wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 21 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 91% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 102,344 times.
Learn more...
The tenor saxophone is a common instrument for clarinet players to switch to, as it has much in common with the clarinet. It's a member of the woodwind family, in the key of Bb, has a similar mouthpiece, and the fingerings are similar to those of the upper register of the clarinet. As a clarinet player, you should have a fairly easy time switching to tenor, whether it's a permanent instrument change, or you're just learning a second instrument. However, there are some things that you'll have to adjust to.
Steps
-
1Be sure that you really want to switch to tenor sax. If you plan for this to be a total switch, keep in mind that you may go from the first chair clarinet player and one of the best players in your band to the last chair tenor and weak link of the band for a while, and you'll be learning everything but reading music all over again. If you think you're up for it, though, go ahead and proceed.
-
2A used tenor saxophone in its case with all the things needed to play and clean it.]] Purchase or borrow a tenor sax in decent condition and all the things necessary to play and maintain it. If you're in a school band, the school will probably have an instrument that you can rent, or you can rent one on a rent-to-own program at your local music store. You will also need a method book or two, preferably the same one you used to learn the clarinet.Advertisement
-
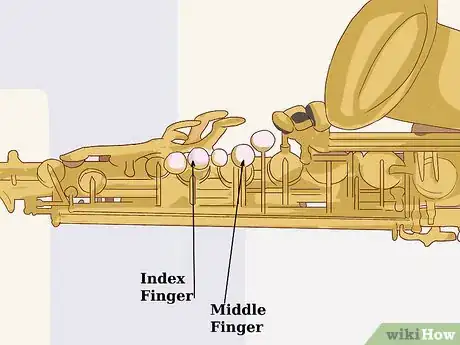
3Assemble a Tenor Saxophone|Assemble the saxophone]]. Put the neck strap on, pick it up, and just walk around with it to get a feel for the weight, size, and different angle of the mouthpiece. Figure out where your fingers are supposed to go. The right hand should be obvious, but there are 5 mother of pearl keys on the upper part of the instrument. Your fingers go on the second, fourth, and fifth ones, in the same way they would on the clarinet. Think of the first one as the A key on the clarinet, and the third one as the little lever that you use to play low Eb and high Bb.[1]
-
4Familiarize yourself with the keys and fingerings, and see how they relate to the clarinet's mechanism. If you study a fingering chart for the tenor sax, you'll see a lot of similarities to the upper register clarinet fingerings. For instance, thumb, register (octave, on the sax), and five tone holes produces a high E, just as it would on a clarinet.
- The key above the thumb key is the octave key, which makes notes higher, just like the clarinet's register key, except it takes them up a whole octave, hence the name. If you finger an E and hit the octave key on the sax, you get a high E, unlike the clarinet, where all the fingerings have two names.[2]
- The three keys at the top of the instrument are operated by your left hand, and are mainly used for notes above the staff (D, D#, E, and F).
- There are four keys with rollers between them that are operated by your left pinky finger, about the same place as the 4 "left pinky" keys on the clarinet. On saxophone, this is commonly referred to as the "table," or "spatula keys."
- L - R: Two bottom keys with rollers (see below), offset key, three aligned keys. View from in case.]]There are four keys on the side of the bottom of the sax that are operated by your right hand. Three are in a row, and one is nestled further in. The top key is used in conjunction with the left hand side keys, and plays high E. The middle one is used as a trill fingering for middle C, and the bottom of the three aligned ones is used for one fingering of Bb.[3]
- There are two keys at the bottom of the sax with rollers between them that are operated by your right pinky. The top one makes an Eb, and the bottom makes a low C. Think of them as the equivalent of the top two of the four keys at the bottom of the clarinet.
-
5Play a few notes -- you'll need a fingering chart for this. You'll soon pick up on the many similarities and will be playing simple music within just a few minutes. Different methods start with different notes, but most suggest starting with the higher notes. As a starting point, you might want to try the notes below. Many simple tunes can be played with only E, D, and C, and F and G just add to the fun. You'll notice how most of these fingerings are the same as the ones for the upper register of the clarinet.[4]
- Top space E: Octave key and first five mother-of-pearl keys.
- Fourth-line D: Octave key and all six mother-of-pearl keys.
- Third space C: Only the second mother-of-pearl key (covered by your left middle finger)
- Top-line F: Octave key and first four mother-of-pearl keys.
- G on top of the staff: Octave key and top three mother-of-pearl keys.
- Releasing the octave key on the G, F, E, and D fingerings produces the same note, but an octave lower. Pressing the octave key for the C sounds a C, but an octave higher.
-
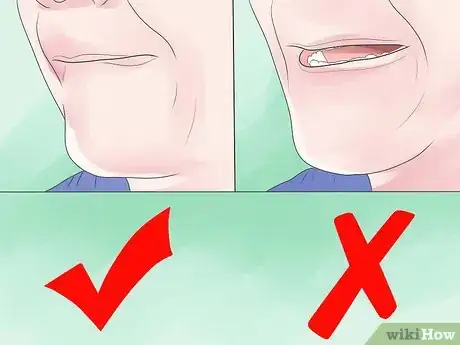
6Adjust your embouchure. As you experimented with the fingering chart, you may have noticed that the octave key doesn't seem to be "working." When you finger a D, the sound is the same with or without the octave key. This is common with clarinet players switching to tenor. It'll take some practice to be able to play low notes well, but it's also considerably due to your embouchure. A clarinet requires a tight embouchure, but a tenor saxophone requires a looser one. Adjusting the position of your tongue in your mouth is crucial to gaining full range on the saxophone. The tongue placement varies based on the range, for example: when playing low notes, your tongue will be low in your mouth. The tongue rests in the middle part of the mouth when playing in the middle and high ranges. When teachers say "Drop your jaw for low notes," this is really what is going on; the placement of the tongue and the jaw coming off of the reed permits it to vibrate at a lower frequency. You may also need to adjust the amount of lip you have rolled over your teeth. Saxophone experts generally say that about 2/3 of your bottom lip should be rolled in. Experiment and practice until your low notes sound as good as your high ones.[5]
-
7Once you've gotten good at the tenor sax and made the commitment to stick with it, ask your director for tenor sax music and start practicing. Over time, you'll be just as good at the saxophone as you are at the clarinet.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionI learned it within 4 hours. I could play 2 medium to hard pieces. Is this normal or am I just a genius?
 PurpleOreoCommunity AnswerClarinet and tenor saxophone are both in the key of B flat and thus are easy to switch out. Clarinet to saxophone is also an easy switch because it requires a loose embouchure and is essentially easier to play than the clarinet.
PurpleOreoCommunity AnswerClarinet and tenor saxophone are both in the key of B flat and thus are easy to switch out. Clarinet to saxophone is also an easy switch because it requires a loose embouchure and is essentially easier to play than the clarinet. -
QuestionWhat size of tenor saxophone mouthpiece is closest to the bass clarinet mouthpiece?
 Community AnswerI don't think it matters. Being a clarinet player myself, the embouchure for clarinet playing is slightly different than playing a sax anyways, but you'll have an advantage if you play that clarinet because it's harder than the sax. Saxophone players never have to worry about covering any holes when they play, so it's always an easier transition to go from clarinet to sax than from sax to clarinet.
Community AnswerI don't think it matters. Being a clarinet player myself, the embouchure for clarinet playing is slightly different than playing a sax anyways, but you'll have an advantage if you play that clarinet because it's harder than the sax. Saxophone players never have to worry about covering any holes when they play, so it's always an easier transition to go from clarinet to sax than from sax to clarinet. -
QuestionGenerally, which instrument is easier, tenor or alto sax?
 Community AnswerThe only thing that really changes is the sheet music. The tenor is larger in size, though, so for some people it is easier to start with a smaller instrument.
Community AnswerThe only thing that really changes is the sheet music. The tenor is larger in size, though, so for some people it is easier to start with a smaller instrument.
Warnings
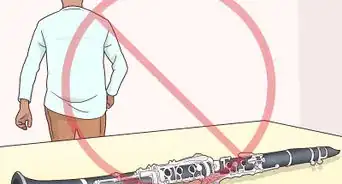
- Obviously, a tenor sax is much heavier than a clarinet, and is also bigger around. You may find that your neck will be a little sore from supporting the instrument the first time you play, and going from carrying a foot-long clarinet case to carrying a three-foot-long tenor case around is going to be a pretty big adjustment.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- If you've tried everything you can think of to get your low notes out, and you still aren't having any luck, the instrument may be partially at fault. Take it to your local music store and let them look at it and make an adjustment, if need be.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Renting an instrument, especially a school instrument (that has been through many hands, some of which may not have taken care of it very well), can be risky. You need a good instrument to learn to play properly, so be prepared to have a used rental overhauled, or realize that you may be buying your own sax soon, if you continue to play.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You'll Need
- Concept of sound is the most important aspect of learning an instrument.
- Tenor saxophone
- Mouthpiece and ligature (if not included with the sax)
- Neck strap
- Several reeds: Classically trained clarinetist generally play reeds on the stiffer side. There are many highly recognized tenor players who play on reeds as soft as a 1 1/2. You need to find the most comfortable set up that yields the best results with the least amount of effort.
- Swab and/or Sax Saver
- Fingering chart
- Method books, if needed or recommended by your director
- Anything else you might need, personally (mouthpiece cushion, sax stand, etc.)
References
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jihxdAtFimQ
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=538dP9X08w0
- ↑ https://westpointsom.org/wpsom_site/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/Tenor-Sax110.pdf
- ↑ https://westpointsom.org/wpsom_site/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/Tenor-Sax110.pdf
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=woQ00Zx-OoY
- ↑ https://www.musikalessons.com/blog/2016/09/types-of-saxophones/
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tenor_saxophone