Kuala Krai District
Kuala Krai District is a district (jajahan) in Kelantan, Malaysia. Historically, it was known as Kuala Lebir.[4]
Kuala Krai District
Kkeghe | |
|---|---|
| Jajahan Kuala Krai | |
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Jawi | كوالا كراي |
| • Chinese | 瓜拉吉赖县 |
| • Tamil | கோலா கிராய் |
 Flag | |
 Location of Kuala Krai District in Kelantan | |
 Kuala Krai District Location of Kuala Krai District in Malaysia | |
| Coordinates: 5°30′N 102°10′E | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Seat | Kuala Krai |
| Local area government(s) | Kuala Krai District Council (North Kuala Krai) Dabong District Council (South Kuala Krai) |
| Government | |
| • District officer | Haji Tengku Ab Rahman bin Tuan Yunus[1] |
| • Administrative office | Kuala Krai Land Officers and Colony |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,275 km2 (878 sq mi) |
| Population (2021)[3] | |
| • Total | 105,900 |
| • Density | 47/km2 (120/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (MST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+8 (Not observed) |
| Postcode | 18xxx |
| Calling code | +6-09-9 |
| Vehicle registration plates | D |

Background
The Kuala Krai district is a landlocked district in the centre of the State of Kelantan in northeastern Malaysia. The land is hilly, and before the 20th century the entire area was tropical rain forest. The territory contains the confluence of two major rivers, the Lebir and Galas, to form the Kelantan River, which then flows some 70 km northwards through one of the most densely populated flood plains on the Malay Peninsula to its estuary in the South China Sea near the State capital of Kota Bharu.
Kuala Krai was the most affected district in Kelantan by a massive 2014 flood known as Bah Kuning that resulted in property loses and in the federal government declaring a State of Emergency. This catastrophic event was cushioned by great societal support and aid from NGOs.
As transport links improved during the 20th century, people moved into the area to take advantage of the abundant land available for farming. A railway was constructed in the 1920s through the undeveloped interior of Malaysia to link Kelantan State with the main centres of population on the west coast. This line ran through Kuala Krai territory, and settlements became established along the route. Road links followed, and towns and villages grew to house the mainly agricultural population. Rubber production was becoming increasingly important throughout Malaysia at the time, and many rubber-tree plantations were set up in this area. Later, the country-wide shift to oil palm in the 1970s and 1980s saw the establishment of oil palm plantations in the territory, some of which replaced rubber.
Kuala Krai was originally part of Ulu Kelantan until it was split following a re-delineation in 1974. Kuala Krai formally gained its own district and municipal administration in 1977.[5]
Infrastructure developed to support the population, and by the end of the 20th century Kuala Krai town had become a busy, thriving town as well as the administrative centre for the territory.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 90,830 | — |
| 2000 | 91,771 | +1.0% |
| 2010 | 104,234 | +13.6% |
| 2020 | 105,007 | +0.7% |
| Source: [6] | ||
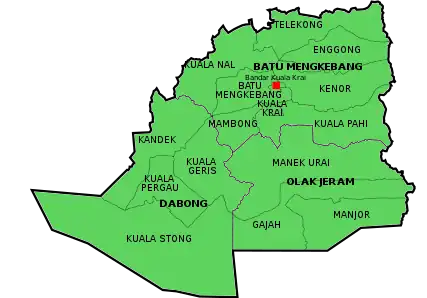
Kuala Krai District has an area of 2329 km² and comprises three subdistricts (daerah):[2]
- Batu Mengkebang (Kuala Krai town) (726.9 km²) with 122 villages
- Dabong (844.5 km²) with 27 villages
- Olak Jeram (Manek Urai)(757.6 km²) with 67 villages
Some of the better known towns and villages in the territory include Dabong, Kemubu, Manek Urai, Kampung Pahi, Kampung Peria and Kampung Laloh.
Secondary schools
The secondary schools in the territory are:[7]
- Maahad Rahmaniah Padang Sembilan (SMU (A)Rahmaniah), 18000 Kuala Krai
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Dabong (SMK Dabong), 18200 Dabong
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Keroh (SMK Keroh), 18000 Kuala Krai
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Laloh (SMK Laloh), 18000 Kuala Krai
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Manek Urai (SMK Manek Urai), 18050 Kuala Krai
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Mengkebang (SMK Mengkebang), 18000 Kuala Krai
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Pahi (SMK Pahi), 18000 Kuala Krai
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Yahya Petra (1) (SMK Sultan Yahya Petra (1)), 18000 Kuala Krai
- Sekolah Menengah Teknik Kuala Krai (SM Teknik Kuala Krai), 18000 Kuala Krai
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Kuala Krai (SMK Kuala Krai), Sungai Durian, 18000 Kuala Krai
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Yahya Petra (2) (SMK Sultan Yahya Petra (2)), 18000 Kuala Krai
- Maktab Rendah Sains Mara Kuala Krai*Fews Sekolah Menengah Ugama
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bandar Kuala krai(SMKBKK)
Population
The population of Kuala Krai territory was 117,800 in 2009.
Ranking Population Jajahan Kuala Krai.
| Rank | Daerah/Mukim | Population 2000 | PBT Council |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Batu Mengkebang | 55,975 | Kuala Krai District Council |
| 2 | Olak Jeram | 24,665 | Dabong District Council |
| 3 | Dabong | 11,131 | Dabong District Council |
Population ethnicity
The population and ethnicity of the territory is as follows:[2]
| Race | 1990 | % | 1995 | % | 2000 | % | 2004 | % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malay | 92,916 | 91.4 | 110,246 | 90.9 | 130,810 | 90.9 | 149,018 | 90.8 | |||
| Chinese | 5,685 | 5.6 | 7,282 | 6.0 | 8,657 | 6.0 | 9,862 | 6.0 | |||
| Indian | 2,650 | 2.6 | 3,364 | 2.7 | 3,990 | 2.8 | 4,545 | 2.7 | |||
| Other | 354 | 0.4 | 121,339 | 0.4 | 463 | 0.3 | 527 | 0.3 |
Attractions
- Taman Tasik Krai
- Taman Chintawangsa
- Taman Masjid Bandar
- Zoo Mini Kuala Krai
- Muzium Kuala Krai
- Tangga Bradley
- Jambatan Sultan Ismail
- Tembikar Kampung Mambong
- Kampung Lemang Manek Urai
- Gunung Stong
- Gua Ikan
- Air Terjun Jelawang
- Lata Berangin
- Lata Chenulang
- Lata Rek
- Lata Y
- Istana Sangkut
Famous people from Kuala Krai
- Loh Sea Keong, Malaysian professional cyclist
- Mee Fong, a commercial photographer, had a studio in Kuala Krai in 1930[8]
- Mohd Khairul Anuar also known as Lan Cairo, who is a Nurse. He was born in Kuala Krai on Dragon Years 27 May 1988. He is very good personal rapport with international people as well as a representative of Malays to the worlds.
- Datuk Rafiah Salim, is the first female Vice-Chancellor in Malaysia, posted to Universiti Malaya.
- T. Wignesan, writer, was born in Kuala Krai in the early 1930s[9][10]
- Tengku Budriah binti Al-Marhum Tengku Ismail, the Raja Perempuan of Perlis, was born in Kuala Krai on 28 March 1925. Her husband, Almarhum Tuanku Syed Putra ibni Almarhum Syed Hassan Jamalullail was elected as the third King of Malaysia (known as Yang di-Pertuan Agong) from 1960 to 1965.[11]
- Terence Fernandez, a Journalist and current deputy editor special reports & investigations of The Sun Newspaper. He was kidnapped in Iraq in 2003 but survived and currently writes a column in The Sun every Tuesday and Thursday, frequently writing on corruption and mismanagement of funds by politicians. He grew up in Kuala Krai and spent his entire childhood and teenage years there.
- Zang Toi, New York fashion designer, was born in Kuala Krai on 11 June 1961[12]
- Muhammad Shahrol Nizam, centerback for UPNM F.C. on 3 September 2019.
Federal Parliament and State Assembly Seats
List of LMS district representatives in the Federal Parliament (Dewan Rakyat)
| Parliament | Seat Name | Member of Parliament | Party |
|---|---|---|---|
| P31 | Kuala Krai | Abdul Latiff Abdul Rahman | PN (PAS) |
List of LMS district representatives in the State Legislative Assembly of Kelantan
| Parliament | State | Seat Name | State Assemblyman | Party |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P31 | N39 | Mengkebang | Muhammad Mat Sulaiman | PN (PAS) |
| P31 | N40 | Guchil | Hilmi Abdullah | PN (PAS) |
| P31 | N41 | Manek Urai | Mohd Fauzi Abdullah | PN (PAS) |
| P31 | N42 | Dabong | Ku Mohd Zaki Ku Hussin | PN (PAS) |
See also
References
- "Pejabat Tanah Dan Jajahan Kuala Krai - Perutusan Ketua Jajahan". www.ptjkk.kelantan.gov.my. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- "Profail Jajahan Kuala Krai". Pejabat Tanah dan Jajahan Kuala Krai. Archived from the original on 12 March 2008. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
- "Population Distribution and Basic Demographic Characteristics, 2010" (PDF). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 May 2014. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- "Map of British Malaya Including The Straits Settlements Federated Malay States and Malay States Not Included In The Federation 1924" (JPG). Raremaps.com. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- "Info Kuala Krai". Majlis Daerah Kuala Krai. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- "Key Findings of Population and Housing Census of Malaysia 2020" (pdf) (in Malay and English). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. ISBN 978-967-2000-85-3.
- "Secondary Schools in Kelantan, Malaysia". Jadn.com. 2007. Retrieved 6 December 2007.
- Cambridge University Library (2004). "Mee Fong, fl 1930, photographer". RCS Photographers Index. Retrieved 14 December 2006.
- Netconcepts, LLC. "T. Wignesan". WritersNet. Retrieved 11 December 2006.
- T Wignesan (2006). "Curriculum Vitae". Stateless.freehosting.net. Retrieved 11 December 2006.
- Perpustakaan Negara Malaysia (2003). "Yang di-Pertuan Agong III". Malaysian Monarchy. Archived from the original on 27 October 2005. Retrieved 10 December 2006.
- Star Publications (Malaysia) (2003). "Designer dreams". All Malaysia.info. Retrieved 10 December 2006.