Acefurtiamine
Acefurtiamine (INN) is a vitamin B1 analog in a manner similar to the GABAergic activity of the thiamine derivative clomethiazole.[1] It functions as an analgesic agent at sufficient doses.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
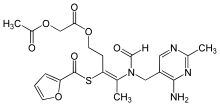
| Formula | C21H24N4O7S |
| Molar mass | 476.50 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- Martindale W (1993). The Extra Pharmacopoeia. Pharmaceutical Press. p. 1053. ISBN 978-0-85369-300-0.
- J. Elks; C. R. Ganellin (1990). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 2–. doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-2085-3. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.