Atlas languages
The Atlas languages are a subgroup of the Northern Berber languages of the Afro-Asiatic language family spoken in the Atlas Mountains of Morocco. By mutual intelligibility, they are a single language spoken by perhaps 14 million people; however, they are distinct sociolinguistically and are considered separate languages by the Royal institute of the Amazigh culture. They are:[2][1]
- Central Atlas Tamazight (Central Atlas Berber), spoken in the central Atlas Mountains
- Shilha (Tashelhiyt; also rendered Tachelhit, Tasusit; includes Judeo-Berber and perhaps the extinct Lisan al-Gharbi), spoken in southern Morocco
- Sanhaja de Srair, spoken in the southern part of the Rif
- Ghomara, spoken in the western part of the Rif
- Lisan al-Gharbi, formerly spoken in western Morocco.
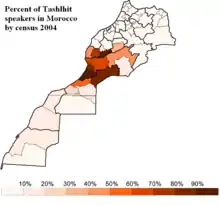
Percent of Tashelhit speakers (use in everyday's communication) in 2004[3]

Percent of Central Tamazight speakers (use in everyday's communication) in 2004[3]
| Atlas languages | |
|---|---|
| Masmuda | |
| Geographic distribution | Atlas Mountains, Souss |
| Linguistic classification | Afro-Asiatic
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Glottolog | atla1275 |
References
- Maarten Kossmann, "Berber subclassification (preliminary version)", Leiden (2011)
- Hammarström, Harald; Forke, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2020). "Atlas Berber". Glottolog 4.3.
- Maaroufi, Youssef. "Recensement général de la population et de l'habitat 2004".
![]()
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.