This article was medically reviewed by Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Dr. Pradeep Adatrow is the only board certified Dentist, Periodontist, and Prosthodontist in the southern United States. With over 15 years of experience, Dr. Adatrow specializes in dental implants, TMJ treatments, periodontal plastic surgery, surgical and non-surgical periodontics, bone regeneration, laser treatments, and soft tissue and gum graft procedures. He received a BS in Epidemiology and Biostatistics from the University of Alabama and earned his Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree from the University of Tennessee College of Dentistry. Dr. Adatrow then completed a three-year postgraduate program in periodontics and implantology at Indiana University and went on to complete another three-year postdoctoral program in advanced prosthodontics from the University of Tennessee. He also serves as a full-time professor and the Director of Surgical Prosthodontics at the University of Tennessee. Dr. Adatrow received the Dean's Junior Faculty Award and the John Diggs Faculty Award, and he was inducted into the Deans Odontological Society. He is board certified by the American Board of Periodontology and is a Fellow of the prestigious International College of Dentistry – a feat that only 10,000 others worldwide can claim.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 117,829 times.
A tooth abscess is a painful bacterial infection that causes pus to gather at the root of the tooth or between the tooth and the gums through a small hole resulting from the bone infection. Abscesses result from severe tooth decay, ignored cavities, or trauma to the tooth.[1] Periapical abscesses form at the tip of a tooth's root, whereas periodontal abscesses impact your surrounding bone and gums.[2] Although you might not experience any symptoms initially, a tooth abscess can cause serious medical problems. It's best to recognize it early before the infection spreads further.
Steps
Identifying a Tooth Abscess
-
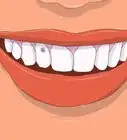
1Watch for a toothache. A toothache is one of the most common symptoms of an abscess. It often occurs as pus produced by bacteria that reached your pulp compresses the nerves in your teeth. You may notice a constant, throbbing pain around the tooth.[3] Biting might be painful. Your tooth pain could cause sleeplessness.
- The pain may be localized around the tooth, but it can also radiate to the ears, jaws, neck, or cheeks.[4] You may not be able to tell exactly where the pain is coming from. You might also feel irritated after spending a night in pain and struggling to sleep.
- The pain may be accompanied by a sense that your tooth is moving. The entire area around the tooth may look red and swollen.
- If you have a severe toothache that goes away, do not assume the abscess is gone. It is more likely that the abscess has killed the pulp and the infection remains. The pain may go for a while, especially if you have taken painkillers or an anti-inflammatory medication, but the infection will form an abscess again in no time.
-
2Note any pain when eating or drinking. An abscess can make chewing painful.[5] Abscesses also can make your teeth sensitive to hot and cold temperatures. If these symptoms last, seek treatment.[6]
- A pericoronitis abscess is one that can be located near the lower wisdom teeth. This type of abscess can cause your masseter muscles to block (also known as trismus), making it almost impossible to open or close your mouth.[7]
Advertisement -
3
-
4Watch for a bad taste or smell in your mouth. If your abscess has ruptured, you will be able to smell or taste the pus. The taste will be bitter but never swallow it.[10] Rinse with chlorhexidine mouthwash or even salt water to get rid of the taste. See your doctor immediately.
-
5Check for other symptoms. As an abscess worsens, you might suffer a fever, and you might notice pus discharging from your gums.[11] You also could have trouble opening your mouth, breathing, or swallowing. Swollen glands or a swollen upper or lower jaw can appear. Feeling generally sick is common.[12] If these symptoms appear, see your dentist immediately.
- If the abscess breaks, you may experience a sudden relief from the pain along with a salty taste.[13] You should still see your dentist right away.
-
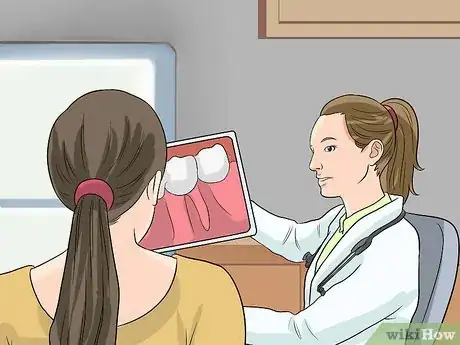
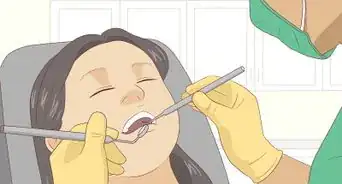
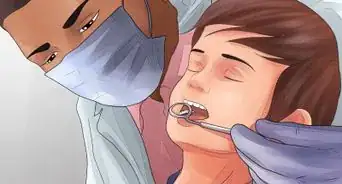
6Visit the dentist. If you have noticed the above symptoms, see a dentist. He or she will tap your tooth to see if it is sensitive. You likely will receive an x-ray. Then your dentist can know for sure whether you have an abscess.[14]
- An abscess is a serious problem. You should visit the dentist as soon as possible. A dentist can identify the source of the abscess, prescribe painkillers and antibiotics, and treat the abscess itself (i.e. through draining, root canal, or tooth extraction).
Preventing a Tooth Abscess
-
1Maintain good dental hygiene. Brush your teeth twice daily. Also, try to floss once daily. If you neglect your teeth, you have a higher risk of developing tooth abscesses.[15]
-
2Avoid sugary foods. If you constantly eat foods high in sugar (e.g. candy, chocolate), you can increase your risk for cavities. Cavities can lead eventually to abscesses. Some sugary foods are fine but eat them in moderation.[16] If possible, brush afterwards.
-
3Watch for cavities and fractures. If you have an untreated cavity or a tooth fracture that reaches the dental pulp (inner part of your tooth), you risk developing an abscess. This happens when bacteria reaches your dental pulp, which is the inside of your tooth. See a dentist as soon as possible, and watch for any symptoms.[17]
- Cavities and trauma typically lead to a “periapical abscess.”
-
4Pay attention to your gums. An injury to the gums can cause an abscess. Gum disease causes the space between the tooth and the gum to widen, which allows bacteria to enter. This bacteria can cause an abscess, even if the teeth are healthy and cavity-free. If you have any issues with your gums, watch for symptoms of an abscess.[18]
- Gum injuries and gum disease typically lead to a particular kind of infection known as a “gingival abscess” (or “gum abscess”). If the infection extends to the gum pockets, and the draining of pus is blocked by the swallowed gum, it is then called a “periodontal abscess.”
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionWhat happens if the abscess ruptures and you swallow the pus?
 Cristian Macau, DDSDr. Macau is an oral surgeon, periodontist, and aesthetician at Favero Dental Clinic in London. He received his DDS from Carol Davila University of Medicine in 2015.
Cristian Macau, DDSDr. Macau is an oral surgeon, periodontist, and aesthetician at Favero Dental Clinic in London. He received his DDS from Carol Davila University of Medicine in 2015.
Doctor of Dental Surgery The bacteria will be destroyed by the acid in your stomach so there is not much of a risk. A part of it may also be retained by your tonsils which can cause tonsillitis. The danger is on the upper teeth where an abscess can reach up to your brain causing meningitis or even death in a worst case scenario.
The bacteria will be destroyed by the acid in your stomach so there is not much of a risk. A part of it may also be retained by your tonsils which can cause tonsillitis. The danger is on the upper teeth where an abscess can reach up to your brain causing meningitis or even death in a worst case scenario. -
QuestionWhat are some symptoms of an abscessed tooth?
 Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MSDr. Pradeep Adatrow is the only board certified Dentist, Periodontist, and Prosthodontist in the southern United States. With over 15 years of experience, Dr. Adatrow specializes in dental implants, TMJ treatments, periodontal plastic surgery, surgical and non-surgical periodontics, bone regeneration, laser treatments, and soft tissue and gum graft procedures. He received a BS in Epidemiology and Biostatistics from the University of Alabama and earned his Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree from the University of Tennessee College of Dentistry. Dr. Adatrow then completed a three-year postgraduate program in periodontics and implantology at Indiana University and went on to complete another three-year postdoctoral program in advanced prosthodontics from the University of Tennessee. He also serves as a full-time professor and the Director of Surgical Prosthodontics at the University of Tennessee. Dr. Adatrow received the Dean's Junior Faculty Award and the John Diggs Faculty Award, and he was inducted into the Deans Odontological Society. He is board certified by the American Board of Periodontology and is a Fellow of the prestigious International College of Dentistry – a feat that only 10,000 others worldwide can claim.
Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MSDr. Pradeep Adatrow is the only board certified Dentist, Periodontist, and Prosthodontist in the southern United States. With over 15 years of experience, Dr. Adatrow specializes in dental implants, TMJ treatments, periodontal plastic surgery, surgical and non-surgical periodontics, bone regeneration, laser treatments, and soft tissue and gum graft procedures. He received a BS in Epidemiology and Biostatistics from the University of Alabama and earned his Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree from the University of Tennessee College of Dentistry. Dr. Adatrow then completed a three-year postgraduate program in periodontics and implantology at Indiana University and went on to complete another three-year postdoctoral program in advanced prosthodontics from the University of Tennessee. He also serves as a full-time professor and the Director of Surgical Prosthodontics at the University of Tennessee. Dr. Adatrow received the Dean's Junior Faculty Award and the John Diggs Faculty Award, and he was inducted into the Deans Odontological Society. He is board certified by the American Board of Periodontology and is a Fellow of the prestigious International College of Dentistry – a feat that only 10,000 others worldwide can claim.
Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon Typically, you'll experience a significant, constant, pulsating toothache that may radiate into your jaw, neck, or ear. Your teeth may be sensitive to hot and cold temporatores, and you may notice pain or sensitivity when you bite or chew. You may also have a fever, swelling of your face and cheek, swollen lymph nodes under your jaw or neck, or pus discharge from your gums.
Typically, you'll experience a significant, constant, pulsating toothache that may radiate into your jaw, neck, or ear. Your teeth may be sensitive to hot and cold temporatores, and you may notice pain or sensitivity when you bite or chew. You may also have a fever, swelling of your face and cheek, swollen lymph nodes under your jaw or neck, or pus discharge from your gums.
Warnings
- Do not attempt to treat an abscess yourself. Ultimately, you will need to see a dentist to resolve it.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- If you have severe pain or experience difficulty breathing or swallowing, go to an emergency room for immediate treatment.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10943-abscessed-tooth
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/dental-abscess/
- ↑ Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon. Expert Interview. 5 November 2020.
- ↑ Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon. Expert Interview. 5 November 2020.
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001060.htm
- ↑ Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon. Expert Interview. 5 November 2020.
- ↑ https://www.aafp.org/afp/2003/0201/p511.html
- ↑ Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon. Expert Interview. 5 November 2020.
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001060.htm
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001060.htm
- ↑ https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/tooth-abscess
- ↑ Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon. Expert Interview. 5 November 2020.
- ↑ Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon. Expert Interview. 5 November 2020.
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10943-abscessed-tooth
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/dental-abscess/
- ↑ https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/tooth-abscess
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10943-abscessed-tooth
- ↑ https://ada.com/conditions/dental-abscess/
About This Article
If you’re concerned you might have a tooth abscess, check for pain in or around your tooth. You might feel it all the time or especially when you eat or drink, and it may radiate to your jaw, cheek, or ear. Additionally, look for redness or swelling of the gums around the affected tooth. You should also make note of a bad taste or smell in your mouth, which can happen if the abscess ruptures and drains into your mouth. If the infection is severe or begins to spread, you may also experience a fever, swollen lymph nodes, or difficulty swallowing. Call your dentist immediately if you have any of these symptoms. For more advice from our Dentist co-author, including how to prevent abscesses, keep reading!
























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...