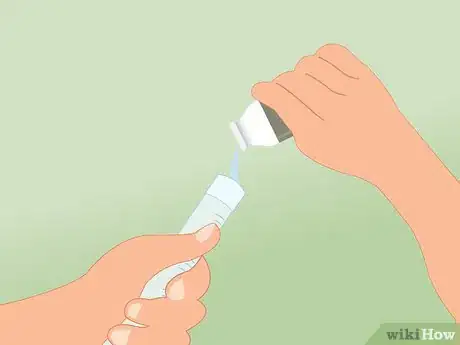wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 56,700 times.
Learn more...
Cyanuric acid is a chlorine stabilizer commonly used in outdoor pools. The presence of cyanuric acid in an outdoor pool is good as long as the amount stays within 30 to 50 ppm (parts per million). You should regularly test the cyanuric acid levels in your pool water to make sure that they stay within this range.
Steps
Keeping Your Pool Maintained
-
1Make sure your state allows cyanuric acid. Every state has different laws and different levels they allow, from 30 ppm as the maximum to 100 ppm as the maximum. It’s essential you know what you are testing for, depending on your location.
-
2Understand the benefit of cyanuric acid. In the right amounts, cyanuric acid protects the chlorine in a pool from ultraviolet sunlight, thereby reducing the amount of chlorine lost over time. As a result, the pool stays disinfected longer and more effectively. In high amounts, however, cyanuric acid can reduce the effectiveness of chlorine as a disinfectant. Bacteria can build up in the water when this happens and create a health risk.Advertisement
-
3Be sure to buy unstabilized chlorine for your pool, either bleach (liquid chlorine, or sodium hypochlorite) or cal-hypo (granular chlorine, or calcium hypochlorite). (With the latter, you need to monitor calcium levels to avoid scaling.) Many pool owners unknowingly add cyanuric acid to their pools because of the kind of chlorine they are adding, namely “dichlor” (sodium dichloro-s-triazinetrione) or “trichlor” (trichloro-s-triazinetrione (“trichlor”), and reach levels that prevent effective sanitation, and can only be reduced by draining and refilling the pool.
-
4Test your pool regularly. Once a week, set a time that you check for cyanuric acid levels. If you have concerns that your cyanuric acid levels aren’t under control, test more often.
Turbidity Tests
-
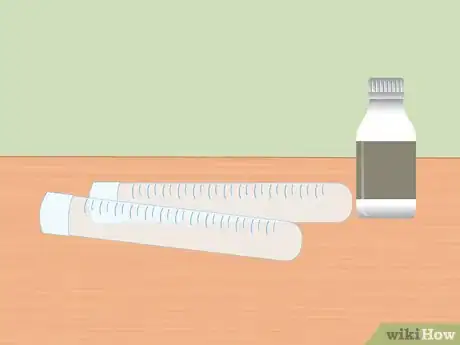
1Get a testing kit. A turbidity testing kit, also called a "disappearing dot" test, should come with a special glass test tube, a separate plastic vessel, and chemical reagent packets. While each kit can vary by manufacturer, many also come with a plastic pipette and a spoon or stirring rod.[1]
- The glass test tube should have a black dot or black line at the bottom of the tube. This mark is crucial to the testing process, so make sure that it is there.
- Sometimes the test tube and the plastic vessel are connected, but there should at least be two separate compartments.
-
2Fill the plastic vessel with sample water. Collect water into the plastic vessel of the testing kit. Be sure to use the amount indicated in the test instructions (25 ml is common). You can do this by directly scooping the water up with the plastic vessel.
- Some testing kits will provide a plastic vessel that has a lid. When this is the case, you can mix the reagent into the sample water by capping the vessel and shaking it for 30 seconds or so.
-
3Add the turbidity solution. Pour one packet of the chemical reagent into the sample water. Use the provided spoon or stirring rod to gently mix the powder into the water until it dissolves. If your kit does not have a spoon or rod provided, use a plastic or glass spoon.
-
4Wait one minute. Doing so will allow the necessary chemical reaction to occur. The reagent reacts with the cyanuric acid in the water to create turbidity, or cloudiness. Cloudier water indicates a higher concentration of cyanuric acid.
-
5Transfer the resulting solution into the test tube. Use the pipette to transfer the testing solution into the marked test tube, one drop at a time. Stand the test tube on a white or light surface so that the black mark is easy to spot. Look into the test tube from above as you drop the testing solution inside.
-
6Stop when the black dot disappears. As soon as you are no longer able to see any of the black mark at the bottom of the tube, stop dropping water inside. Make sure that you are viewing the test tube from the top and not the side.[2]
-
7Check the liquid level. Read the graduated line on the test tube that hits the surface of the testing liquid. This line will tell you the concentration of cyanuric acid in your sample. If the mark disappears when the liquid is under the 100 ppm mark, the cyanuric acid concentration is greater than 100 ppm. If it disappears above the 10 ppm mark, it is lower than 10 ppm. The ideal range for pool water is between 30 and 50 ppm.
-
8Run the test over, if the level is too high or too low. If the level of cyanuric acid is above 100 ppm, you will need to dilute another water sample and try the test again to determine the exact value. Take another sample, measuring out only 20 ml of pool water. Add 20 ml of distilled water to the sample water and mix to combine. Run through the test in the same exact way as before, but this time, use the newly prepared diluted sample.
-
9Adjust your water as needed and retest. Add as much cyanuric acid or fresh water to the pool as needed and retest the levels after the acid has had a chance to distribute itself evenly. This typically takes about four hours. Retest the water using the same steps performed to test the water the first time.
Test Strips
-
1Purchase a package of testing strips. Cyanuric acid strips have a unique chemical composition that is sensitive to the presence of cyanuric acid. Cyanuric acid testing strips are sold separately instead of being sold in kits since you can submerge the strip directly into the water without collecting a sample. Make sure that the package of testing strips you purchase comes with a color identification chart.
-
2Read the instructions. There is some difference between the strips, so make sure that you are using them properly. If any of the instructions vary from those indicated here, follow those instructions instead of these since they apply to the specific product you have on hand.
-
3Lower a strip into the pool water. When you are ready to test the water in your pool, remove one strip and submerge the test patch portion into the water for 30 seconds. Chemicals in the testing strip react with cyanuric acid in the water, producing a color on the testing patch of the strip.
-
4Compare the color on the strip with the color chart. Remove the strip from the water and compare the color to the color identification chart that came with your testing strips. The color or shade on the testing strip should correspond to a color on the identification chart. Each color will indicate a certain level of cyanuric acid, and those levels should be marked on the chart.
-
5Adjust the water as needed and retest. If you need to add cyanuric acid or dilute the pool water based on the amount detected by the testing strip, do so now and retest the level of cyanuric acid again afterward. You need to give the cyanuric acid a chance to distribute itself evenly throughout the water before retesting. The test strip instructions may provide further insight on how long to wait, but usually, you should wait at least four hours.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionCan I add cyanuric acid to lower my pool levels?
 Community AnswerLevels of what? I will assume chlorine. Adding cyanuric acid will not lower your pool's chlorine levels, however, it will stabilize them, meaning you will have to add less chlorine. Check with your local pool store to find out if cyanuric acid is appropriate for you.
Community AnswerLevels of what? I will assume chlorine. Adding cyanuric acid will not lower your pool's chlorine levels, however, it will stabilize them, meaning you will have to add less chlorine. Check with your local pool store to find out if cyanuric acid is appropriate for you. -
QuestionHow accurate is the test strips method compared to the turbidity method?
 TashTishCommunity AnswerTest strips are always inferior to drop tests or turbidity tests. The drop/turbidity tests from Taylor Technologies are considered best in class.
TashTishCommunity AnswerTest strips are always inferior to drop tests or turbidity tests. The drop/turbidity tests from Taylor Technologies are considered best in class. -
QuestionI imagine that the above questioner is wondering if cyanuric acid (CYA) will lower pH levels (increase acidity). I know it's not designed for this purpose, but do wonder if it's a side effect.
 TashTishCommunity AnswerSince it is a (weak) acid, one pound of cyanuric acid will lower pH by around 0.2.
TashTishCommunity AnswerSince it is a (weak) acid, one pound of cyanuric acid will lower pH by around 0.2.
References
About This Article
Cyanuric acid is a chlorine stabilizer commonly used in outdoor pools. You should test your pool once a week to make sure your cyanuric acid levels are under control. There are 2 main types of testing kit you can buy. With a test strip, all you need to do is submerge it in your pool for 30 seconds, then compare the color of the strip with the supplied chart. With a turbidity test, you’ll need to mix your pool water with a chemical reagent and use the pipette to drop this into the test tube until the black dot at the bottom disappears. Then, check the level on the test tube to measure your cyanuric acid level. Any level between 30 and 50 parts per million is safe, but check your state law for local restrictions. To learn the benefit of cyanuric acid in your pool, read on!