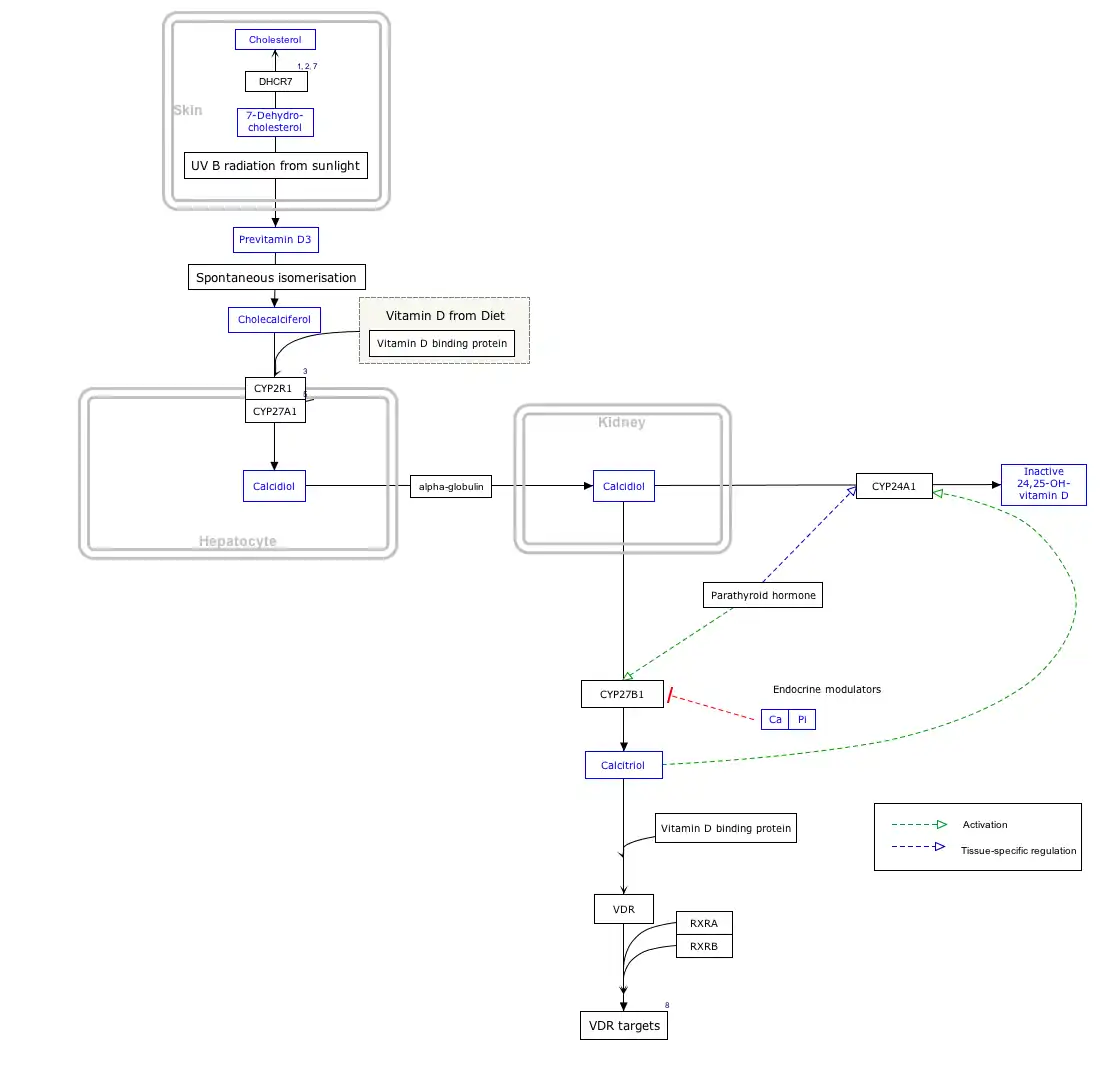
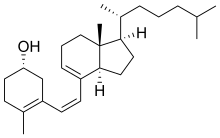
Previtamin D3
Previtamin D3 is an intermediate in the production of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3).
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3S,6Z)-9,10-Secocholesta-5(10),6,8-trien-3-ol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1S)-4-Methyl-3-[(Z)-2-{(1R,3aR,7aR)-7a-methyl-1-[(2R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-2,3,3a,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-yl}ethen-1-yl]cyclohex-3-en-1-ol | |
| Other names
Previtamin D3 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.304 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Previtamin+D(3) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H44O | |
| Molar mass | 384.648 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It is formed by the action of UV light, most specifically UVB light of wavelengths between 295 and 300 nm, acting on 7-dehydrocholesterol in the epidermal layers of the skin.[1][2][3]
The B ring of the steroid nucleus structure is broken open, making a secosteroid. This then undergoes spontaneous isomerization into cholecalciferol, the prohormone of the active form of vitamin D, calcitriol.
The synthesis of previtamin D3 is blocked effectively by sunscreens.[4]
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
References
- MacLaughlin JA, Anderson RR, Holick MF (May 1982). "Spectral character of sunlight modulates photosynthesis of previtamin D3 and its photoisomers in human skin". Science. 216 (4549): 1001–3. Bibcode:1982Sci...216.1001M. doi:10.1126/science.6281884. PMID 6281884.
- Webb AR (September 2006). "Who, what, where and when-influences on cutaneous vitamin D synthesis". Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. 92 (1): 17–25. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2006.02.004. PMID 16766240.
- Pope SJ, Holick MF, Mackin S, Godar DE (2008). "Action spectrum conversion factors that change erythemally weighted to previtamin D3-weighted UV doses". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 84 (5): 1277–83. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.2008.00373.x. PMID 18513232. S2CID 23246616.
- Sayre RM, Dowdy JC (2007). "Darkness at noon: sunscreens and vitamin D3". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 83 (2): 459–63. doi:10.1562/2006-06-29-RC-956. PMID 17115796. S2CID 23767593.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.