Lasinavir
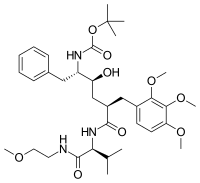
Lasinavir (INN,[1] previously known as BMS-234475 and CGP-61755) is an experimental peptidomimetic protease inhibitor researched by Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb as a treatment for HIV infection. It was originally discovered by Novartis at Basel (Switzerland).[2] Its investigation was terminated after Phase I on October 09, 2002.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
tert-Butyl (3S,4S,6R,9S)-13-benzyl-12-hydroxy-6,9-dioxo-7-(propan-2-yl)-10-[(2,3,4-trimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-2-oxa-5,8,14-triazapentadecan-15-oate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C35H53N3O9 | |
| Molar mass | 659.81 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). RECOMMENDED International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 38" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. World Health Organization. 11 (3): 170. 1997. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- B2 US patent 7348345 B2, James Patrick Dunn, Steven Swallow, Zachary Kevin Sweeney, "Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors", issued 2008-08-02
- "Drug Profile: Lasinavir". AdisInsight. Adis International Ltd, part of Springer Science+Business Media. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.