This article was medically reviewed by Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Dr. Pradeep Adatrow is the only board certified Dentist, Periodontist, and Prosthodontist in the southern United States. With over 15 years of experience, Dr. Adatrow specializes in dental implants, TMJ treatments, periodontal plastic surgery, surgical and non-surgical periodontics, bone regeneration, laser treatments, and soft tissue and gum graft procedures. He received a BS in Epidemiology and Biostatistics from the University of Alabama and earned his Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree from the University of Tennessee College of Dentistry. Dr. Adatrow then completed a three-year postgraduate program in periodontics and implantology at Indiana University and went on to complete another three-year postdoctoral program in advanced prosthodontics from the University of Tennessee. He also serves as a full-time professor and the Director of Surgical Prosthodontics at the University of Tennessee. Dr. Adatrow received the Dean's Junior Faculty Award and the John Diggs Faculty Award, and he was inducted into the Deans Odontological Society. He is board certified by the American Board of Periodontology and is a Fellow of the prestigious International College of Dentistry – a feat that only 10,000 others worldwide can claim.
There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 634,361 times.
Bleeding gums are the first sign that gum disease - including gingivitis and the more severe periodontitis - is on the way. While three quarters of the population experiences gum disease in their lifetime, it's usually curable if you practice excellent dental hygiene.
Steps
Understanding the Problem
-
1Figure out why your gums are bleeding. Bleeding gums aren't always a symptom of gum disease, though that's the most common reason they occur. Bleeding gums can be a symptom of other medical issues having nothing to do with your dental hygiene. If you suspect your bleeding gums are related to something other than poor brushing and flossing habits, see your doctor to discuss ways to address the problem. Bleeding gums can be related to the following conditions:[1]
- Hormonal changes.
- Diabetes.
- Heart disease.
- Clotting disorders.
- Cancers, like Leukemia.
- AIDS.
- Scurvy.
- Blood thinning medications.
- Genetic factors/genetic syndromes.
- Contraceptive pills.
-
2Know why it's important to stop gum disease in its tracks. Gum disease, which is caused by the buildup of plaque on the gums and teeth, is very common among adults over the age of 35. It starts with gingivitis, which is the inflammation and swelling of the gums that leads to bleeding and pain. Left untreated, gingivitis can turn into the more severe periodontitis, which causes the gums and oral bones to weaken and can lead to tooth loss. This process may be slow lasting several years, or fast if aggressive bacteria are involved and the periodontitis has a rapid and progressive evolution.[2]
- Gum disease is also related to other severe medical conditions like heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease because of constantly storing bacteria that can easily enter the bloodstream.
Advertisement -
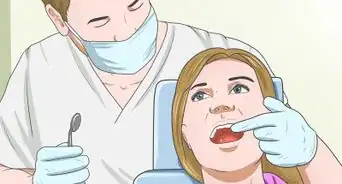
3Take a trip to the dentist. The best way to fight gum disease is to get a head start by going to the dentist for a deep cleaning. Your dentist will help you figure out why your gums are bleeding. Your dentist can demonstrate the proper way to brush and floss, clean away your built-up plaque, and let you know whether you need to be treated for periodontitis.[3]
- Regular trips to the dentist - at least once every six months - are an important way to combat gum disease. It's not possible to brush and floss away every little bit of plaque before it turns into hard tartar on your teeth, unless the brush used is accurate in allowing small up/down movements, and once it becomes tartar you can't remove it yourself. Your dentist has the right tools to get rid of the tartar that's leading to bleeding gums.[4]
- Using x-rays, the dentist can show you whether dangerous tartar has formed underneath the gums. This type of tartar is difficult to remove just with regular dental hygiene. You may need surgery, but this will save your teeth for a long time.
- Seek medical attention soon if you notice the following symptoms in addition to gum bleeding:[5]
- Pockets formed between your teeth and gums.
- Loose teeth.
- A change in the way your teeth fit together.
- Receding gums leaving sensitive teeth and dark triangles between teeth.
- Swollen, red and tender gums or even abscess of the gums where pus is visible.
- Gums that bleed a lot when you brush your teeth.
Using Dentist-Approved Methods for Stopping Bleeding and Disease
-
1Change the way you brush. If you're in the camp that thinks that the harder you brush, the cleaner your teeth will get, your brushing habits might be the culprit here. Gums are composed of soft, fragile tissue that doesn't need to be scrubbed hard to get clean. Choose a brush with soft, blunt bristles - never get the kind labeled "medium" or "hard." Brush twice a day using the right technique - a soft, circular motion on all sides of the teeth and gums along with vertical strokes, which include brushing the gums to stimulate the blood flow for better protection.
- Consider getting an electric toothbrush. Electric toothbrushes are gentle on your teeth and very effective at reaching to the back to remove plaque. Choose a brush that has been approved by the American Dental Association (ADA).
- If there's one particular part of your mouth that feels sensitive, or seems to bleed more often, spend more time gently brushing that area. Gently massage the spot with your toothbrush for 3 minutes. This will help remove the plaque affecting the area.
-
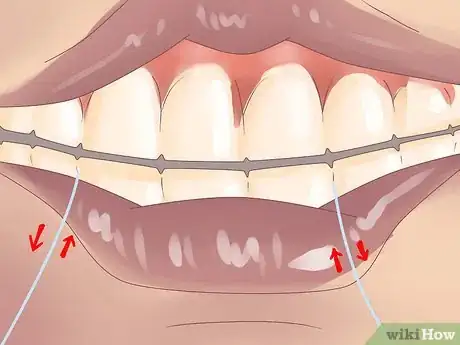
2Floss without hurting your gums. Flossing once a day is absolutely essential for stopping gums from bleeding.[6] There's no other way to get to the bits of food and plaque building up between your teeth and underneath the gingival margin called the sulcus. But there's a right way and a wrong way to floss, and doing it correctly can make all the difference when it comes to stopping gums from bleeding.[7]
- Don't snap the floss violently between your teeth. This doesn't get them cleaner; it just hurts your fragile gums.
- Gently pull the floss between your teeth and swipe your gums. Clean the front of your teeth by holding the floss in a U-shape at the top of each tooth and gently swiping downward. Go as far back as you can and floss both surfaces of the papilla, meaning that you need to floss the tooth in front and the tooth behind each time.
-
3Try gum irrigation. Many people find that using a gum irrigation device, called a water pik, helps to alleviate bleeding gums by gently cleaning them more thoroughly. Gum irrigation devices attach to your sink's plumbing and should be used after brushing to thoroughly cleanse the gums.[8]
- There is also an electric device which sprays water similar to a shower through a small tip called oral irrigator. The advantage is that you can add mouthwash for increased antibacterial protection.
-
4Use non-alcoholic mouthwash. Alcohol-based mouthwashes can dry out the gums and cause more irritation and bleeding. It's better to use a non-alcoholic, peroxide-based mouthwash. You can also make your own mouthwash by simply rinsing with saltwater.[9]
-
5Consider professional medical treatments. If your gums don't stop bleeding and it doesn't seem as though good hygiene is making a difference, your dentist may recommend a treatment designed to get rid of the plaque and allow your gums to recover. Here are the options:[10]
- Scaling and root planing. The dentist administers local anesthetic and scrapes away the tartar as well as smoothing rough spots.[11] This is usually done when there is tartar buildup under the gum line and there is an incipient stage of periodontitis.
- Flap surgery and pocket reduction. If you have advanced gum disease, your dentist may decide that surgery is the best option.[12] Flap surgery reduces the space between the gum and the tooth so that plaque can't form underneath so easily. This helps the bone to recover and eliminates anaerobic bacteria which is the main cause of periodontitis. Flap surgery has a better long term result than any other type of treatment.
- Grafts of tissue or bones. If periodontitis has cause your gums to recede and your bones to deteriorate, tissue and bone can be grafted from other parts of the mouth to the affected area.[13] Your periodontist may also choose to graft artificial bone which can be either hydroxyapatite or bovine bone.
Making Lifestyle Changes
-
1Eat a healthy diet. Gums, like the rest of your body's tissues, are affected by the vitamins and nutrients you take in. If you eat loads of sugar and flour-based items and not a lot of fruits, veggies and nutritionally dense food, your gums will suffer for it. For improved oral health, try the following:[14]
- Cut back on sugar. Eating a lot of sugar causes tartar to build up fast - faster than you can brush or floss it away. Cutting back should help your gums heal quickly.
- Eat fruits and vegetables high in vitamin C, like kale, mangoes, broccoli and grapefruit.
- Eat high-calcium foods like spinach and dairy products.
-
2Stop smoking. Smoking is very detrimental to oral health. The toxins in cigarettes and other tobacco produces can lead to gum inflammation and disease.[15] In fact, smokers are six times more likely to develop serious gum disease than nonsmokers.[16]
- Smoking inhibits blood circulation in the gums, causing the gums to be much more prone to getting diseased because the blood has plenty of factors to fight against bacteria and reducing the circulation also reduces protection.
- Smoking actually lowers the success rate of gum disease treatments.
-
3Drink a lot of water. Drinking at least 8 glasses of water throughout the day can help keep your gums and mouth healthy. Drinking water rinses bacteria from your teeth and helps prevent the buildup of plaque. Replace your sugary drinks, coffee and tea with water as much as you can.[17]
Expert Q&A
-
QuestionWhat causes your gums to bleed?
 Joseph Whitehouse, MA, DDSDr. Joseph Whitehouse is a board certified Dentist and the Former President of the World Congress on Minimally Invasive Dentistry (WCMID). Based in Castro Valley, California, Dr. Whitehouse has over 46 years of dental experience and counseling experience. He has held fellowships with the International Congress of Oral Implantology and with the WCMID. Published over 20 times in medical journals, Dr. Whitehouse's research is focused on mitigating fear and apprehension patients associate with dental care. Dr. Whitehouse earned a DDS from the University of Iowa in 1970. He also earned an MA in Counseling Psychology from California State University Hayward in 1988.
Joseph Whitehouse, MA, DDSDr. Joseph Whitehouse is a board certified Dentist and the Former President of the World Congress on Minimally Invasive Dentistry (WCMID). Based in Castro Valley, California, Dr. Whitehouse has over 46 years of dental experience and counseling experience. He has held fellowships with the International Congress of Oral Implantology and with the WCMID. Published over 20 times in medical journals, Dr. Whitehouse's research is focused on mitigating fear and apprehension patients associate with dental care. Dr. Whitehouse earned a DDS from the University of Iowa in 1970. He also earned an MA in Counseling Psychology from California State University Hayward in 1988.
Board Certified Dentist Bleeding gums are one of the most common signs of gum disease, so you may need to see your dentist to look into that. If you don't have gum disease, bleeding gums are a sign that you need to spend a little more time brushing and flossing in that part of your mouth.
Bleeding gums are one of the most common signs of gum disease, so you may need to see your dentist to look into that. If you don't have gum disease, bleeding gums are a sign that you need to spend a little more time brushing and flossing in that part of your mouth. -
QuestionWhat is scaling?
 Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MSDr. Pradeep Adatrow is the only board certified Dentist, Periodontist, and Prosthodontist in the southern United States. With over 15 years of experience, Dr. Adatrow specializes in dental implants, TMJ treatments, periodontal plastic surgery, surgical and non-surgical periodontics, bone regeneration, laser treatments, and soft tissue and gum graft procedures. He received a BS in Epidemiology and Biostatistics from the University of Alabama and earned his Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree from the University of Tennessee College of Dentistry. Dr. Adatrow then completed a three-year postgraduate program in periodontics and implantology at Indiana University and went on to complete another three-year postdoctoral program in advanced prosthodontics from the University of Tennessee. He also serves as a full-time professor and the Director of Surgical Prosthodontics at the University of Tennessee. Dr. Adatrow received the Dean's Junior Faculty Award and the John Diggs Faculty Award, and he was inducted into the Deans Odontological Society. He is board certified by the American Board of Periodontology and is a Fellow of the prestigious International College of Dentistry – a feat that only 10,000 others worldwide can claim.
Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MSDr. Pradeep Adatrow is the only board certified Dentist, Periodontist, and Prosthodontist in the southern United States. With over 15 years of experience, Dr. Adatrow specializes in dental implants, TMJ treatments, periodontal plastic surgery, surgical and non-surgical periodontics, bone regeneration, laser treatments, and soft tissue and gum graft procedures. He received a BS in Epidemiology and Biostatistics from the University of Alabama and earned his Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree from the University of Tennessee College of Dentistry. Dr. Adatrow then completed a three-year postgraduate program in periodontics and implantology at Indiana University and went on to complete another three-year postdoctoral program in advanced prosthodontics from the University of Tennessee. He also serves as a full-time professor and the Director of Surgical Prosthodontics at the University of Tennessee. Dr. Adatrow received the Dean's Junior Faculty Award and the John Diggs Faculty Award, and he was inducted into the Deans Odontological Society. He is board certified by the American Board of Periodontology and is a Fellow of the prestigious International College of Dentistry – a feat that only 10,000 others worldwide can claim.
Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon Scaling is a process that involves removing tartar and bacteria from the tooth surfaces and under the gums. The dentist can do it with instruments, a laser, or an ultrasound.
Scaling is a process that involves removing tartar and bacteria from the tooth surfaces and under the gums. The dentist can do it with instruments, a laser, or an ultrasound. -
QuestionWhat is root planing?
 Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MSDr. Pradeep Adatrow is the only board certified Dentist, Periodontist, and Prosthodontist in the southern United States. With over 15 years of experience, Dr. Adatrow specializes in dental implants, TMJ treatments, periodontal plastic surgery, surgical and non-surgical periodontics, bone regeneration, laser treatments, and soft tissue and gum graft procedures. He received a BS in Epidemiology and Biostatistics from the University of Alabama and earned his Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree from the University of Tennessee College of Dentistry. Dr. Adatrow then completed a three-year postgraduate program in periodontics and implantology at Indiana University and went on to complete another three-year postdoctoral program in advanced prosthodontics from the University of Tennessee. He also serves as a full-time professor and the Director of Surgical Prosthodontics at the University of Tennessee. Dr. Adatrow received the Dean's Junior Faculty Award and the John Diggs Faculty Award, and he was inducted into the Deans Odontological Society. He is board certified by the American Board of Periodontology and is a Fellow of the prestigious International College of Dentistry – a feat that only 10,000 others worldwide can claim.
Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MSDr. Pradeep Adatrow is the only board certified Dentist, Periodontist, and Prosthodontist in the southern United States. With over 15 years of experience, Dr. Adatrow specializes in dental implants, TMJ treatments, periodontal plastic surgery, surgical and non-surgical periodontics, bone regeneration, laser treatments, and soft tissue and gum graft procedures. He received a BS in Epidemiology and Biostatistics from the University of Alabama and earned his Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree from the University of Tennessee College of Dentistry. Dr. Adatrow then completed a three-year postgraduate program in periodontics and implantology at Indiana University and went on to complete another three-year postdoctoral program in advanced prosthodontics from the University of Tennessee. He also serves as a full-time professor and the Director of Surgical Prosthodontics at the University of Tennessee. Dr. Adatrow received the Dean's Junior Faculty Award and the John Diggs Faculty Award, and he was inducted into the Deans Odontological Society. He is board certified by the American Board of Periodontology and is a Fellow of the prestigious International College of Dentistry – a feat that only 10,000 others worldwide can claim.
Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon Root planing smoothes the root surfaces, prevents additional tartar and bacteria from accumulating, and eliminates bacterial byproducts that cause inflammation and delay gum healing.
Root planing smoothes the root surfaces, prevents additional tartar and bacteria from accumulating, and eliminates bacterial byproducts that cause inflammation and delay gum healing.
Warnings
- Remember also flossing is an important part of a complete dental home care program!⧼thumbs_response⧽
- The colloidal silver solution may turn your skin grayish or blueish, so be careful not to spill it.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- To prevent gum disease and other forms of mouth disease, see your dentist at least once a year. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, and use your irrigator at least twice a day and after meals.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/gum-problem-basics-sore-swollen-and-bleeding-gums#1
- ↑ https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/gingivitis-periodontal-disease#1
- ↑ Joseph Whitehouse, MA, DDS. Board Certified Dentist. Expert Interview. 9 April 2020.
- ↑ https://www.ada.org/en/press-room/news-releases/2013-archive/june/american-dental-association-statement-on-regular-dental-visits
- ↑ http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/gum-problem-basics-sore-swollen-and-bleeding-gums
- ↑ Joseph Whitehouse, MA, DDS. Board Certified Dentist. Expert Interview. 9 April 2020.
- ↑ https://www.ada.org/en/member-center/oral-health-topics/floss
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19138181
- ↑ http://www.evansondds.com/alcohol-vs-alcohol-free-mouthwash/
- ↑ https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/features/gums-problems-gingivitis#1
- ↑ Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon. Expert Interview. 30 September 2020.
- ↑ Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon. Expert Interview. 30 September 2020.
- ↑ Pradeep Adatrow, DDS, MS. Board Certified Dentist & Oral Surgeon. Expert Interview. 30 September 2020.
- ↑ http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/diet-oral-health
- ↑ Joseph Whitehouse, MA, DDS. Board Certified Dentist. Expert Interview. 9 April 2020.
- ↑ https://www.dentalhealth.org/smoking-and-oral-health
- ↑ https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/nutrition/food-tips/water-best-beverage
About This Article
You can stop your gums from bleeding and avoid gingivitis or periodontitis by flossing your teeth gently once a day. Properly flossing is the only way to get the bits of food and plaque between your teeth that can build up and cause gum disease. You should also brush with a soft-bristled toothbrush in a circular motion along all sides of your teeth and gums to stimulate blood flow. If a part of your mouth feels sensitive or bleeds more often, spend some extra time gently brushing that area for 3 minutes to help remove any plaque that may be causing trouble. As for mouthwash, use a non-alcohol based product, because alcohol will dry out the gum and only cause more irritation and bleeding. Instead, simply rinse with saltwater. For more advice from our Dental co-author, including how to make lifestyle changes to avoid gum disease, read on!



































































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...