beta-Funaltrexamine
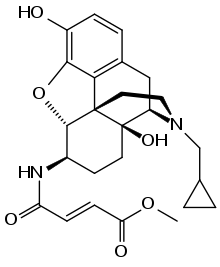
β-Funaltrexamine (β-FNA) is an irreversible (covalently bonding) opioid antagonist that was used to create the first crystal structure of the μ-opioid receptor.[1] Chemically, it is a naltrexone derivative with a methyl-fumaramide group in the 6-position.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl (2E)-4-{[17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-3,14-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxymorphinan-6β-yl]amino}-4-oxobut-2-enoate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl (2E)-4-{[(4R,4aS,7R,7aR,12bS)-3-(cyclopropylmethyl)-4a,9-dihydroxy-2,3,4,4a,5,6,7,7a-octahydro-1H-4,12-methano[1]benzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-yl]amino}-4-oxobut-2-enoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | β-FNA |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H30N2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 454.523 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Manglik A, Kruse AC, Kobilka TS, Thian FS, Mathiesen JM, Sunahara RK, et al. (March 2012). "Crystal structure of the µ-opioid receptor bound to a morphinan antagonist". Nature. 485 (7398): 321–6. doi:10.1038/nature10954. PMC 3523197. PMID 22437502.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.