.




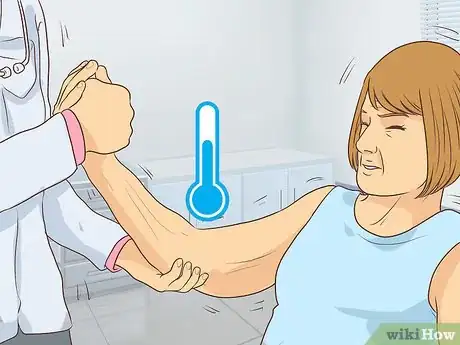


























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...