Emivirine
Emivirine (MKC-442) is a failed experimental agent for the treatment of HIV. It is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor.[1] While emivirine showed promising antiviral activity in vitro, it failed to show sufficient efficacy in human trials. However it is still notable as an early proof of concept, which led to the discovery of a number of related antiviral drugs.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
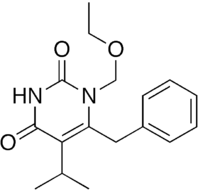
| Preferred IUPAC name
6-Benzyl-1-(ethoxymethyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H22N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 302.36818 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- "Emivirine".
- Calenbergh SV, Herdewijn P. A heterogeneous collection of novel antiviral pyrimidines. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents 2000; 10(3):289-295. DOI:10.1517/13543776.10.3.289
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.