2023 Maluku earthquake
A moment magnitude 7.6 earthquake struck offshore near the Tanimbar Islands, Maluku, Indonesia, at a depth of 105.1 km, on 10 January 2023.[4]
  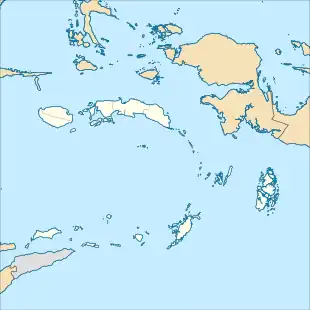  | |
| UTC time | 2023-01-09 17:47:34 |
|---|---|
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | 10 January 2023 |
| Local time | 02:47 WIT (Eastern Indonesia Time) |
| Magnitude | 7.6 Mw |
| Depth | 105.1 km (65 mi) |
| Epicenter | 7.085°S 130.939°E |
| Type | Oblique-slip |
| Areas affected | Banda Sea, Indonesia |
| Max. intensity | VI (Strong)[1] |
| Tsunami | 9 cm (0.30 ft) |
| Aftershocks | Mw 5.4[2] |
| Casualties | 11 injured[lower-alpha 1] |
Tectonic setting
Tectonic activity in North Maluku is filled with subduction and strike-slip fault lines. Intermediate to deep focus earthquakes with a focal depth of 60 km or greater are considered too deep to directly generate a significant tsunami. The 1938 Banda Sea earthquake, an intermediate depth magnitude 8.5–8.6 event, caused a relatively small tsunami [1.5 m (5 ft)].[5] A magnitude 8.1 earthquake struck about 37 km (23 mi) to the west in October 1963.[6] The most recent major earthquake prior to the 2023 event occurred in December 2021, measuring a magnitude of 7.3.[7] The region around Saumlaki has experienced earthquakes of intensities between IV (Light) to VI (Strong) in 1920, 1995, 2006, and 2009.[8]
Earthquake
The earthquake occurred at 02:47 WIT and had a magnitude of 7.5, according to the Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency (BMKG), while the United States Geological Survey and the European-Mediterranean Seismological Centre reported a magnitude of 7.6.[4] The epicentre of the quake was located around 430 km (270 mi) southeast of the city of Ambon and 341 km (212 mi) southwest of Tual.[4]
Intensity
According to the BMKG, the earthquake was felt with a maximum intensity of VI (Strong) in parts of Yamdena,[1] with intensity V (Moderate) being felt in the town of Saumlaki. It was also felt with an intensity of IV (Light) in the cities of Sorong, Kaimana, Waingapu, Waijelu and Tiakur, and the islands of Alor and Lembata.[9]
Tsunami
The Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency had issued a tsunami warning for the region, which was later cancelled.[10] Ecuadorian and Chilean officials said there was no tsunami threat to their countries.[11] The tsunami triggered by the earthquake only reached 9 cm (3.5 in) in Seira, Tanimbar Islands.[12]
Ground effects
Off the northern coast of Yamdena, an "island" was reported to have emerged from the sea shortly after the earthquake.[13] This triggered panic among residents, leading to a nearby village being temporarily evacuated.[13] Officials said that this phenomenon was likely an eruption of a mud volcano,[13] and similar phenomena have been observed in 1945, 1952, 1957, 2001, 2004, and 2013.[14]
Impact
A diver was killed after being struck by rocks and coral during a dive, however the BNPB said the person did not die during the earthquake, nor was it related.[3] 4 others were slightly injured,[15] 15 houses collapsed, and 523 others sustained light to heavy damage in the Tanimbar Islands.[16][17][18][19] In the neighbouring Southwest Maluku Regency, 344 houses and several schools were damaged, 39 of them severely. At least seven residents were also injured there.[8][20][18][19][15] At least two schools, seven health facilities, twelve churches, and eight government buildings were also affected.[19] In Selaru, three houses sustained repairable damages, while the wall of a high school collapsed.[17] A hotel that was once occupied by the President of Indonesia was also badly damaged.[17] Electricity was also disrupted.[21] In South Central Timor Regency, about 300 m (1,000 ft) was severely cracked and buckled after the earthquake, affecting transport and blocking access to five villages.[22] In total, around 400 people were left homeless by the earthquake.[19]
The earthquake was felt as far away as East Timor and northern Australia. Reports of the quake described it as being a strong and long-lasting tremor, with some people saying that their whole house was shaking and that they could hear the earth rumbling.[23][24]
References
Notes
Citations
- "Peta Isoseismal Gempabumi Maluku Tenggara Barat, 10 Januari 2022". BMKG (in Indonesian). 10 January 2023.
- National Earthquake Information Center (9 January 2023). "M 5.4 - Kepulauan Tanimbar, Indonesia". United States Geological Survey.
- "BPBD Maluku: Satu warga meninggal di Tanimbar bukan karena gempa M7,9". Antara (in Indonesian).
- National Earthquake Information Center (9 January 2023). "M 7.6 - Kepulauan Tanimbar, Indonesia". United States Geological Survey.
- Pranantyo, I.R.; Cummins, P.R. (2020). "The 1674 Ambon Tsunami: Extreme Run-Up Caused by an Earthquake-Triggered Landslide" (PDF). Pure and Applied Geophysics. 177 (3): 1639–1657. doi:10.1007/s00024-019-02390-2. hdl:1885/219284. S2CID 212731869. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- "M 8.1 - Banda Sea". United States Geological Survey. November 4, 1963.
- "M 7.3 - 121 km NNE of Lospalos, Timor Leste". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2021-12-29.
- "[Update] – Teridentifikasi 92 Rumah Warga Tanimbar Rusak Pascagempa M7,5" (in Indonesian). 10 January 2023.
- "Gempabumi Dirasakan". BMKG (in Indonesian). Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- Liam Coleman (9 January 2023). "Tsunami warning after 7.9 magnitude earthquake strikes Indonesia". Metro Radio.
- "Terremoto de 7.6 sacude a Indonesia; descartan tsunami en Ecuador y Chile" (in Spanish). 9 January 2023.
- "Tsunami Event: BANDA SEA". ngdc.noaa.gov. 10 January 2023.
- "Island' sighted near Tanimbar Islands after 7.5M quake". Antara. 10 January 2023.
- "Ini Daftar 'Pulau Baru' yang Pernah Muncul Usai Gempa Mirip di Maluku". Detik.com. 10 January 2023.
- "11 Orang Luka Akibat Gempa" (in Indonesian). 11 January 2023.
- "689 Rumah Rusak akibat Gempa M 7,5 di Maluku, Paling Banyak di Kepulauan Tanimbar" (in Indonesian). Kompas.com. 18 January 2023.
- "Catat! Ini Data Kerusakan Akibat Gempa M 7,9 di Tanimbar" [Note it! This is Damage Data from the M 7.9 Earthquake in Tanimbar] (in Indonesian). Maluku Terkini. 10 January 2023. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- "290 Rumah di Maluku Rusak akibat Gempa M 7,5, Paling Banyak di Tanimbar" [290 houses in Maluku were damaged by the M 7.5 earthquake, mostly in Tanimbar] (in Indonesian). Kompas.com. 11 January 2023. Retrieved 11 January 2023.
- "Update Dampak Gempa M 7,5 Maluku: 359 Rumah Rusak, 8 Korban Luka, 400 Warga Mengungsi" [Update on the Impact of the M 7.5 Maluku Earthquake: 359 Damaged Houses, 8 Injured Victims, 400 Refugees] (in Indonesian). Kompas.com. 11 January 2023. Retrieved 11 January 2023.
- "[Update] - Pascagempa M7,5 BPBD Maluku Barat Daya Laporkan 73 Rumah Rusak" (in Indonesian). 10 January 2023.
- "Gempa kuat musnahkan puluhan rumah, penduduk lari dalam gelap" (in Malay). 10 January 2023.
- "Terdampak Gempa M 7,5 Maluku, Jalanan di TTS NTT Ambles". Kompas (in Indonesian). January 10, 2023.
- "Powerful quake hits off Indonesia, rattles islands". The Manila Times. Agence France Presse. Retrieved 2023-01-10.
- "Tremors from magnitude-7.6 Indonesia earthquake felt in northern Australia". ABC News. 2023-01-09. Retrieved 2023-01-11.