Metre-gauge railway
Metre-gauge railways (US: meter-gauge railways) are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) or 1 metre.[1]
| By transport mode | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By size (list) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change of gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By location | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
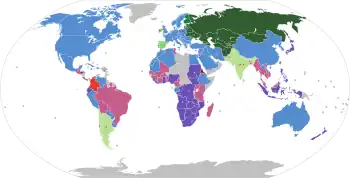 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The metre gauge is used in around 95,000 kilometres (59,000 mi) of tracks around the world. It was used by European colonial powers, such as the French, British and German Empires in their colonies. In Europe, large metre-gauge networks remain in use in Switzerland, Spain and many European towns with urban trams, but most metre-gauge local railways in France, Germany and Belgium closed down in the mid-20th century, although many still remain. With the revival of urban rail transport, metre-gauge light metros were established in some cities, and in other cities, metre gauge was replaced by standard gauge. The slightly-wider 1,009 mm (3 ft 3+23⁄32 in) gauge is used in Sofia.
Examples of metre-gauge
| Country/territory | Railway |
|---|---|
| Argentina | 11,080 km (6,880 mi) |
| Austria |
|
| Bangladesh | 1,830 km (1,140 mi), out of which 365 km (227 mi) are dual gauge with 1,676 mm (5 ft 6 in) gauge |
| Belgium |
|
| Benin | 578 km (359 mi) |
| Bolivia | 3,600 km (2,200 mi) |
| Brazil |
23,489 km (14,595 mi)
|
| Bulgaria | 154 km (96 mi) of 1,009 mm (3 ft 3+23⁄32 in) gauge
|
| Burkina Faso |
|
| Burma | 3,200 kilometres (2,000 mi) 160 kilometres (99 mi)
|
| Cambodia | 612 km (380 mi) |
| Cameroon | 1,104 km (686 mi) |
| Chile | 2,923 km (1,816 mi) |
| China |
|
| Croatia |
|
| Czech Republic | Like other Sudeten cities, the trams of Liberec used metre gauge in the past. All lines however have been rebuilt to standard gauge. |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | Several metre gauge railways |
| Denmark |
A few local railways. Only one remains, but regauged to standard gauge.
|
| Egypt |
|
| Finland |
|
| France | Historically used in many local and regional railways, only a few of which remain today.
|
| Germany |
|
| Greece | The Piraeus, Athens and Peloponnese Railways used to be the largest metre-gauge network in Europe but are now largely abandoned. Only the suburban rail service of Patras, and the Olympia–Katakolo tourist railway still use the network. |
| Hungary |
|
| India | Nilgiri Mountain Railway (operating) |
| Iraq | Mesopotamian Railways |
| Israel | Sections of 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) railways, later converted to 1,050 mm (3 ft 5+11⁄32 in) or 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) gauge |
| Italy |
|
| Ivory Coast |
|
| Kenya |
|
| Laos | A 3.5 km extension of the metre-gauge State Railway of Thailand network across the border into Laos |
| Latvia | Liepāja tramway (operating) |
| Madagascar | 875 km (544 mi). There are two unconnected systems operated by Madarail |
| Malaysia | |
| Mali |
641 km (398 mi) Dakar–Niger Railway |
| Malta | Malta Railway |
| Morocco | Several industrial railways in former Spanish Morocco |
| New Zealand | Wellington Cable Car (operating) |
| Norway |
|
| Pakistan |
|
| Poland |
|
| Portugal | Several mainly mountainous branch lines, mostly abandoned in the 1990s, never fully interconnected — connected to the REFER network by means of shared stations and some dual-gauge stretches. Metro de Mirandela and Vouga line remain in use. Other metric networks include Funchal rack railway (defunct in 1943), Coimbra trams (defunct in 1980), and Sintra trams. |
| Puerto Rico | Full network of Puerto Rican 1000mm railways in 1920: 654 km (406 mi)[2]
|
| Romania |
|
| Russia |
|
| Senegal | Dakar–Niger Railway – 1,287 km (800 mi) |
| Serbia | Belgrade Tram (operating) |
| Singapore | Singapore span of the Keretapi Tanah Melayu (Malayan Railway) for shuttle service. |
| Slovakia |
|
| Spain |
|
| Sweden | Skansens bergbana (operating) |
| Switzerland | Many narrow-gauge railways: suburban railways, mountain railways, rack railways, some long-distance railways and trams.
|
| Tanzania | Tanzania Railways Corporation – about 2,600 km (1,600 mi) (break of gauge with 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) TAZARA Railway) |
| Thailand | State Railway of Thailand, 4,346 km (2,700 mi). |
| Togo | 568 km (353 mi). |
| Tunisia | 1,674 km (1,040 mi) used along with standard gauge (471 km (293 mi)) |
| Turkey |
|
| Uganda | Uganda Railway run by Uganda Railways Corporation |
| Ukraine |
|
| United Kingdom |
|
| United States |
|
| Vietnam | Vietnam Railways and KunHe Railway |
See also
References
- Raja, K. "Complete information on Railway Gauges". Retrieved April 30, 2017.
- «Los ferrocarriles de uso público en Puerto Rico (1870-1990)», Antonio Santamaría García (1994). Revista Complutense de Historia de América XX: pp. 207-228
- Contexto histórico e inventario del ferrocarril en Puerto Rico, 1850-1953 - Primera parte: Trasfondo histórico
- «Conservando una Romántica Tradición», Dave Deyo, Railroading, Number 43, Second Quarter (1972): pp. 6-18]
- Brandon, Andrew. "The Sierra Lumber Company". Pacific Narrow Gauge.
