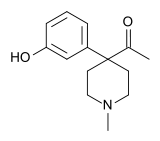
Methylketobemidone
Methylketobemidone is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of ketobemidone. It was developed in the 1950s during research into analogues of pethidine and was assessed by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime but was not included on the list of drugs under international control, probably because it was not used in medicine or widely available.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H19NO2 |
| Molar mass | 233.311 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Methylketobemidone is so named because it is the methyl ketone analogue of bemidone (hydroxypethidine). The more commonly used ethyl ketone ("ethylketobemidone") is simply called ketobemidone, as it is the only drug of this family to have been marketed.
Presumably methylketobemidone produces similar effects to ketobemidone and other opioids, such as analgesia and sedation, along with side effects such as nausea, itching, vomiting and respiratory depression which may be harmful or fatal.