Lille-Europe station
Lille-Europe station (French: Gare de Lille-Europe) is a SNCF railway station in Lille, France, on the LGV Nord high-speed railway. The station is primarily used for international Eurostar and long-distance SNCF TGV services, although some high-speed regional trains also call at the station. The station was built in 1993 to be used as a through station for trains between the UK, Belgium, and the Netherlands, as well as French TGV services, except those coming from Paris which normally terminate at Lille-Flandres station. There is a 400-metre (1,300 ft) walking distance between the two stations, which are also connected by the Lille Metro and Lille tramway.
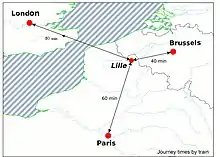
Eurostar services | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fastest timetabled journeys from London St Pancras International | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Connections
For travellers from the United Kingdom to destinations not served directly by Eurostar, connections are available here on trains towards Disneyland Paris, Charles de Gaulle International Airport, Lyon, Valence, then Avignon, Aix-en-Provence, Marseille St. Charles (and also on to Cannes and Nice); and Nîmes, Montpellier and Perpignan.
After the 'Additional Protocol to the Sangatte Protocol' was signed by France and the United Kingdom on 29 May 2000, juxtaposed controls were set up in the station. Eurostar passengers travelling to the UK clear exit checks from the Schengen Area (carried out by the French Border Police) as well as UK entry checks (conducted by the UK Border Force) in the station before boarding their train.[6]
Train services
The following services call at Lille:
- International high-speed services (Eurostar) London – Lille – Brussels – Amsterdam
- International high-speed services (Eurostar) London – Lille – Paris
- High-speed services (TGV) Calais – Lille – Paris
- High-speed services (TGV) (Rang-du-Fliers -) Boulogne – Calais – Lille – Paris
- High-speed services (TGV) Dunkerque – Lille – Paris
- High-speed services (TGV) Lille – Aéroport CDG – Lyon – Marseille
- High-speed services (TGV) Lille – Aéroport CDG – Lyon – Nîmes – Montpellier
- High-speed services (TGV) Lille – Aéroport CDG – Tours – Poitiers – Bordeaux
- High-speed services (TGV) Lille – Aéroport CDG – Le Mans – Rennes
- High-speed services (TGV) Lille – Aéroport CDG – Le Mans – Angers – Nantes
- High-speed services (TGV) Lille – Arras – Aéroport CDG – Lyon – Nîmes – Montpellier
- High-speed services (TGV) Lille – Arras – Aéroport CDG – Lyon – Marseille
- International high-speed services (TGV) Brussels – Lille – Aéroport CDG – Lyon – Marseille
- International high-speed services (TGV) Brussels – Lille – Aéroport CDG – Lyon – Nîmes – Montpellier – Perpignan
- High-speed regional services (TER GV) Dunkirk – Lille
- High-speed regional services (TER GV) Rang-du-Fliers – Boulogne – Calais – Lille
Ouibus
Since 23 July 2012, SNCF's international coach network, iDBUS (now BlaBlaBus), serves Lille Europe.
Coach services from Lille are:
- Paris – Lille
- Paris – Lille – Brussels
- Paris – Lille – Amsterdam
- Paris – Lille – London
See also
Notes
- Due to the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, Ashford and Ebbsfleet will not be served by Eurostar trains until 2025.[3]
- Due to the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, Calais, Lyon, Avignon, and Marseille, are not served by Eurostar trains for the foreseeable future.[4]
- Due to the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, Disneyland Paris services will be suspended from 6 June 2023.[5]
References
- Airport information for Gare de Lille Europe at Transport Search website.
- "Fréquentation en gares". SNCF. Retrieved 3 May 2019.
- "Coronavirus: Eurostar trains will not stop in Kent until at least 2023". BBC News. Royal Tunbridge Wells: BBC English Regions. 16 September 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2022.
- "TIMETABLES". Eurostar4Agents. 29 June 2021. Retrieved 7 June 2022.
- "Important information about trains to Disneyland® Paris - Summer 2023". Eurostar4Agents. 25 August 2022. Retrieved 27 September 2022.
- "Lords Hansard text for 16 March 2001 (210316-05)". Department of the Official Report (Hansard), House of Lords.
External links
- Lille-Europe station at "Gares & Connexions", the official website of SNCF (in French)
