Immigration to Spain
Immigration to Spain increased significantly in the beginning of the 21st century. In 1998, immigrants accounted for 1.6% of the population, and by 2009, that number had jumped to above 12% — one of the highest in Europe at the time. Until 2014, the numbers were decreasing due to the economic crisis, but since then, immigration to Spain has increased again since 2015,[2] especially after 2021.[3]
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 8,307,497 born abroad (17.23%)
6,227,092 foreign citizenship (12.92%) 48,196,693 Total population of Spain (2023) |
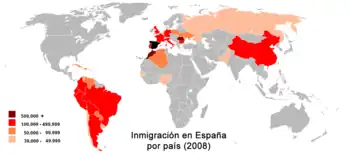
As of 2023, there were 8,307,497 foreign-born people in Spain, making up to 17.23% of the Spanish population, including 5,308,314 (11.14%) born in a non-European country. Of these, 6,227,092 (12.92%) didn't have Spanish citizenship.[4] This makes Spain one of the world's preferred destinations to immigrate to, being the 4th country in Europe by immigration numbers and the 10th worldwide. Spain attracts significant immigration from Latin America and Eastern Europe. The fastest-growing immigrant groups in 2017 were Venezuelans, Colombians, Italians, Ukrainians, and Argentines.[5]
The population of Spain doubled during the 20th century due to the spectacular demographic boom in the 1960s and early 1970s. The birth rate then plunged by the 1980s, and Spain's population became stagnant, its demographics showing one of the lowest sub-replacement fertility rate in the world..
During the early 21st century, the average year-on-year demographic growth set a new record with its 2003 peak variation of 2.1%, doubling the previous record reached back in the 1960s when a mean year on year growth of 1% was experienced.[6] This trend is far from being reversed at the present moment and, in 2005 alone, the immigrant population of Spain increased by 700,000 people.[7]
Spain accepted 478,990 new immigrant residents in the first six months of 2022 alone. During these first six months, 220,443 people also emigrated from Spain, leaving a record-breaking net migration figure of 258,547.[8] The data shows that more women than men chose to move to Spain during 2022, this is due to higher rates of emigration from Latin America.[8]
Currently
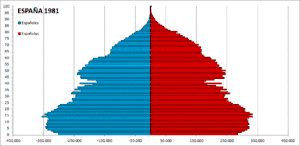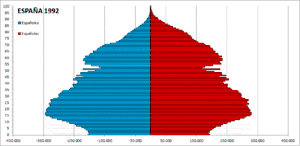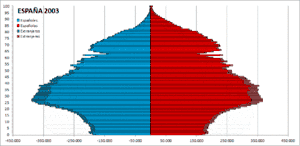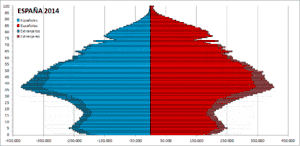
| Foreign population in Spain[9][10][11] | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Population | % total | |||||||||||||||||
| 1981 | 198,042 | 0.52% | |||||||||||||||||
| 1986 | 241,971 | 0.63% | |||||||||||||||||
| 1991 | 360,655 | 0.91% | |||||||||||||||||
| 1996 | 542,314 | 1.37% | |||||||||||||||||
| 1998 | 637,085 | 1.60% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2000 | 923,879 | 2.28% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2001 | 1,370,657 | 3.33% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2002 | 1,977,946 | 4.73% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2003 | 2,664,168 | 6.24% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2004 | 3,034,326 | 7.02% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | 3,730,610 | 8.46% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 4,144,166 | 9.27% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 4,519,554 | 9.9% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 5,268,762 | 11.4% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 5,648,671 | 12.1% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2010 | 5,747,734 | 12.2% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | 5,751,487 | 12.2% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 5,736,258 | 12.1% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 5,546,238 | 11.8% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 5,023,487 | 10.7% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | 4,729,644 | 10.1% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 4,618,581 | 9.9% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 4,572,807 | 9.8% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 4,663,726 | 10.0% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 5,023,279 | 10.7% | |||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 5,434,153 | 11.5% | |||||||||||||||||
According to the United Nations, there were 5,947,106 immigrants in Spain in early 2018, 12.8% of population of Spain.[12] According to the Spanish government, there were 5.6 million foreign residents in Spain in 2010; independent estimates put the figure 14% of total population (Red Cross, World Disasters Report 2006). According to the official 2011 census data, almost 800,000 were Romanian, 774,000 were Moroccan, 317,000 were Ecuadorian, 312,000 were British and 250,000 were Colombian . Other important foreign communities are Bolivian (4.1%), German (3.4%), Italian (3.1%), Bulgarian (2.9%), Chinese (2.6%) and Argentine (2.5%). In 2005, a regularization programme increased the legal immigrant population by 700,000 people. Since 2000, Spain has experienced high population growth as a result of immigration flows, despite a birth rate that is only half of the replacement level.
According to Eurostat, in 2010, there were 6.4 million foreign-born residents in Spain, corresponding to 14.0% of the total population. Of these, 4.1 million (8.9%) were born outside the EU and 2.3 million (5.1%) were born in another EU Member State.[13]
As of 2005 Spain had the second highest immigration rates within the EU, just after Cyprus, and the second highest absolute net migration in the World (after the USA).[14] This can be explained by a number of reasons including its strong economic growth at the time, the large size of its underground economy and the strength of the agricultural and construction sectors which demand more low cost labour than can be offered by the national workforce, as well as business opportunities for immigrants coming from other developed countries. In fact, booming Spain was Europe's largest absorber of migrants from 2002 to 2007, with its immigrant population more than doubling as 2.5 million people arrived.
Over 920,000 immigrants arrived in Spain during 2007, on top of the 802,971 new arrivals in 2006, 682,711 new arrivals in 2005, and 645,844 new arrivals in 2004.[15]
Although the number of immigrants in Spain, officially, is smaller than that of other countries in the EU, the following data should be taken into consideration:

- Immigrants from countries belonging to the former Spanish Empire (mainly in Central and South America–Latin America–, Asia–the Philippines– and Africa–Equatorial Guinea and Western Sahara–) can obtain Spanish nationality after legal and continuous residence of 2 years in Spain, after which naturalized citizens are no longer counted as immigrants.
- In order to avoid statelessness, Spain automatically grants Spanish nationality to the children of immigrants born in Spain whose parents' nationality of origin is not transferred jus sanguinis upon their child's birth abroad. This is unlike many other countries in the EU. It is for this reason that although the Latin American immigrants of origin are most numerous, the Romanians or the Moroccans surpassed them in the official statistics.
In the same way the majority of children born in Spain between 2000 and 2010 are children of immigrants despite not counting as such. Considering these data, there are sectors of Spanish society who oppose immigration that affirm the real number of immigrants in Spain is 10–11 million, or about 25% of the total population.
As for nationalities outside of this category, in order to stay in Spain for more than 3 months, a residence card, residence visa or work permit is required.[16]
In all, two distinct groups can be identified: those immigrants (mostly in working age) originating from countries mostly located in Eastern Europe, South America or Africa, with lower GDP per capita than Spain, comprising most of the immigrating population, and those (whom many are retired) immigrants originating from northern European or another western countries with a higher GDP per capita than Spain.[17]
Immigrants from Europe
Immigrants from Europe make up a growing proportion of immigrants in Spain. The main countries of origin are Romania, the United Kingdom, Germany, Italy, and Bulgaria.
The British authorities estimate that the real population of British citizens living in Spain is much bigger than Spanish official figures suggest, establishing them at about 1,000,000, about 800,000 being permanent residents.[18] Of these, according to the BBC and contrary to popular belief, only about 21.5% are over the age of 65.[19]
In fact, according to the Financial Times, Spain is the most favoured destination for West Europeans considering to move from their own country and seek jobs elsewhere in the EU.[20]
Social attitudes to immigration
Unlike other countries in the EU, Spain has not recorded any relevant anti-immigration about until fairly recently.[21] According to some analysts, the causes behind this are multiple. Drawing from the experience of many Spaniards during the 1960s and then again in the beginning of the 21st century when the crisis struck the country, there may be also a collective understanding that hardships force people to seek work abroad.[21]
A January 2004 survey by Spanish newspaper El País showed that the "majority" of Spaniards believe immigration was too high.[22] Small parties, such as Movimiento Social Español, openly campaign using nationalist or anti-immigrant rhetoric as do other small far-right parties such as National Democracy (Spain) and España 2000. These parties have never won national or regional parliamentary seats. However, since its foundation in recent years, the far-right politicl party Vox has managed to disrupt mainstream politics, favouring tough stance against immigration.[23]
Immigration by country of origin
Population by country of birth as of 2021:[24]
| Country | Population |
|---|---|
| 935,089 | |
| 556,204 | |
| 514,110 | |
| 416,527 | |
| 413,662 | |
| 302,406 | |
| 268,957 | |
| 244,827 | |
| 210,529 | |
| 208,788 | |
| 186,395 | |
| 178,829 | |
| 167,388 | |
| 164,853 | |
| 156,499 | |
| 143,151 | |
| 133,297 | |
| 116,155 | |
| 113,194 | |
| 107,354 | |
| 101,406 | |
| 97,447 | |
| 95,221 | |
| 82,353 | |
| 79,903 | |
| 71,474 | |
| 63,375 | |
| 62,410 | |
| 61,276 | |
| 60,637 | |
| 58,458 | |
| 56,847 | |
| 52,426 |
Recent trends
| Country | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31,553 | 52,385 | 71,666 | 73,932 | |
| 30,097 | 40,372 | 61,715 | 73,560 | |
| 24,844 | 36,678 | 56,253 | 80,054 | |
| 23,876 | 28,875 | 31,276 | 37,617 | |
| 27,860 | 30,235 | 28,030 | 25,675 | |
| 11,074 | 18,573 | 23,671 | 29,185 | |
| 18,526 | 22,203 | 22,002 | 21,517 | |
| 9,711 | 15,945 | 21,463 | 31,307 | |
| 10,852 | 14,904 | 19,166 | 31,132 | |
| 11,954 | 14,816 | 17,863 | 18,703 | |
| 13,341 | 16,290 | 16,210 | 16,543 | |
| 12,349 | 15,600 | 15,893 | 17,635 | |
| 8,122 | 10,280 | 14,265 | 17,588 | |
| 9,942 | 12,719 | 13,853 | 15,050 | |
| 10,505 | 12,714 | 13,314 | 13,262 | |
| 10,552 | 11,779 | 12,182 | 12,757 | |
| 4,250 | 6,330 | 11,732 | 17,410 | |
| 9,709 | 11,324 | 10,813 | 11,037 | |
| Total | 414,746 | 532,132 | 643,684 | 748,759 |
| Place of Birth | Year | |
|---|---|---|
| 2011[26][27] | ||
| Number | % | |
| Place of Birth in Reporting Country (Spain) | 41,153,550 | |
| Place of Birth Not in Reporting Country | 5,648,995 | |
| Other EU Member State | 1,890,605 | |
| Outside EU but within Europe | 239,880 | |
| Outside Europe/ Non-European | 3,758,390 | |
| Africa | 945,905 | |
| Asia | 259,345 | |
| North America | 41,220 | |
| Caribbean, South or Central America | 2,265,685 | |
| Oceania | 6,360 | |
| Total | 46,815,910 | 100% |
| Foreign Population by Nationality[28] | Number | % |
| 2022 | ||
| TOTAL FOREIGNERS | 5,542,932 | |
| EUROPE | 2,205,961 | |
| EUROPEAN UNION | 1,617,911 | |
| OTHER EUROPE | 588,050 | |
| AFRICA | 1,217,706 | |
| SOUTH AMERICA | 1,173,900 | |
| CENTRAL AMERICA | 368,461 | |
| NORTH AMERICA | 76,628 | |
| ASIA | 493,065 | |
| OCEANIA | 3,580 | |
| Instituto Nacional de Estadística | ||
Major immigration
This chart shows the numbers and difference of foreign nationals in Spain after 2000. European Union member states are indicated with the EU flag in regional European sub-divisions. The number of Latin American immigrants decreased massively after 2009 mostly due to the naturalization of hundreds of thousands of these citizens who achieved the Spanish citizenship and therefore do not count as immigrants anymore on the official statistics.[29] See the chart from below from the "Naturalizations" paragraph for further information.
| Origin | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020[30] | Article |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 173,158 | 511,294 | 754,080 | 750,883 | 865,945 | Moroccans in Spain | |
| 6,410 | 317,366 | 831,235 | 752,268 | 667,378 | Romanians in Spain | |
| 25,247 | 271,239 | 292,641 | 151,258 | 273,050 | Colombians in Spain | |
| 99,017 | 227,187 | 387,677 | 283,243 | 262,885 | British migration to Spain | |
| 27,874 | 95,377 | 184,277 | 179,363 | 252,008 | Italians in Spain | |
| 19,191 | 87,731 | 158,244 | 191,638 | 232,807 | Chinese people in Spain | |
| 12,119 | 49,206 | 60,399 | 48,421 | 189,110 | Venezuelans in Spain | |
| 20,481 | 497,799 | 399,586 | 176,397 | 130,919 | Ecuadorians in Spain | |
| 3,031 | 93,037 | 169,552 | 142,328 | 122,375 | Bulgarians in Spain | |
| 1,293 | 7,017 | 27,363 | 43,283 | 121,963 | - | |
| 1,646 | 65,667 | 83,313 | 91,004 | 115,186 | Ukrainians in Spain | |
| 88,651 | 133,588 | 195,824 | 130,911 | 111,937 | Germans in Spain | |
| 46,375 | 77,791 | 123,870 | 99,598 | 108,275 | French in Spain | |
| 27,422 | 85,029 | 140,182 | 71,112 | 106,712 | Peruvians in Spain | |
| 11,126 | 54,115 | 117,808 | 73,863 | 98,655 | - | |
| 4,195 | 31,913 | 56,877 | 77,695 | 97,705 | Pakistanis in Spain | |
| 43,339 | 66,236 | 142,520 | 98,751 | 97,628 | Portuguese in Spain | |
| 2,117 | 97,947 | 213,169 | 126,375 | 92,630 | Bolivians in Spain | |
| 23,351 | 152,975 | 132,249 | 75,313 | 89,029 | Argentines in Spain | |
| 711 | 16,295 | 85,687 | 69,451 | 87,045 | Paraguayans in Spain | |
| 5,199 | 36,319 | 49,820 | 68,387 | 82,788 | Russians in Spain | |
| 7,526 | 29,608 | 61,970 | 61,798 | 76,973 | - | |
| 24,847 | 57,134 | 91,212 | 75,315 | 75,261 | Dominicans in Spain | |
| 10,759 | 46,278 | 58,743 | 62,398 | 66,893 | - | |
| 17,814 | 45,009 | 54,954 | 46,397 | 64,634 | - | |
| 700 | 1,953 | 12,190 | 20,941 | 57,530 | - | |
| 6,807 | 17,558 | 32,947 | 36,724 | 54,387 | Indians in Spain | |
| 8,164 | 36,477 | 86,324 | 63,324 | 53,418 | Poles in Spain | |
| 21,763 | 33,845 | 53,983 | 45,844 | 46,891 | - | |
| 15,720 | 25,831 | 25,771 | 30,183 | 40,712 | Americans in Spain | |
| TOTAL | 923,879 | 3,730,610 | 5,747,734 | 4,729,644 | 5,036,878 |
Europe
European Union member states are indicated with the EU flag in regional European sub-divisions.
| Origin | 2007 | 2006 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,353 | 1,316 | [31] | |
| 1,022 | 1,075 | ||
| 8,651 | 7,776 | ||
| 3,135 | 3,262 | ||
| 1,659 | 1,827 | ||
| 1,649 | 1,788 | ||
| 146 | 130 | ||
| 6,423 | 5,160 | ||
| 10,906 | 9,977 | ||
| 984 | 784 | ||
| 9,990 | 9,313 | ||
| 7,355 | 6,284 | ||
| 3,567 | 3,027 | ||
| 4,597 | 3,344 | ||
| 1,083 | 920 | ||
| 13,279 | 11,495 | ||
| 2,128 | 1,741 | ||
| 48 | 117 | ||
| 18,528 | 15,200 | ||
| 562 | 1,336 | ||
| 407 | 440 | ||
| 152 | 129 | ||
| 12,801 | 11,330 | ||
| 15,630 | 14,154 | ||
| 3,133 | 3,474 | ||
| 5,999 | 4,515 | ||
| 799 | 619 | ||
| 20,058 | 18,096 | ||
| 16,361 | 15,385 | ||
| Rest of European countries | 66 | 83 | |
| TOTAL EUROPE | 1,895,727 | 1,609,856 |
Africa
| Origin | 2007 | 2006 | Article |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2,114 | 3,698 | ||
| 2,998 | 3,611 | ||
| 4,029 | 3,955 | ||
| 1,801 | 1,888 | ||
| 1,636 | 1,759 | ||
| 2,566 | 3,634 | Egyptians in Spain | |
| 17,393 | 13,627 | ||
| 12,699 | 13,133 | ||
| 9,159 | 9,901 | ||
| 13,129 | 19,456 | Spanish Equatoguineans | |
| 5,229 | 5,274 | ||
| 581 | 1,167 | ||
| 17,094 | 14,497 | ||
| 9,271 | 9,308 | ||
| 1,008 | 1,548 | ||
| 989 | 1,487 | ||
| 704 | 2,086 | ||
| 1,544 | 2,194 | Tunisians in Spain | |
| Rest of African countries | 5,041 | 8,679 | |
| TOTAL | 806.795 |
Central America
| Origin | 2007 | 2006 |
|---|---|---|
| 1,320 | 2,373 | |
| 3,795 | 5,102 | |
| 2,417 | 4,321 | |
| 14,253 | 10,652 | |
| 4,547 | 4,204 | |
| 1,794 | 3,520 | |
| Rest of Central America countries | 1,002 | 2,517 |
| TOTAL | 139.945 |
North America
| Origin | 2007 | 2006 |
|---|---|---|
| 2,419 | 5,420 | |
| 22,082 | 32,626 | |
| 21,107 | 40,574 | |
| TOTAL | 45.608 |
Asia
| Origin | 2007 | 2006 | Article |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9,582 | 9,365 | Armenians in Spain | |
| 54,385 | 51,368 | Filipinos in Spain | |
| 22,465 | 13,144 | Koreans in Spain | |
| 21,296 | 23,296 | Indians in Spain | |
| 6,480 | 6,130 | ||
| 12,334 | 4,568 | Iranians in Spain | |
| 880 | 1,706 | Iraqi people in Spain | |
| 1,713 | 2,427 | ||
| 11,636 | 7,684 | Japanese Spaniards | |
| 1,088 | 2,082 | Jordanian people in Spain | |
| 6,250 | 2,750 | Lebanese people in Spain | |
| 6,129 | 4,575 | Syrian people in Spain | |
| 1,758 | 1,656 | Turks in Spain | |
| Rest of Asian countries | 6,430 | 2,517 | |
| TOTAL | 219.843 |
Oceania
| Origin | 2007 | 2006 |
|---|---|---|
| 1,455 | 5,131 | |
| 301 | 298 | |
| Rest of Oceanian countries | 494 | 1,099 |
| TOTAL | 2.271 |
Comparison with other countries from European Union
According to Eurostat 47.3 million people lived in the European Union in 2010 who were born outside their resident country. This corresponds to 9.4% of the total EU population. Of these, 31.4 million (6.3%) were born outside the EU and 16.0 million (3.2%) were born in another EU member state. The largest absolute numbers of people born outside the EU were in Germany (6.4 million), France (5.1 million), the United Kingdom (4.7 million), Spain (4.1 million), Italy (3.2 million), and the Netherlands (1.4 million).[13]
| Country | Total population (millions) | Total Foreign-born (millions) | % | Born in other EU state (millions) | % | Born in a non EU state (millions) | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | 81.802 | 9.812 | 12.0 | 3.396 | 4.2 | 6.415 | 7.8 |
| France | 64.716 | 7.196 | 11.1 | 2.118 | 3.3 | 5.078 | 7.8 |
| United Kingdom | 62.008 | 7.012 | 11.3 | 2.245 | 3.6 | 4.767 | 7.7 |
| Spain | 45.989 | 6.422 | 14.0 | 2.328 | 5.1 | 4.094 | 8.9 |
| Italy | 60.343 | 4.798 | 8.0 | 1.592 | 2.6 | 3.205 | 5.3 |
| Netherlands | 16.575 | 1.832 | 11.1 | 0.428 | 2.6 | 1.404 | 8.5 |
| Greece | 11.305 | 1.256 | 11.1 | 0.315 | 2.8 | 0.940 | 8.3 |
| Sweden | 9.340 | 1.337 | 14.3 | 0.477 | 5.1 | 0.859 | 9.2 |
| Austria | 8.367 | 1.276 | 15.2 | 0.512 | 6.1 | 0.764 | 9.1 |
| Belgium | 10.666 | 1.380 | 12.9 | 0.695 | 6.5 | 0.685 | 6.4 |
| Portugal | 10.637 | 0.793 | 7.5 | 0.191 | 1.8 | 0.602 | 5.7 |
| Denmark | 5.534 | 0.500 | 9.0 | 0.152 | 2.8 | 0.348 | 6.3 |
| EU 27 | 501.098 | 47.348 | 9.4 | 15.980 | 3.2 | 31.368 | 6.3 |
Irregular migration
The concept of an "irregular", "undocumented", or "illegal" migrant did not become meaningful in Spain's social imaginary until the passing of the Ley de Extranjería in 1985, a year before Spain's entry into the European Communities.[32]
Even though the main paths for the entry of clandestine migration have traditionally been airports and land borders, the sea route has proven to have a "profound impact at the social level" owing to qualitative, rather than quantitative, reasons.[33]
Regarding the governance of the migration of Sub-Saharan people from Morocco (and Western Sahara) into Spain (which include crossings into the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, as well as a sea route to the Canary Islands), the Moroccan and Spanish authorities follow necropolitical forms of border control which are complemented with the favouring of the idea of "advancing borders" by reaching deals with origin or transit countries such as Guinea Conakry, Mali, Ivory Coast, and Gambia.[34]
Naturalizations
From 2005 to 2022 alone, more than 2.2 million foreigners were granted with the Spanish citizenship through naturalization.[35]
Since the end of the 20th century the number of foreigners who have obtained Spanish nationality has grown steadily, as Spain has been the EU country with the biggest number of approved naturalizations since 2010 until 2015. 1 out of 4 naturalizations made in the European Union in 2014 were belonging to Spain. Most of these naturalizations went to citizens coming from Latin America (which explains the massive decrease of these citizens counting as immigrants in Spain) mainly from Colombia, Ecuador and Perú, although Morocco was amongst the top 3 as well.[36] After 4 years being the first, Spain dropped to the 3rd position in 2015 due to the stricter laws to naturalize citizens. Still, 114.351 foreigners became Spanish citizens in 2015, the majority being Latin Americans.[37]
| Year | Naturalizations |
|---|---|
| 2005 | 42,829 |
| 2006 | 62,339 |
| 2007 | 71,810 |
| 2008 | 84,170 |
| 2009 | 79,597 |
| 2010 | 123,721 |
| 2011 | 114,599 |
| 2012 | 115,557 |
| 2013 | 261,295 |
| 2014 | 205,880 |
| 2015 | 114,351 |
| 2016 | 150,944 |
| 2017 | 66,498 |
| 2018 | 90,774 |
| 2019 | 98,954 |
| 2020 | 126,266 |
| 2021 | 202,336 |
| 2022 | 181,581 |
Immigration detention
There are nine detention centers in Spain, known as CIEs (Centro de Internamiento de Extranjeros), run by the Ministry of the Interior, which can be found in the cities of Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, Algeciras, Tarifa, Malaga, and in the islands of Gran Canaria, Fuerteventura, and Tenerife.[41]
Expulsion paperwork can be initiated when a foreign person is in one of the following situations:[42]
- Lacking documentation in Spanish territory.
- Working without a work permit, even if they have a valid resident permit.
- Be involved in activities that violate public order or interior or exterior state security or any activity contrary to Spanish interests or that could put in danger Spain's relations with other countries.
- Be convicted inside or outside of Spain of a crime punishable by incarceration for greater than one year.
- Hiding or falsifying their situation from the Ministry of the Interior.
- Lacking a legal livelihood or taking part in illegal activity.
Crime rates
A 2008 study finds that the rates of crimes committed by immigrants are substantially higher than nationals.[44] The study finds that "the arrival of immigrants has resulted in a lack of progress in the reduction of offences against property and in a minor increase in the number of offences against Collective Security (i.e. drugs and trafficking). In the case of nationals, their contribution to the increase in the crime rate is primarily concentrated in offences against persons."[44] By controlling for socioeconomic and demographic factors, the gap between immigrants and natives is reduced but not fully. The authors also find "that a higher proportions of American, non-UE European, and African immigrants tend to widen the crime differential, the effect being larger for the latter ones".[44] The same paper provides supports for the notion that labour market conditions impact the relationship between crime and immigration. Cultural differences were also statistically detected.[44] This study has been criticized for not using strong instruments for identifying causality: the "instruments (lagged values of the covariates and measures of the service share of GDP in a province) are not convincing in dealing with the endogeneity of migrant location choice."[45]
Spanish National Statistics Institute (INE) published a study that analyzes records in the Register of Convicted in 2008. The data show that immigrants are overrepresented in the crime statistics: 70% of all crimes were committed by Spaniards and 30% by foreigners.[46] Foreigners make up 15% of the population.[46]See also
References
- "Estadística Continua de Población (ECP) a 1 de abril de 2023. Datos provisionales" (PDF). ine.es (in Spanish). Instituto Nacional de Estadística.
- "Sube el número de inmigrantes que viven en España". Datosmacro (in Spanish). 2017. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Estadística del Padrón Continuo". ine.es. Instituto Nacional de Estadística.
- "Estadística Continua de Población (ECP) a 1 de abril de 2023. Datos provisionales" (PDF). ine.es (in Spanish). Instituto Nacional de Estadística.
- R. Sanmartín, Olga (25 June 2018). "La llegada de inmigrantes a España aumenta un 28% y hace crecer la población por segundo año consecutivo". El Mundo (in Spanish). Madrid: Unidad Editorial. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "Official report on Spanish recent Macroeconomics, including data and comments on immigration" (PDF). La Moncloa: 13–43. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 July 2008. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- "Evolution of the foreign population in Spain since 1998". Instituto Nacional de Estadística (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- Betty Henderson (26 January 2023). "Immigration resumes to pre-pandemic levels in Spain with more women immigrants than men". EuroWeekly News.
- Fuente: para los años 1981, 1986 y 1991, los datos se refieren tan sólo a extranjeros con permiso de residencia a 31 de diciembre y proceden del Ministerio de Trabajo y Asuntos Sociales, citado en (tomando, para el porcentaje de 1986, la población española de hecho según la estimación intercensal del INE para el 1 de julio ). Para los datos de 1996 y posteriores, todos los datos proceden del INE
- "For 2013 and 2014" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 December 2018. Retrieved 30 October 2014.
- "Población por comunidades, edad (grupos quinquenales), Españoles/Extranjeros, Sexo y Año". INE.
- "España - Inmigración 2019". Datosmacro.com.
- 6.5% of the EU population are foreigners and 9.4% are born abroad Archived August 12, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Eurostat, Katya VASILEVA, 34/2011.
- Eurostat – Population in Europe in 2005 Archived August 19, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. (PDF) . Retrieved on 2011-11-14.
- Kern, Soeren (13 May 2009), "Immigration Policy a Casualty of Unemployment in Spain", World Politics Review, archived from the original on 1 June 2020, retrieved 29 June 2009
- Zelmenis, Artis (11 September 2013), "Spanish Immigration Policy", Baltic Legal
- Membrado, Joan Carles (21 May 2014). "Pensioners' Coast. Migration of Elderly North Europeans to the Costa Blanca". Mètode (in Catalan). University of Valencia (81). doi:10.7203/metode.81.3111. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- Archived 15 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine Archived 8 April 2013 at the Wayback Machine Archived 4 April 2020 at the Wayback Machine Archived 20 January 2020 at the Wayback Machine "British Immigrants Swamping Spanish Villages?". Archived from the original on 23 December 2010. Retrieved 25 January 2011. Archived 4 April 2020 at the Wayback Machine Archived 4 April 2020 at the Wayback Machine Archived 4 April 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- Special Reports | Brits Abroad Archived 15 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine. BBC News. Retrieved on 2011-11-14.
- News.bg – Europeans Favour Spain for Expat Jobs Archived 10 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine. International.ibox.bg. Retrieved on 2011-11-14.
- Buck, Tobias (17 January 2017). "No right turn for Spanish politics". Financial Times. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
- Staff writer (23 June 2004). "Immigration time-bomb". Expatica. Archived from the original on 28 May 2006. Retrieved 11 August 2010.
- "Vox party puts 'menace' of migrant children at centre of election drive". The Guardian. 10 November 2019. Retrieved 28 September 2022.
- "Población (españoles/extranjeros) por País de Nacimiento, sexo y año". Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Retrieved 28 April 2021.
- Immigration flow from abroad by year, sex and age Archived 28 November 2020 at the Wayback Machine at INE (Spanish Bureau Office).
- "CensusHub2". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 12 July 2023.
- "CensusHub2". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 13 July 2023.
- "Población extranjera por Nacionalidad, comunidades, Sexo y Año". INE (in European Spanish). Retrieved 13 July 2023.
- "Uno de cada cuatro extranjeros que obtuvieron la nacionalidad en la UE en 2014 la lograron en España". 13 June 2016.
- "Población extranjera por Nacionalidad, comunidades, Sexo y Año".
- "Población extranjera por Nacionalidad, Sexo y Año". Instituto Nacional de Estadística (in Spanish). Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- Inglada Galiana, Elena; Sastre Centeno, José Manuel; Miguel Bilbao, Maria Cristina de (2019). "La inmigración irregular en España y Europa: situación y perspectiva" [Illegal immigration in Spain and Europe: Situation and outlook]. Revista Galega de Economia. 28 (1): 121–122. doi:10.15304/rge.28.1.6143. ISSN 2255-5951.
- Inglada Galiana, Sastre Centeno & Miguel Bilbao 2019, p. 125.
- Fernández Labayen, Miguel; Gutiérrez, Irene (2022). "Physical, affective and symbolic immobility in the videos made by Sub-Saharan migrants at the EU external borders in Northern Africa". In Trandafoiu, Ruxandra (ed.). Border Crossings and Mobilities on Screen. Routledge. p. 28–29; 34. doi:10.4324/9781003127703.
- "Estadística de adquisiciones de nacionalidad española de residentes. Año 2022". INE. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- Martínez, Silvia (13 June 2016). "Uno de cada cuatro extranjeros que obtuvieron la nacionalidad en la UE en 2014 la lograron en España". El Periódico (in Spanish). Grupo Zeta. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "España fue el tercer país de la UE que más extranjeros nacionalizó en 2015, según Eurostat". Europa Press (in Spanish). 23 April 2017. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "Población (españoles/extranjeros) por País de Nacimiento, sexo y año". Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "Adquisiciones de nacionalidad por sexo y nacionalidad previa(15071)". INE.
- "Estadística de adquisiciones de nacionalidad española de residentes". INE. Retrieved 19 November 2022.
- Devlin, Cloe, translator. 2011. "Report on immigration detention centers in Spain for Migreurop" [Executive summary]. Asociación Pro Derechos Humanos de Andalucía.
- Gobierno, de España (1985). Boletín Oficial del Estado número 158 (ed.). "Ley Orgánica 7/1985, de 1 de julio, sobre derechos y libertades de los extranjeros en España" [Organic Law 7/1985, of July 1, on the rights and freedoms of foreigners in Spain] (PDF). Boletín Oficial del Estado (in Spanish). Kingdom of Spain. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 April 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2011.
- APDHA (2014). "Andalucía Acoge junto a SOS Racismo y APDHA recurren ante el Tribunal Supremo el Reglamento de los Centro de Internamiento de Extranjeros" [Andalucía Acoge, SOS Racismo and APDHA appeal CIE regulations to the Supreme Court] (Press release). Asociación Pro Derechos Humanos de Andalucía. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017.
- Alonso, Cesar; Garoupa, Nuno; Perera, Marcelo; Vazquez, Pablo (1 January 2008). "Immigration and Crime in Spain, 1999–2006". Working Papers. FEDEA.
- Bell, Brian; Machin, Stephen (2013). Immigration and crime. pp. 353–372. doi:10.4337/9781782546078.00028. ISBN 9781782546078.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - "El 70% de la delincuencia es perpetrada por españoles según el INE". tercerainformacion.es.
External links
- ASESER Teranga: Asociación de Inmigrantes Senegaleses Residentes en A Coruña Archived 19 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine