Kerala Police
The Kerala Police[3][4] is the law enforcement agency for the Indian state of Kerala.[5] Kerala Police has its headquarters in Thiruvananthapuram, the state capital. The motto of the force is "Mridhu Bhave Dhrida Kruthye" which means "Soft in Temperament, Firm in Action" in Sanskrit.[6]
| Kerala State Police കേരള പോലീസ് | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | KP |
| Motto | മൃദു ഭാവെ ദൃഢ കൃത്യേ
"Mridhu Bhave Dhrida Kruthye" |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | November 1, 1956 |
| Annual budget | ₹4,406 crore (US$550 million) (2021–22 est.)[1] |
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| Operations jurisdiction | Kerala, IN |
 | |
| Jurisdiction of Kerala Police | |
| Size | 15,008.13 sq mi (38,870.88 km2) |
| Population | 34,630,192 |
| Legal jurisdiction | As per operations jurisdiction |
| Governing body | Government of Kerala |
| Constituting instrument | |
| General nature | |
| Operational structure | |
| Overviewed by | Department of Home, Government of Kerala |
| Headquarters | Vazhuthacaud, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala – 695010 |
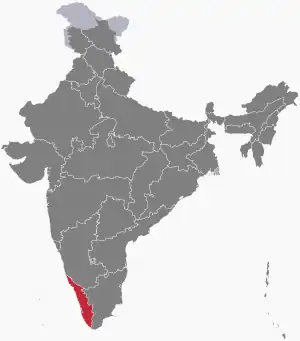
 Map of Kerala Police Department's jurisdiction. The map on left shows Kerala in India and on right shows the State with Thiruvananthapuram district in red. | |
| Sworn members | 62,618 (Sanctioned) [2]
57,819 (Actual) |
| Minister responsible | |
| Agency executive |
|
| Units | List of units
|
| Specialized Units | List of units
|
| Facilities | |
| Police Stations | 564 (as of 2021)[2] |
| Police vehicles | Force Gurkha Mahindra Bolero Tata Sumo Mahindra TUV300 Toyota Innova Chevrolet Tavera Mahindra Thar Swift Dzire |
| Boats | Speed boats |
| Dogs | 82 (41 Sniffer Dogs) |
| Horses | 25 |
| Notables | |
| Programme |
|
| Significant Operation |
|
| Website | |
| keralapolice | |
Kerala Police has a reputation for being one of the best-managed state police forces in the nation, and the state ranks among the top states for maintaining law and order. One of the first police forces in South Asia to put community policing into practise is Kerala Police, which was one of the first to do so through legislation. The term "Janamaithri" Policing, which means "people-friendly Policing," is used to refer to it.
According to the data from Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD), there are a total of 564 police stations in Kerala.[7] Out of these, 382 police stations are located in rural areas, while 102 police stations are located in urban areas. Additionally, there are 80 special purpose police stations in Kerala.[8]
The rural police stations account for the majority of police stations in Kerala, comprising approximately 68% of the total. The urban police stations account for about 18% of the total, while the special purpose police stations account for about 14% of the total.
History
Prior to independence, the Kerala Police was governed by different administrations.[9]
Kerala Police traces its roots to the erstwhile Travancore State Police, which was established in 1936. After the integration of the princely states of Travancore and Cochin, the present-day Kerala Police was formed in 1956. The first Director General of Police of Kerala Police was Shri. T. K. Joseph IPS.
Current office holders
| Name | Status | Rank |
|---|---|---|
Shaik Darvesh Saheb IPS | State Police Chief |  |
Manoj Kumar IPS | Intelligence |  |
M.R Ajithkumar IPS | Law and Order |  |
H Venkatesh IPS | ADGP, Armed Police Battalion & Crime Branch EOW |  |
Gopesh Agrawal IPS | Director, Kerala Police Academy |  |
Neeraj Kumar Gupta IPS | IGP, Head Quarters |  |
Gugulloth Lakshman IPS |
IGP, Training KEPA |
 |
S Syamsundar IPS |
Internal Security,
Security (Addl.Charge) |
 |
K. Sethu Raman IPS |
IGP, North Zone |
 |
G. Sparjan Kumar IPS |
IGP, South Zone |
 |
Nagaraju Chakilam IPS |
Commissioner of Police,
Thiruvananthapuram City |
 |
A Akbar IPS |
Commissioner of Police,
Kochi City, Coastal police(Full Addl.Charge) |
 |
Organization

Kerala Police is headed by the State Police Chief. He is the senior most Indian Police Service officer in the State and is of the rank of Director General of Police. State Police Chief is designated as the Head of the department for all administrative and operational purposes. State Police Chief is assisted by officers in the rank of Additional Director General of Police.
Law and Order
Additional DGP (ADGP, L&O) heads this wing. The state of Kerala is divided into two police zones, North Zone and South Zone. each zone is headed by The Inspector Generals of Police (IGP). There are 20 police districts in Kerala in total.
Each Police district is divided into some subdivisions to supervise activities of several police stations under its jurisdiction. There are 91 police sub-divisions in Kerala. Each sub-division is headed by a Deputy Superintendent of Police (DySP) or an Assistant Commissioner of Police (ACP) in the case of city police sub-divisions.
The police officer in charge of a sub division is called Sub Divisional Police Officer (SDPO). DySPs or ASPs are posted as SDPOs. The Sub Divisional Offices are headed by Sub Divisional Police Officers in the rank of Deputy superintendent of police or Assistant superintendent of police. A Sub Division is further divided into Police Station areas, each of which is under an Inspector of Police designated as Station House Officer (SHO). Inspectors in charge of police stations are known as Inspector SHOs (ISHO). In small police stations sub-inspectors are appointed as SHOs. The SHO is assisted by Sub Inspectors of Police, Assistant Sub Inspectors of Police, Senior Civil Police Officers and Civil Police Officers. The section known as General Executive is working in the police stations of Kerala.[10]

- Police Zones are headed by an Inspector General of Police (IGPs)
- Police Ranges are headed by a Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIGs)
- Police Districts are headed by a District Police Chief of the rank of Superintendent of Police (SPs)
- Thiruvananthapuram City and Ernakulam City Police districts are headed by a District Police Chief of the rank of Inspector General of Police (IG). Kozhikode City Police district is headed by a District Police Chief of the rank of Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG).
- The IGs of cities reports directly to Additional Director General of Police, L&O
Zones, ranges and districts
| Zone | Range | Police Districts |
|---|---|---|
| South Zone. | Thiruvananthapuram Range | Thiruvananthapuram Rural,[11] Kollam City, Kollam Rural (HQ: Kottarakkara),[12] Pathanamthitta |
| Ernakulam Range | Alappuzha, Kottayam, Idukki, Ernakulam Rural (HQ: Aluva),[13] | |
| North Zone. | Thrissur Range | Thrissur City, Thrissur Rural (HQ: Irinjalakuda), Palakkad, Malappuram[14] |
| Kannur Range | Kozhikode City, Kozhikode Rural (HQ: Vadakara), Wayanad, Kannur City, Kannur Rural, Kasargod |
Rural Police Districts
| Sl.No | Rural Police District | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Thiruvananthapuram Rural | Thiruvananthapuram |
| 2 | Kollam Rural | Kottarakkara |
| 3 | Pathanamthitta | Pathanamthitta |
| 4 | Alappuzha | Alappuzha |
| 5 | Kottayam | Kottayam |
| 6 | Idukki | Painavu |
| 7 | Ernakulam Rural | Aluva |
| 8 | Thrissur Rural | Irinjalakuda |
| 9 | Palakkad | Palakkad |
| 10 | Malappuram | Malappuram |
| 11 | Kozhikode Rural | Vadakara |
| 12 | Kannur Rural | Mangattuparamba / Thaliparamba |
| 13 | Wayanad | Kalpetta |
| 14 | Kasaragod | Kasaragod |
Hierarchy
Officers
- Director General of Police & State Police Chief (DGP & SPC)
- Additional Director General of Police (ADGP)
- Inspector General of Police (IG)
- Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG)
- Superintendent of Police (SP)
- Additional Superintendent of Police (Addl.SP)
- Assistant Superintendent of Police (ASP) [IPS]
- Deputy Superintendent of Police (DySP) KPS
Sub-ordinates
- Inspector of Police (IP)
- Sub-Inspector of Police (SI)
- Assistant Sub-Inspector of Police (ASI)
- Senior Civil Police Officer (SCPO)
- Civil Police Officer (CPO)
Insignia of Kerala Police (State Police)
| Insignia |  |
 |
 |
No insignia | |||||||||||||||||
| Rank | Inspector of Police[note 3] | Sub Inspector of Police | Assistant Sub Inspector | Senior Civil Police Officer[note 4] | Civil Police Officer | ||||||||||||||||
| Abbreviation | IP | SI | ASI | SCPO | CPO | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||


Police Commissionerates
Thiruvananthapuram City Police and Kochi City Police[20] are headed by Commissioner of Police of the rank of Inspector General of Police. Kozhikode City Police is headed by the Commissioner of Police of the rank of Deputy Inspector General of Police. Thrissur City Police, Kannur City Police[21] and Kollam City Police are headed by Commissioner of Police of the rank of Superintendent of Police. The Commissioner of Police is assisted by Deputy Commissioners of Police (DCPs) of the rank of Deputy Inspector General of Police or Superintendent of Police and Assistant Commissioners of Police (ACPs) of the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police.[4]
| Post/Designation | Abrv. | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Commissioner of Police, Thiruvananthapuram City | CP | IG |
| Commissioner of Police, Kochi City | CP | IG |
| Commissioner of Police, Kozhikode City | CP | DIG |
| Commissioner of Police, Kollam City, Thrissur City, Kannur City | CP | SP |
| Deputy Commissioner of Police, TVM City, Kochi City, Kozhikode City. | DCP | SP |
| Additional Deputy Commissioner of Police | ADCP | Addl.SP |
| Assistant Commissioner of Police | ACP | DySP |
| Station House Officer | SHO | IP |
Crime Branch
| Crime Branch | |
|---|---|
| ക്രൈം ബ്രാഞ്ച് | |
| Agency | Kerala Police |
| Type | Criminal Investigation Department |
| Role | Investigation of:
|
| Headquarters | Thiruvananthapuram |
| Common name | CB-CID, CBCID |
| Abbreviation | CB |
| Structure | |
| Ranges | |
| Districts | 14 |
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | Additional Director General of Police (Crimes) |
The Crime Branch is the specialized investigation wing of the Kerala police. It is headed by an officer of the rank of Additional Director General of Police.
Crime Branch investigates cases that are entrusted to it by the State Police Chief or the Government or the High Court of Kerala. The Cyber Crime Police Stations and Hi-Tech Crime Enquiry Cell of the Kerala Police are functioning under the Crime Branch. This department was earlier known as Crime Branch-Criminal Investigation Department (CBCID).
Crime Branch is the Nodal agency for Interpol related matters in the State and conducts verifications or enquiries on behalf of Interpol.
Crime Branch is specialized in investigation of complex organized crimes, financial frauds, economic offences with huge ramifications, undetected or sensitive crime cases, cases with inter-state ramifications, etc.
Apart from this, the District Crime Branch (C-Branch) functions under the respective District Police Chiefs. District C-Branch is headed by a Deputy Superintendent of Police. District C Branch acts as specialized investigating wing of the District Police Chief which is mandated to help in investigating sensational cases at the district level.
Hierarchy of Crime Branch
- Addl. Director General of Police, Crimes
- Inspector General of Police, Crime Branch
- Superintendent of Police, Crime Branch
- Deputy Superintendent of Police, Crime Branch
- Detective Inspector
- Detective Sub Inspector
- Detective Assistant Sub Inspector
- Detective Sr. Police Officer
- Detective Police Officer
State Special Branch
| State Special Branch | |
|---|---|
| സംസ്ഥാന സ്പെഷ്യൽ ബ്രാഞ്ച് | |
| Agency | Kerala |
| Type | state intelligence agency |
| Role | intelligence gathering on:
|
| Common name | SBCID, SB-CID |
| Abbreviation | SSB |
| Structure | |
| Ranges | 4 |
| Detachments | 17 |
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | Additional Director General of Police (Intelligence) |
The State Special Branch is the intelligence wing of the Kerala police. This wing is headed by an officer of the rank of Additional Director General of Police. The ADGP (intelligence) is assisted by Inspectors General of Police, Deputy Inspectors General of Police, Superintendents of Police and subordinate officers. The State Special Branch (SSB) is primarily concerned with the collection, collation and dissemination of intelligence on and about various political, communal, terrorist, national security, and labour activities and with relation to various law and order issues like agitations, strikes, demonstrations, protests, etc. The SSB functions as the eyes and ears of the government.
Armed police battalions

This wing is headed by an officer of the rank of Additional Director General of Police (ADGP APBn). There are eleven armed police battalions in the state, which serve as reserve forces to be deployed whenever and wherever district police fall short of manpower in the maintenance of law and order. Each battalion is headed by a Commandant of the rank of Superintendent of Police.[22] Malabar Special Police is the oldest paramilitary force of India after Assam Rifles.
Battalions
- Kerala Armed Police KAP-I (Thrissur)
- Kerala Armed Police KAP-II (Palakkad)
- Kerala Armed Police-III (Adoor)
- Kerala Armed Police-IV (Kannur)
- Kerala Armed Police-V (Kuttikanam)
- Malabar Special Police- MSP (Malappuram)
- Special Armed Police - SAP (Thiruvananthapuram)
- Rapid Response and Rescue Force - RRRF (Pandikkad)
- India Reserve Battalion (IRBn) (Thrissur)
- State Industrial Security Force (SISF)
- Armed Women Police Battalion (AWPBn)
Hierarchy of Armed Police
- Additional Director General of Police (APBn)
- Deputy Inspector General of Police (APBn)
- Commandant (equivalent to SP)
- Deputy Commandant (equivalent to rank of Addl.SP)
- Assistant Commandant (equivalent to rank of DySP)
- Armed Police Inspector
- Armed Police Sub Inspector
- Armed Police Asst. Sub Inspector
- Havildar
- Armed Police Head Constable
- Armed Police Constable
Specialised units
Tourism Police
Tourism Police wing has been functioning in the state for maintaining law and order, preventing attack and harassment on tourists. They also assist the tourists for getting tourist related information, guidance, etc.[23] The uniform of Tourism Police Officers is sky blue shirt and khakee pants. International Tourism Police Station and Police Museum at Mattancherry in Ernakulam district is the first of its kind in the country which not only addresses grievances of tourists but also showcases the history of the Kerala Police. The primary aim of the station is to make the state of Kerala more tourist-friendly.[24]
Coastal Police
Coastal Police Stations handle the security of the coasts and carry out the patrolling in the sea up to 12 nautical miles. The cases reported on the sea (in the Territorial Waters) will be investigated by the Coastal Police. The headquarters of Kerala Coastal Police is situated at Kochi.
Railway Police
The responsibility of the Kerala Railway Police is to maintain law and order, prevent and detect crime on the railways and railway stations in Kerala.[25]
The Superintendent of Police (Railways) is under supervision of A.D.G.P (Intelligence & Railways). There are 13 Railway Police Stations in Kerala. They are located in the main Railway station premises at Trivandrum Central, Parassala, Kollam, Punalur, Alappuzha, Kottayam, Ernakulam Junction, Thrissur, Shornur, Palakkad, Kozhikode, Kannur and Kasargod.[26]
Pink Police Patrol
The main objectives of Pink Patrol are to prevent violence and crimes against women and children.[27] As part of improving women safety in public places, Kerala Police has rolled out a special patrol team called pink patrol with all women police officers, patrolling across all the busy areas of the various cities of Kerala. The team has been allotted pink Maruti Suzuki sedan cars. The Pink patrol vehicles are fitted with GPS and other smart equipments for faster response and assistance as well as has on-board cameras and scanning systems to identify potential offenders.
Narcotic Cell
Narcotic Cell collects intelligence on Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) and pass it on to concerned police stations according to the gravity of cases. Monitoring and Supervising cases registered under NDPS Act is also done by this wing. Abkari raids are being conducted by Narcotic Cell on information. District Narcotic Cell is functioning in all police districts, headed by an officer of the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police, and under supervision of District Police Chiefs.
Women Cell
State Women Cell is headed by a Superintendent of Police. In addition, One District Women Cell is also functioning in all Police Districts, each headed by a Woman Inspector. The State Women Cell is functioning at the Police Headquarters in Thiruvananthapuram. The first Woman Police Station started at Kozhikode in 1973.[28]
Thunderbolts
Thunderbolts is the elite commando unit of Kerala Police. It performs perilous counter-terrorism, jungle-warfare, and hostage-rescue operations. Thunderbolts are a form of SPG and NSG, which are trained to take on air, water and land attacks.
Recruitment
IPS officers are recruited through the Civil Service Examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). They are also promoted from the State Police Service. The first posting of a direct recruit IPS officer is to the post of Assistant Superintendent of Police.
According to the Indian Police Service (Appointment by Promotion) Regulations, 1955, Kerala Police Service officers are eligible for promotion to the IPS after completing eight years of service. But in reality, officers are generally promoted to the IPS after two and a half decades of service. KPS or State Police Service officers are inducted into the IPS by promotion from the rank of Superintendent of Police (non-IPS). After completing two decades of service, KPS officers get promoted to the Indian Police Service, after confirmation by the Ministry of Home Affairs of the Government of India and the Union Public Service Commission. One-third of the total IPS strength in Kerala is reserved for KPS officers (SPS quota).
Unlike other state police forces, there is no direct recruitment for the Group A (gazetted) post of Deputy Superintendent of Police in the Kerala Police. Recruitment to the Kerala Police Service (Group-A) is by promotion from the rank of Inspector of Police.
Recruitment to the post of Sub Inspector of Police (Trainee) to the Kerala Civil Police Cadre is done through the competitive exam and departmental promotion tests conducted by the Kerala Public Service Commission. Recruitment to the post of Sub Inspector (General Executive) is done through direct and indirect means in the ratio of 1:1.
Recruitment to the post of Civil Police Officer in the Kerala civil police cadre is done through a competitive exam conducted by the Kerala Public Service Commission. Apart from this, the Kerala PSC conducts direct recruitment for various technical and special category posts like police constable (driver), armed police constable, police constable (commando wing), police constable (telecom), fingerprint expert, forensic expert, etc.[29]
Training
The training wing of state police is headed by an officer of the rank of Additional Director General of Police (Training).

Kerala Police Academy
The Kerala Police Academy is headed by the Director of the rank of Additional Director General of Police. The Director is assisted by Joint Directors, assistant directors, HODs,etc. The academy is situated at Thrissur. The academy will cater to the training needs of all officers of police department including IPS officers.
Police Training College
The head of Police Training College is Principal in the rank of Superintendent of Police. It is situated in Thiruvananthapuram. The Basic Training and In-service courses are key Training programmes carried out in PTC. Apart from giving Basic Training, many In-Service Courses such as Refresher courses, Re-orientation courses, Familiarization courses, Cader courses are also being undertaken at PTC. Basic training for Excise Inspectors, Forest Officers are also now being conducted. Training of Probationary Officers is carried out in PTC.
Positions (Ranks)
The ranks in the Kerala Police range from Civil Police Officer (CPO) to DGP.
Promotion
The Government of Kerala has decided to give the rank of Senior Civil Police Officer (Grade) to Civil Police Officers (CPOs) who have completed 12 years of service in the civil police unit (local police). Senior Civil Police Officers who have completed 20 years of service will be given the rank of Assistant Sub Inspector (Grade), and Assistant Sub Inspectors who have completed 25 years of service will be given the rank of Sub Inspector of Police (Grade) or Grade SI. They will continue to carry the duties and responsibilities of the rank when they receive the honorary grade.
- Senior Civil Police Officer Grade - 12yrs of service as Civil Police Officer (CPO).
- Assistant Sub Inspector (Grade)- 20yrs of service as SCPO.
- Sub Inspector (Grade) - 25yrs of service as ASI.
Designations
| Designation/Post | Abrv. | Rank | note; |
|---|---|---|---|
| State Police Chief | SPC | DGP | Head of the police department. |
| Additional Director General of Police | ADGP | ADGP | Head of a particular function/wing. e.g.:- Training, Intelligence, Law and Order, Crimes, SCRB, Armed Police Battalion, Headquarters etc. |
| Inspector General of Police | IGP | IG | Head of a police zone, head of a division or unit within the department, Police Commissioners of Thiruvananthapuram and Kochi. Zones: South Zone, North Zone |
| Deputy Inspector General of Police, Range | Range DIG | DIG | Head of a police range, head of a unit within the branch or wing. Ranges: Thiruvananthapuramam Range, Ernakulam Range, Thrissur Range, Kannur Range. |
| Assistant Inspector General of Police | AIG | SP | It is an administrative position. Incharge of administrative functions in police headquarters. |
| District Police Chief | DPC | SP | Head of a police district. This post is held by IPS officers. |
| Additional Superintendent Of Police, Administration | (Addl.SP, Admin) | Addl.SP | Officials in Additional SP Post were assigned to assist district police chief. This post is held by State Police Service (KPS) officers.[31] |
| Sub Divisional Police Officer | SDPO | DySP/ASP | Officer in charge of a Police Subdivision. The Sub Division is headed by SDPO in the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police [KPS] or Assistant Superintendent Of Police [IPS]. |
| Inspector Station House Officer | ISHO / IP SHO | Inspector of police | Officer incharge of a Police Station.
Prior to 2017, the station house officer was an officer of the rank of sub inspector (SI).[32] Since 2017 Circle Inspectors (CIs) take charge as station house officer.[33] the nomenclature of Circle Inspector has been changed to Inspector/SHO or simply IP (Inspector of Police). |
List of former chiefs
| S.No | Name | Date of Assumption of Charge |
|---|---|---|
Inspector General of Police | ||
| 1 | Chandrasekaran Nair IPS | 1956 – 1957 |
| 2 | M. Krishna Menon IPS | 1957 – 1961 |
| 3 | K.N.R Sreenivasan Iyer IPS | 1959 |
| 4 | V.P Nair IPS | 1961 – 1964 |
| 5 | N. Rama Iyer IPS | 1964 – 1967 |
| 6 | M.Gopalan IPS | 1967 – 1972 |
| 7 | M. Singaravelu IPS | 1972 – 1974 |
| 8 | V.N Rajan IPS | 1974 – 1978 |
| 9 | V. Subramanian IPS | 1980 |
Director General of Police | ||
| 10 | T. Anantha Sankara Iyer IPS | 1978 — 1982 |
| 11 | P. Vijayan IPS | 1982 – 1983 |
| 12 | M.K. Joseph IPS | 1983 – 1988 |
| 13 | K. John Mathai IPS | 1989 |
| 14 | Raj Gopal Narayan IPS | 1988 – 1991 |
| 15 | A.V Venkatachalam IPS | 1991 |
| 16 | C. Subramaniam IPS | 1991 – 1993 |
| 17 | R.Jayaram Padikkal IPS | 1993 – 1994 |
| 18 | T.V Madhusudanan IPS | 1994 – 1995 |
| 19 | K.V Rajagopalan Nair IPS | 1995 – 1996 |
| 20 | R. Radhakrishanan IPS | 1996 – 1997 |
| 21 | M. Adbul Sathar Kunju IPS | 05-06-1997 to 30-06-1997 |
| 22 | C.A Chaly IPS | 30-06-1997 to 31-03-1998 |
| 23 | B.S Sasthri IPS | 31-03-1998 to 25-07-2000 |
| 24 | P.R Chandran IPS | 26-07-2000 to 31-05-2001 |
| 25 | R. Padmanabhan IPS | 31-05-2001 to 31-10-2001 |
| 26 | W. Joseph Dawson IPS | 31-10-2001 to 31-01-2002 |
| 27 | K.J Joseph I.P.S | 2000 to 2003 |
| 28 | P.K Hormese Tharakan I.P.S | 2003 to 2005 |
| 29 | Raman Srivastava I.P.S | 2005 to 2008 |
State Police Chief | ||
| 30 | Jacob Punnoose I.P.S | 2008 to 2012 |
| 31 | K.S Balasubramanian I.P.S | 2012 to 2015 |
| 32 | T.P Senkumar I.P.S | 01-06-2015 to 31-05-2016 |
| 33 | Lokanath Behera I.P.S | 01-06-2016 to 06-05-2017 |
| 34 | T. P. Senkumar I.P.S | 06-05-2017 to 30-06-2017 |
| 35 | Lokanath Behera I.P.S | 01-07-2017 to 30-06-2021 |
| 36 | Anil Kant I.P.S | 01-07-2021 to 30-06-2023 |
| 37 | Sheikh Darvesh Saheb I.P.S | incumbent |
Achievements
Kerala Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan has termed Kerala Police as best in the country.[34] In 2021 Kerala Police bagged the National e-Governance Award.[35] Kerala Police has achieved several significant milestones over the years. Some of the notable achievements include:
- Women Police Stations: Kerala Police was the first in the country to establish women police stations, which exclusively deal with crimes against women.
- Cyberdome: Kerala Police established Cyberdome, a state-of-the-art facility for cyber security and cybercrime investigation.
- Janamaithri Suraksha: Kerala Police launched the Janamaithri Suraksha Project, a community policing initiative aimed at building a relationship of trust between the police and the public.
- Pink Patrol: Kerala Police launched Pink Patrol, a patrol team consisting of women police officers, to ensure the safety and security of women in public places.
- The Public Affairs Index selected Kerala as the best state in 2016 and 2017 considering its excellence in law and order.[36]
- According to the grading conducted by Plan India for Women's Safety, Kerala ranks second in the country in terms of ensuring women's safety (Gender Vulnerability Index).[37]
- Kollam City Police achieved ISO 9001 certification for excellence in office functioning and maintaining high levels of quality control in day-to-day activities in January 2018.[38]
- Valapatnam Police Station has been selected as one of the top ten police stations in the country based on the inspection and study of the Union Ministry of Home Affairs. The handling of criminal cases, effective implementation of anti-drug activities and public involvement of the police helped the Valapatanam police station to achieve this achievement.
- COPS Today International, a journal published by the Foundation for Research, recently honored Kerala Police's Community Policing Program Janmaitri Police Project with the Police Excellence Award.
Controversies
Kerala Police has also faced several controversies over the years. Some of the notable controversies include:
- Custodial Deaths: Kerala Police has faced allegations of custodial deaths, where suspects died in police custody.[39]
- Encounter Killings: Kerala Police has faced allegations of fake encounter killings, where suspects were killed in fake encounters.[40]
- Police Brutality: Kerala Police has faced allegations of police brutality, where suspects were subjected to excessive force during arrest or interrogation.[41]
There have been several allegations of irregularities and brutalities by Kerala Police officials.[42] Kerala Police has been accused of failure in curbing violence[43] and failure to act on intelligence reports.[44] Indian poet Tapan Kumar Pradhan in his books and social media posts has exposed several irregularities in criminal investigation by Kerala Police,[45] especially in Hemangi Sharma Fraud Case.[46]
See also
Notes
- Rank insignia of DGP is similar to additional DGP.
- The newly created Additional SP post is held by state police service [KPS] officers.
- Police Circles have been abolished and Circle Inspectors have been appointed as Inspector / Station House Officer. Nomenclature of CI is changed to IP/SHO.
- The Senior Civil Police Officer rank is informally known as Head Constable and Civil Police Officer rank is informally known as Constable.
References
- "Kerala Budget Analysis 2021-2022" (PDF). prsindia.org. 2021. Retrieved 15 January 2021.
- https://bprd.nic.in/WriteReadData/News/DoPO-21f%20%20.pdf Archived 2023-03-05 at the Wayback Machine
- "Kerala police see a top deck shuffle". The New Indian Express. Archived from the original on 4 April 2023. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- "Police roll out 'e-challan'". The Hindu. 22 September 2020. Archived from the original on 23 September 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- "Spl squad to tackle goonda menace". The New Indian Express. 28 October 2016. Archived from the original on 1 February 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- "Soft skills training to make police 'polite and firm'". The New Indian Express. 22 August 2016. Archived from the original on 25 June 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2016.
- "Data on Police Organizations:Bureau Of Police Research And Development, Government of India". bprd.nic.in. Archived from the original on 2021-01-26. Retrieved 2023-03-05.
- "Data on Police Organisations 2021, BPRD" (PDF). Bureau of Police Research and Development. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-03-05. Retrieved 2023-03-05.
- Institutional History of Kerala Police (PDF). Kerala Police. 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-06-28. Retrieved 2023-05-28.
- Staff Reporter (8 September 2020). "Key postings made in Kerala Police". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 20 September 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- "Thiruvananthapuram Rural Police".
- "Kollam Rural Police". Kollam Rural Police. Archived from the original on 2022-06-29. Retrieved 2022-06-28.
- "Ernakulam Rural Police". ernakulamrural.keralapolice.gov.in. Archived from the original on 15 June 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
- Saikiran, KP (September 10, 2020). "Kerala police history will soon be on record". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 10 April 2023. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- "Police Ranks" (PDF). Maharashtra Police. Retrieved August 14, 2017.
- "Governance of Kerala Police". Kerala Police. Retrieved August 14, 2017.
- "Police Ranks and Badges". Odisha Police. Retrieved August 15, 2017.
- "Police Ranks" (PDF). Maharashtra Police. Retrieved August 14, 2017.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-06-02. Retrieved 2023-05-01.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "IG Vijay Sakhare takes charge as Kochi commissioner". 14 June 2019. Archived from the original on 4 April 2023. Retrieved 28 June 2022.
- "Kanpur police completes one year of the Commissionerate system, organises walkathon". Archived from the original on 2022-06-28. Retrieved 2022-06-28.
- "Kerala Armed Police Battalions". Archived from the original on 2021-10-20. Retrieved 2022-06-28.
- "Facts about Kerala Police Department". www.swapdial.com. Archived from the original on 2022-09-07. Retrieved 2022-09-07.
- "India's first tourist police station opens in Kochi". www.oneindia.com. 2010-03-01. Archived from the original on 2022-09-07. Retrieved 2022-09-07.
- "Ministry of Railways (Railway Board)". indianrailways.gov.in. Archived from the original on 2022-09-07. Retrieved 2022-09-07.
- "Official Website of Kerala Police - Railway Police". keralapolice.gov.in. Archived from the original on 2022-09-07. Retrieved 2022-09-07.
- "Iraq: The UN must take immediate action to prevent further mass atrocities against minorities". Human Rights Documents online. doi:10.1163/2210-7975_hrd-0035-2014222. Archived from the original on 2022-09-07. Retrieved 2022-09-07.
- "Official Website of Kerala Police - Women Cell". keralapolice.gov.in. Archived from the original on 2022-09-07. Retrieved 2022-09-07.
- "Kerala Public Service Commission". Kerala Public Service Commission. Archived from the original on 2022-10-05. Retrieved 2022-09-06.
- "Kerala: Government relaxes grade norms for police officers | Thiruvananthapuram News - Times of India". The Times of India. TNN. Oct 28, 2019. Archived from the original on 2022-06-28. Retrieved 2022-06-28.
- "Home dept creates Additional SP post in Kerala police". English Archives. 19 December 2018. Archived from the original on 2022-07-02. Retrieved 2022-07-02.
- "Circle Inspectors to be Station House Officers". The New Indian Express. Archived from the original on 2022-07-02. Retrieved 2022-07-02.
- "CIs take charge as station house officers". The Times of India. January 1, 2018. Archived from the original on 2022-07-02. Retrieved 2022-07-02.
- "Kerala Police best in the country". Malayala Manorama. 2022-10-23. Archived from the original on 2022-10-23. Retrieved 2022-10-30.
- "Kerala Police gets national e-governance award". English Deepika. Archived from the original on 2022-10-31. Retrieved 2022-10-30.
- "Survey places Kerala Police at top in India for efficient service". English.Mathrubhumi. 18 November 2021. Archived from the original on 2022-11-10. Retrieved 2022-11-10.
- "Kerala police ranked fourth in Smart Policing Index of IPF". The New Indian Express. Archived from the original on 2022-11-10. Retrieved 2022-11-10.
- "ISO for Kollam Police Commissioner office". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 2023-04-05. Retrieved 2023-03-04.
- "Nedumkandam custodial death: Action against 5 cops". The Hindu. June 2021. Archived from the original on 2023-03-09. Retrieved 2023-03-09.
- "Kerala: Maoist a Velmurugan was killed in fake encounter, claims family". The Times of India. 5 November 2020. Archived from the original on 15 November 2020. Retrieved 9 March 2023.
- "False accusation, third grade treatment: Police officers transferred for torturing bothers in Kollam". 19 October 2022. Archived from the original on 9 March 2023. Retrieved 9 March 2023.
- "Why Kerala Police remains a problem for Pinarayi Govt". India Today. Archived from the original on 2021-11-29. Retrieved 2021-11-30.
- "State Police failed to curb violence". India Today. 2022-09-24. Archived from the original on 2022-10-31. Retrieved 2022-10-30.
- "Police failure despite intelligence alerts". Malayala Manorama. 2022-07-06. Archived from the original on 2022-10-31. Retrieved 2022-10-30.
- Tapan Kumar Pradhan (June 2019). I, She and the Sea. New Delhi: Kohinoor Books. pp. 217–228. ISBN 978-81-942835-9-1.
- Case No 166/DPTN/B5/17R dated 26 July 2017 of Kerala Police, Museum PS







