Bellerophon-class battleship
The Bellerophon-class battleship was a group of three dreadnought battleships that were built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. The sister ships spent most of their careers assigned to the Home and Grand Fleets. Aside from participating in the Battle of Jutland in May 1916, and the inconclusive action of 19 August several months later, their service during the First World War generally consisted of routine patrols and training in the North Sea.
_(14572599557).jpg.webp) Superb at anchor, shortly after commissioning | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Operators | |
| Preceded by | HMS Dreadnought |
| Succeeded by | St Vincent class |
| Built | 1906–1909 |
| In service | 1909–1921 |
| In commission | 1909–1921 |
| Completed | 3 |
| Scrapped | 3 |
| General characteristics (as built) | |
| Type | Dreadnought battleship |
| Displacement | 18,596 long tons (18,894 t) (normal) |
| Length | 526 ft (160.3 m) (o/a) |
| Beam | 82 ft 6 in (25.1 m) |
| Draught | 27 ft (8.2 m) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | 4 × shafts; 2 × steam turbine sets |
| Speed | 21 knots (39 km/h; 24 mph) |
| Range | 5,720 nmi (10,590 km; 6,580 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement | 680–840 |
| Armament |
|
| Armour | |
In late 1918, Temeraire and Superb were transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet and supported Allied forces in the Mediterranean and the Black Sea after the war ended in November. The Bellerophons were deemed obsolete by this time and were reduced to reserve in 1919 and were then used as training ships. Superb was used for gunnery experiments in 1920 and then became a target ship in 1922 before being sold for scrap later that year. Bellerophon and Temeraire were sold in late 1921 and subsequently broken up.
Background and description
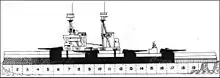
The Admiralty's 1905 draft building plan envisioned four battleships in the 1906–1907 Naval Programme, but the new Liberal government cut one of these ships in mid-1906. The Bellerophon-class design was a slightly larger and improved version of the revolutionary[Note 1] preceding HMS Dreadnought, with better underwater protection and a more powerful secondary armament.[2]
The Bellerophon-class ships had an overall length of 526 feet (160.3 m), a beam of 82 feet 6 inches (25.1 m),[3] and a normal draught of 27 feet (8.2 m).[4] They displaced 18,596 long tons (18,894 t) at normal load and 22,211–22,540 long tons (22,567–22,902 t) at deep load. Their crews numbered about 680 officers and ratings upon completion and 840 in 1914.[3]
The Bellerophons were powered by two sets of Parsons direct-drive steam turbines, each of which was housed in a separate engine room. The outer propeller shafts were coupled to the high-pressure turbines and these exhausted into low-pressure turbines which drove the inner shafts. Separate cruising turbines were provided for each shaft. The turbines used steam from eighteen water-tube boilers at a working pressure of 235 psi (1,620 kPa; 17 kgf/cm2). They were rated at 23,000 shaft horsepower (17,000 kW) and were intended to give the ships a maximum speed of 21 knots (39 km/h; 24 mph). Refinements to the hull shape allowed the larger Bellerophon class to match Dreadnought's speed despite the same horsepower rating. During their sea trials, the ships handily exceeded their designed speed and horsepower. To save weight, they carried slightly less fuel than Dreadnought: 2,648 long tons (2,690 t) of coal and an additional 840 long tons (853 t) of fuel oil that was sprayed on the coal to increase its burn rate. This gave them a range of 5,720 nautical miles (10,590 km; 6,580 mi) at a cruising speed of 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph).[5]
Armament and armour

In the interest of saving time, the Bellerophons retained the same main battery and turret layout as Dreadnought:[6] ten breech-loading (BL) 12-inch (305 mm) Mk X guns in five twin-gun turrets, three along the centreline and the remaining pair as wing turrets. The centreline turrets were designated 'A', 'X' and 'Y', from front to rear, and the port and starboard wing turrets were 'P' and 'Q' respectively. The guns could initially be depressed to −5° and elevated to +13.5°, although the turrets were modified to allow 16° of elevation during the First World War. They fired 850-pound (390 kg) projectiles at a muzzle velocity of 2,746 ft/s (837 m/s); at +13.5°, this provided a maximum range of 16,500 yd (15,100 m) with armour-piercing (AP) 2 crh shells. Using the more aerodynamic, but slightly heavier, 4 crh AP shells at the same elevation, the range was extended to 18,850 yd (17,240 m). The rate of fire of these guns was about two rounds per minute[7] and the ships carried 80 shells per gun.[3]
The 12-pounder (3-inch (76 mm)) guns with which Dreadnought was equipped to provide protection from torpedo boats were recognised as being insufficiently powerful and sixteen 4-inch (102 mm) guns replaced the twenty-eight guns on Dreadnought. These were 50-calibre BL 4-inch Mark VII guns. Pairs of these guns were installed in unshielded mounts on the roofs of 'A', 'P', 'Q' and 'Y' turrets, and the other eight were positioned in single mounts at forecastle-deck level in the superstructure.[8][Note 2] The guns had a maximum elevation of +15° which gave them a range of 11,400 yd (10,424 m). They fired 31-pound (14.1 kg) projectiles at a muzzle velocity of 2,821 ft/s (860 m/s).[11] They were provided with 200 rounds per gun. Four 3-pounder (1.9 in (47 mm)) saluting guns were also carried. The ships were equipped with three 18-inch (450 mm) submerged torpedo tubes, one on each broadside and another in the stern, for which fourteen torpedoes were provided.[3]
In order to accommodate the weight of the enlarged anti-torpedo bulkheads, the thickness of the waterline belt of the Bellerophon-class ships was reduced from 11 to 10 inches (279 to 254 mm) in thickness. The belt consisted of Krupp cemented armour that extended between 'A' and 'Y' barbettes, reducing to a thickness of 6 inches (152 mm) forward and 5 inches (127 mm) aft before it reached the ships' ends. It covered the side of the hull from the middle deck down to 5 feet 2 inches (1.6 m) below the normal waterline where it tapered to 8 inches (203 mm) on the bottom edge. Above this was a strake of armour 8 inches thick that had its top edge 8 feet 6 inches (2.6 m) above the waterline. An 8-inch oblique bulkhead connected the thickest parts of the waterline and upper armour belts to the rear barbette; there was no forward equivalent.[12]
The three centreline barbettes were protected by armour 9 inches (229 mm) thick above the main deck that thinned to 5 inches (127 mm) below it, except for the rear barbette which was 9 inches thick for its entire height. The wing barbettes were similar except that they had 10 inches (254 mm) of armour on their outer faces. The gun turrets had 11-inch (279 mm) faces and sides with 3-inch roofs. The three armoured decks ranged in thicknesses from 0.75 inches (19 mm) to 4 inches. The front and sides of the forward conning tower were protected by 11-inch plates, although the rear and roof were 8 inches and 3 inches thick, respectively. The aft conning tower had 8-inch sides and a 3-inch roof. While Dreadnought had torpedo bulkheads that protected only the magazines, the Bellerophons had complete longitudinal bulkheads, 0.75 to 3 inches thick, that covered the sides of the hull between the fore and aft magazines.[12]
Fire control

Dreadnought's tripod foremast was positioned behind the forward funnel to allow the vertical leg to serve as a support for the boat-handling derrick. This meant that the hot funnel gases could render the spotting top uninhabitable in conditions of little or no wind. The Bellerophons had the foremast moved forward of the funnels to reduce the problem in the spotting top and a second tripod mast was added to handle the derrick, but it had to be positioned in front of the aft funnel to do that, which rendered the aft spotting top almost useless as it could be exposed to the exhaust plumes from both funnels under certain circumstances.[13]
The control positions for the main armament were located in the spotting tops at the head of the fore and mainmasts. Data from a 9-foot (2.7 m) Barr and Stroud coincidence rangefinder located at each control position was input into a Dumaresq mechanical computer and electrically transmitted to Vickers range clocks located in the transmitting station located beneath each position on the main deck, where it was converted into range and deflection data for use by the guns. The target's data was also graphically recorded on a plotting table to assist the gunnery officer in predicting the movement of the target. The turrets, transmitting stations, and control positions could be connected in almost any combination.[14] As a backup, 'A' and 'Y' turrets in each ship could take over if necessary.[15]
An experimental fire-control director was fitted in the forward spotting top and evaluated in May 1910. This electrically provided data to the turrets via pointers, which the turret crew were to follow. The director layer fired the guns simultaneously which aided in spotting the shell splashes and minimised the effects of the roll on the dispersion of the shells.[16] The director was subsequently removed, but Superb had a production model installed by May 1915 and both Temeraire and Bellerophon received theirs by May 1916.[17] The latter's director, however, was not fully installed by the date of the Battle of Jutland at the end of the month and she fought without it.[18] Furthermore, they were fitted with Mark I Dreyer Fire-control Tables by early 1916 in the transmission stations. It combined the functions of the Dumaresq and the range clock.[19]
Modifications

The guns on the forward turret roof were transferred to the superstructure in 1913–1914 on Bellerophon and on her sisters in 1914. During the first year of the war, the guns on the wing turrets were moved into the aft part of the superstructure. Sometime around 1915, the guns on the stern turret were removed as were a pair from the superstructure, which reduced their secondary armament to a total of twelve guns. About that time, a pair of 3-inch (76 mm) anti-aircraft (AA) guns were added. Approximately 23 long tons (23 t) of additional deck armour were added after the Battle of Jutland in May 1916. By April 1917, the sisters mounted single 4-inch and 3-inch AA guns and the stern torpedo tube had been removed. One additional 4-inch gun was removed from Superb in 1917–1918. In 1918, a high-angle rangefinder was fitted on the forward spotting top and flying-off platforms were installed on the roofs of the fore and aft turrets of Bellerophon. After the war, Temeraire had four 4-inch guns removed to make space for naval cadets and the AA guns were stripped from her and Superb.[20]
Ships
| Ship | Builder[9] | Laid down[9] | Launched[9] | Commissioned[21] | Cost (including armament) according to | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burt[3] | Parkes[8] | |||||
| Bellerophon | HM Dockyard, Portsmouth | 6 December 1906 | 27 July 1907 | 20 February 1909 | £1,763,491 | £1,765,342 |
| Temeraire | HM Dockyard, Devonport | 1 January 1907 | 24 August 1907 | 15 May 1909 | £1,744,287 | £1,751,144 |
| Superb | Armstrong Whitworth, Elswick | 6 February 1907 | 7 November 1907 | 9 June 1909 | £1,676,529 | £1,641,114 |
Careers

Upon commissioning, all three ships were assigned to the 1st Division of the Home Fleet and were reviewed by King Edward VII and Tsar Nicholas II of Russia during Cowes Week on 31 July 1909. They participated in the Coronation Fleet Review for King George V at Spithead on 24 June 1911. Less than a year later, the 1st Division was renamed the 1st Battle Squadron (BS) on 1 May 1912. Superb and Temeraire visited Cherbourg, France, in July 1913. Bellerophon was transferred to the 4th BS in March 1914, followed by Temeraire in July. Each of the sisters underwent a lengthy refit before the First World War began in August.[22]
Between 17 and 20 July 1914, the sisters took part in a test mobilisation and fleet review as part of the British response to the July Crisis. Afterwards, they were ordered to proceed with the rest of the Home Fleet to Scapa Flow[22] to safeguard the fleet from a possible surprise attack by the Imperial German Navy. After the British declaration of war on Germany on 4 August, the Home Fleet was reorganised as the Grand Fleet, and placed under the command of Admiral John Jellicoe.[23] According to pre-war doctrine, the role of the Grand Fleet was to fight a decisive battle against the German High Seas Fleet. This grand battle was slow to happen, however, because of the Germans' reluctance to commit their battleships against the superior British force. As a result, the Grand Fleet spent its time training in the North Sea, punctuated by the occasional mission to intercept a German raid or major fleet sortie. Superb joined her sisters in the 4th BS in November 1915.[24]
Battle of Jutland
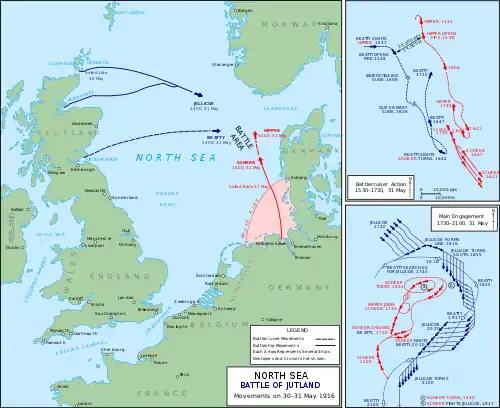
In an attempt to lure out and destroy a portion of the Grand Fleet, the German High Seas Fleet departed the Jade Bight early on the morning of 31 May 1916 in support of Rear Admiral Franz von Hipper's battlecruisers which were to act as bait. The Royal Navy's Room 40 had intercepted and decrypted German radio traffic containing plans of the operation, so the Admiralty ordered the Grand Fleet to sortie the night before to cut off and destroy the High Seas Fleet.[25]
Once Jellicoe's ships had rendezvoused with the 2nd Battle Squadron, coming from Cromarty, Scotland, on the morning of 31 May, he organised the main body of the Grand Fleet in parallel columns of divisions of four dreadnoughts each. The two divisions of the 2nd BS were on his left (east), the 4th BS was in the centre and the 1st BS on the right. When Jellicoe ordered the Grand Fleet to deploy to the left and form line astern in anticipation of encountering the High Seas Fleet, this naturally placed the 4th and 1st Battle Squadrons in the center and rear of the line of battle, respectively, which meant that the sisters were in the middle of the Grand Fleet once it finished deploying.[26] All three ships fired at the crippled light cruiser SMS Wiesbaden, possibly scoring some hits, as well as the battlecruiser SMS Derfflinger. Temeraire was the only one of the sisters to score a hit on the battlecruiser, although it did little damage. Bellerophon and Temeraire also fired at German destroyers, but failed to make any hits. None of the sisters fired more than 62 rounds from their main guns during the battle.[27]
Subsequent activity
The Grand Fleet sortied on 18 August to ambush the High Seas Fleet while it advanced into the southern North Sea, but a series of miscommunications and mistakes prevented Jellicoe from intercepting the German fleet before it returned to port. Two light cruisers were sunk by German U-boats during the operation, prompting Jellicoe to decide to not risk the major units of the fleet south of 55° 30' North due to the prevalence of German submarines and mines. The Admiralty concurred and stipulated that the Grand Fleet would not sortie unless the German fleet was attempting an invasion of Britain or there was a strong possibility it could be forced into an engagement under suitable conditions.[28]

During June–September 1917, Bellerophon served as the junior flagship of the 4th BS while the regular flagship was being refitted.[29] The Grand Fleet sortied on the afternoon of 23 April 1918 after radio transmissions revealed that the High Seas Fleet was at sea after a failed attempt to intercept the regular British convoy to Norway. The Germans were too far ahead of the British, and no shots were fired.[30] In October, Superb and Temeraire were transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet[31] and Superb became the fleet flagship. The ship led an Allied squadron that entered the Ottoman capital, Constantinople, on 13 November, following the Armistice of Mudros.[32] Bellerophon was present at Rosyth, Scotland, when the German fleet surrendered on 21 November and she became a gunnery training ship in March 1919 at the Nore as the class was obsolescent.[29]
Superb and Temeraire returned home the following month after supporting Allied operations in the Eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea and were placed into reserve. Later that year, Temeraire was converted into a cadet training ship and continued on that duty until early 1921 when she was paid off. In the meantime Superb relieved Bellerophon as a gunnery training ship in late 1919 and the latter was reduced to reserve. Superb was relieved in her turn at the end of 1919 and was paid off in early 1920. The ship was used for gunnery trials beginning at the end of the year and was used as a target ship during 1922 before being sold, the last of the sisters still in existence as Temeraire and Bellerophon had been sold for scrap in late 1921.[22]
Notes
- Dreadnought was the first battleship with a homogenous main battery, and was the most powerful and fastest battleship in the world at the time of her completion. She made all other battleships obsolete and gave her name to all the subsequent battleships of her type.[1]
- Sources disagree on the type and composition of the secondary armament. Burt claims that they were the older quick-firing QF Mark III guns.[3] Neither book by Preston identify the type, but he does call them quick-firers.[4][9] Parkes also does not identify the type, but he does say that they were 50-calibre guns[8] and Preston agrees.[9] Friedman shows the QF Mark III as a 40-calibre gun and states that the 50-calibre BL Mark VII gun armed all of the early dreadnoughts.[10]
Citations
- Konstam, pp. 4–5
- Friedman 2015, pp. 95–97
- Burt, p. 64
- Preston 1972, p. 125.
- Burt, pp. 31, 64
- Friedman 2015, p. 97
- Friedman 2011, pp. 59–61
- Parkes, p. 498
- Preston 1985, p. 22
- Friedman, pp. 97–98
- Friedman 2011, pp. 97–98
- Burt, pp. 62, 64; Parkes, p. 498
- Brooks 1995, pp. 41–42
- Brooks 1995, pp. 40–41
- Brooks 2005, p. 61
- Brooks 2005, p. 48
- Brooks 1996, p. 168
- "H.M.S. Bellerophon (1907)". The Dreadnought Project. Retrieved 17 February 2017.
- Brooks 2005, pp. 157–158, 175
- Burt, pp. 66, 68–71
- Burt, pp. 71–73
- Burt, pp. 71–74
- Massie, pp. 19, 69
- Burt, p. 73
- Tarrant, pp. 54–55, 57–58
- Corbett, p. 431 and frontispiece map
- Campbell, pp. 156–57, 208, 210, 212, 231–32, 349
- Halpern 1995, pp. 330–32
- Burt, p. 71
- Massie, p. 748
- Newbolt, p. 353
- Burt, p. 73; Halpern 2011, pp. 3, 12, 14–15, 17–18, 25
Bibliography
- Brooks, John (2005). Dreadnought Gunnery and the Battle of Jutland: The Question of Fire Control. London: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-40788-5.
- Brooks, John (1995). "The Mast and Funnel Question: Fire-control Positions in British Dreadnoughts". In Roberts, John (ed.). Warship 1995. London: Conway Maritime Press. pp. 40–60. ISBN 0-85177-654-X.
- Brooks, John (1996). "Percy Scott and the Director". In McLean, David; Preston, Antony (eds.). Warship 1996. London: Conway Maritime Press. pp. 150–170. ISBN 0-85177-685-X.
- Brown, David K. (1999). The Grand Fleet: Warship Design and Development 1906–1922. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-55750-315-X.
- Burt, R. A. (1986). British Battleships of World War One. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-863-8.
- Campbell, N. J. M. (1986). Jutland: An Analysis of the Fighting. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-324-5.
- Corbett, Julian (1997) [1940]. Naval Operations. History of the Great War: Based on Official Documents. Vol. III (Second ed.). London and Nashville, Tennessee: Imperial War Museum in association with the Battery Press. ISBN 1-870423-50-X.
- Friedman, Norman (2015). The British Battleship 1906–1946. Barnsley, UK: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-225-7.
- Friedman, Norman (2011). Naval Weapons of World War One: Guns, Torpedoes, Mines and ASW Weapons of All Nations; An Illustrated Directory. Barnsley, UK: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-100-7.
- Halpern, Paul, ed. (2011). The Mediterranean Fleet 1920–1929. Navy Records Society Publications. Vol. 158. Farnham, UK: Ashgate. ISBN 978-1-4094-2756-8.
- Halpern, Paul G. (1995). A Naval History of World War I. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-55750-352-4.
- Jellicoe, John (1919). The Grand Fleet, 1914–1916: Its Creation, Development, and Work. New York: George H. Doran Company. OCLC 13614571.
- Konstam, Angus (2013). British Battleships 1914-18 (1): The Early Dreadnoughts. New Vanguard. Vol. 200. Botley, UK: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-78096-167-5.
- Massie, Robert K. (2003). Castles of Steel: Britain, Germany, and the Winning of the Great War at Sea. New York: Random House. ISBN 0-679-45671-6.
- Newbolt, Henry (1996) [1931]. Naval Operations. History of the Great War Based on Official Documents. Vol. V. Nashville, Tennessee: Battery Press. ISBN 0-89839-255-1.
- Parkes, Oscar (1990) [1966]. British Battleships, Warrior 1860 to Vanguard 1950: A History of Design, Construction, and Armament (New & rev. ed.). Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-55750-075-4.
- Preston, Antony (1972). Battleships of World War I: An Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Battleships of All Nations 1914–1918. New York: Galahad Books. ISBN 0-88365-300-1.
- Preston, Antony (1985). "Great Britain and Empire Forces". In Gray, Randal (ed.). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. pp. 1–104. ISBN 0-85177-245-5.
- Tarrant, V. E. (1999) [1995]. Jutland: The German Perspective: A New View of the Great Battle, 31 May 1916. London: Brockhampton Press. ISBN 1-86019-917-8.
External links
- World War I Naval Combat - HMS Bellerophon
- MaritimeQuest Bellerophon Class Overview
- Dreadnought Project Technical material on the weaponry and fire control for the ships