Coxa valga
Coxa valga is a deformity of the hip where the angle formed between the head and neck of the femur and its shaft is increased, usually above 135 degrees.
| Coxa valga | |
|---|---|
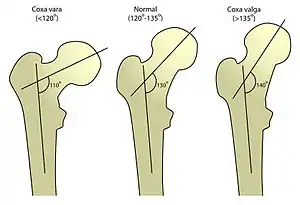 | |
| Left to right: coxa vara, normal femur, coxa valga | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
The differential diagnosis includes neuromuscular disorders (i.e. cerebral palsy, spinal dysraphism, poliomyelitis), skeletal dysplasias, and juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Coxa valga deformity is a common pathologic condition in children with cerebral palsy and they may be predisposed to hip subluxation or dislocations.[1]
See also
References
- Hsieh, H. C.; Wang, T. M.; Kuo, K. N.; Huang, S. C.; Wu, K. W. (2019). "Guided Growth Improves Coxa Valga and Hip Subluxation in Children with Cerebral Palsy". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 477 (11): 2568–2576. doi:10.1097/CORR.0000000000000903. PMC 6903837. PMID 31425278.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.