4-Hydroxytestosterone
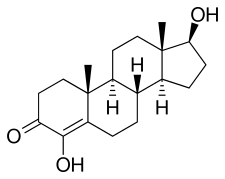
4-Hydroxytestosterone (4-OHT), also known as 4,17β-dihydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of testosterone that was never marketed. It was first patented by G.D. Searle & Company in 1955[1] and is testosterone with a hydroxy group at the four position. 4-OHT has moderate anabolic, mild androgenic, and anti-aromatase properties and is similar to the steroid clostebol (4-chlorotestosterone).[2]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 4,17β-Dihydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one; Androst-4-ene-4,17β-diol-3-one; Desmethylenestebol |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H28O3 |
| Molar mass | 304.430 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- US 2762818, Levy H, Mednick ML, "4-Hydroxytestosterone and esters", issued 11 September 1956, assigned to GD Searle.
- Kohler M, Parr MK, Opfermann G, Thevis M, Schlörer N, Marner FJ, Schänzer W (March 2007). "Metabolism of 4-hydroxyandrostenedione and 4-hydroxytestosterone: Mass spectrometric identification of urinary metabolites". Steroids. 72 (3): 278–86. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2006.11.018. PMID 17207827. S2CID 34982808.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.