Luigi Russolo
Luigi Carlo Filippo Russolo (30 April 1885 – 4 February 1947) was an Italian Futurist painter, composer, builder of experimental musical instruments, and the author of the manifesto The Art of Noises (1913).[1] Russolo completed his secondary education at Seminary of Portograuro in 1901, after which he moved to Milan and began gaining interest in the arts.[2] He is often regarded as one of the first noise music experimental composers with his performances of noise music concerts in 1913–14 and then again after World War I, notably in Paris in 1921.[3] He designed and constructed a number of noise-generating devices called Intonarumori.
Luigi Russolo | |
|---|---|
 Luigi Russolo ca. 1916 | |
| Background information | |
| Birth name | Luigi Russolo |
| Born | 30 April 1885 Portogruaro, Italy |
| Died | 4 February 1947 (aged 61) Laveno Mombello, Italy |
| Genres | |
| Occupation(s) |
|
| Years active | 1901–1947 |
Biography
%252C_1913.jpg.webp)
Luigi Russolo was perhaps the first noise artist.[4][5] His 1913 manifesto, L'Arte dei Rumori (The Art of Noises), stated that the industrial revolution had given modern men a greater capacity to appreciate more complex sounds. Russolo found traditional melodic music confining, and he envisioned noise music as its future replacement.[6]
Russolo designed and constructed a number of noise-generating devices called Intonarumori, and assembled a noise orchestra to perform with them. A performance of his Gran Concerto Futuristico (1917) was met with strong disapproval and violence from the audience, as Russolo himself had predicted.
None of his intoning instruments have survived: some were destroyed in World War II; while others have been lost.[7] Replicas of the instruments have since been built and performed. (See the Intonarumori page.)
Although Russolo's works bear little resemblance to modern noise music, his pioneering creations cannot be overlooked as an essential stage in the evolution of the several genres in this category.[8][9] Many artists are now familiar with Russolo's manifesto.[10]
Connections to Fascism
Russolo, like many other Futurist artists, is often associated with Italian fascism. In addition to his association with the Futurist artist and poet F. T. Marinetti, who co-authored the Fascist Manifesto (1919), Russolo presented his work at exhibitions sponsored by Mussolini's government.[11]
Collaboration with Antonio Russolo
Antonio Russolo, another Italian Futurist composer and Luigi's brother, produced a recording of two works featuring the original Intonarumori. The phonograph recording, made in 1921, included works entitled Corale and Serenata, which combined conventional orchestral music set against the sound of the noise machines. It is the only surviving contemporaneous sound recording of Luigi Russolo's noise music.[12] Russolo and Filippo Tommaso Marinetti gave the first concert of Futurist music, complete with intonarumori, in April 1914, causing a riot.[13] The program comprised four Noise Networks.[14]
Gallery
%252C_oil_on_canvas%252C_99_x_99_cm%252C_private_collection.jpg.webp) Souvenir d'une nuit (Memories of a Night), 1911 oil on canvas, 99 × 99 cm, private collection
Souvenir d'une nuit (Memories of a Night), 1911 oil on canvas, 99 × 99 cm, private collection%252C_oil_on_canvas%252C_86_x_65_cm%252C_Mus%C3%A9e_de_Grenoble.jpg.webp) Sintesi plastica dei movimenti di una donna, 1912 oil on canvas, Museum of Grenoble
Sintesi plastica dei movimenti di una donna, 1912 oil on canvas, Museum of Grenoble Self-portrait with Skulls, 1909 painting
Self-portrait with Skulls, 1909 painting Russolo's Grave in Laveno-Mombello
Russolo's Grave in Laveno-Mombello.jpg.webp) Profumo (meaning "scent", "fragrance", 1910)
Profumo (meaning "scent", "fragrance", 1910) La Rivolta (The Revolt), 1911 oil on canvas
La Rivolta (The Revolt), 1911 oil on canvas La Musica (a pianist playing for his audience), 1911–12 oil on canvas
La Musica (a pianist playing for his audience), 1911–12 oil on canvas Solidity of Fog, 1912 oil on canvas
Solidity of Fog, 1912 oil on canvas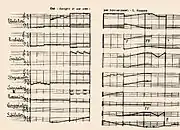 1913 score of en-harmonic notation, for Intonarumori
1913 score of en-harmonic notation, for Intonarumori Intonarumori, 1913, instruments built for music-piece Bruitism, partly operating on electricity
Intonarumori, 1913, instruments built for music-piece Bruitism, partly operating on electricity Dynamism of a Car, 1913 oil painting
Dynamism of a Car, 1913 oil painting Soap-dish, 1929 oil painting
Soap-dish, 1929 oil painting Landscape with trees, c. 1940s painting
Landscape with trees, c. 1940s painting
Notes
- Chilvers & Glaves-Smith, p. 619.
- Chessa, Luciano (31 March 2012). Luigi Russolo, Futurist: Noise, Visual Arts, and the Occult. University of California Press. p. 69. ISBN 9780520270633.
- Chilvers & Glaves-Smith, p. 620.
- In Futurism and Musical Notes, Daniele Lombardi discusses the French composer [Louis] Carol-Bérard (1881–1942); a pupil of Isaac Albéniz, Carol-Bérard is said to have composed a Symphony of Mechanical Forces in 1910 – but little evidence as emerged thus far to establish this assertion.
- Luigi Russolo, "The Art of Noises"
- Chessa, Luciano, Luigi Russolo, Futurist: Noise, Visual Arts, and the Occult, University of California Press, 2012, p. 3
- Barclay Brown, "The Noise Instruments of Luigi Russolo", Perspectives of New Music 20, nos. 1 & 2 (Fall–Winter 1981, Spring–Summer 1982): 31–48; citation on 36
- Paul Hegarty, Noise/Music: A History (London: Continuum International Publishing Group, 2007), pp. 13–14
- László Moholy-Nagy in 1923 recognized the unprecedented efforts of the Italian Futurists to broaden our perception of sound using noise. In an article in Der Sturm #7, he outlined the fundamentals of his own experimentation: "I have suggested to change the gramophone from a reproductive instrument to a productive one, so that on a record without prior acoustic information, the acoustic information, the acoustic phenomenon itself originates by engraving the necessary Ritzschriftreihen [etched grooves]." He presents detailed descriptions for manipulating discs, creating "real sound forms" to train people to be "true music receivers and creators" (" A Brief history of Anti-Records and Conceptual Records" by Ron Rice via UbuWeb, from Unfiled: Music Under New Technology, Chris Cutler (ed.) 1994
- Chessa, Luciano, Luigi Russolo, Futurist: Noise, Visual Arts, and the Occult, University of California Press, 2012, p. 3
- Tracy, Peter. "Luigi Russolo's Cacophonous Futures". The Public Domain Review. Retrieved 10 February 2023.
- Albright, Daniel (ed.) Modernism and Music: An Anthology of Source. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2004. p. 174
- Larry Sitsky (2002). Music of the Twentieth-century Avant-garde: A Biocritical Sourcebook. Westport and London: Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 415. ISBN 978-0-313-29689-5.
- Luigi Russolo, The Art of Noise (Futurist Manifesto, 1913), translated by Robert Filliou. p. 14
References
- Chilvers, Ian; Glaves-Smith, John (2009). A Dictionary of Modern and Contemporary Art. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199239665.
- Chessa, Luciano: Luigi Russolo, Futurist: Noise, Visual Arts, and the Occult. University of California Press, 2012.
- Luigi Russolo, The Art of Noise (Futurist Manifesto, 1913), translated by Robert Filliou
External links
- Printed works by Luigi Russolo digitalized on Internet Archive by the Archivio del '900 of Mart Museum, Rovereto, Italy.
- Russolo, Luigi Carlo Filippo. Dizionario Biografico degli Italiani (2017). (in Italian)
- Media Art Net | Russolo, Luigi: Intonarumori (at medienkunstnetz.de)
- Archive Russolo recordings at LTM
- Peggy Guggenheim Collection: Luigi Russolo
- Bob Osborn's Futurism: Luigi Russolo
- Prof. Russolo & His Noise Intoners
- Audio
- Corale, Serenata by Antonio Russolo and Luigi Russolo (1924) were published on cassette in 1988 in the Audio By Visual Artists edition of Tellus Audio Cassette Magazine #21 and are archived on the internet at Ubuweb
- Three audio clips by Luigi Russolo: Serenata, Corale and Risveglio di una città
- Video
