Dinitrogen trioxide
Dinitrogen trioxide (also known as nitrous anhydride) is the chemical compound with the formula N2O3. It is one of the simple nitrogen oxides. It forms upon mixing equal parts of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide and cooling the mixture below −21 °C (−6 °F):[4]
- NO + NO2 ⇌ N2O3
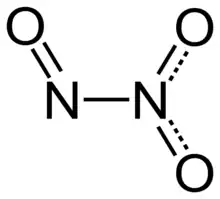 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-Oxonitramide[1] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.013 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2421 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 76.011 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Deep blue liquid |
| Density |
|
| Melting point | −100.7[2] °C (−149.3 °F; 172.5 K) |
| Boiling point | 3.5 °C (38.3 °F; 276.6 K) (dissociates[2]) |
| very soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in ether |
| −16.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| planar, Cs | |
| 2.122 D | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
65.3 J/(mol·K) |
Std molar entropy (S⦵298) |
314.63 J/(mol·K) |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
91.20 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[3] | |
    | |
| Danger | |
| H270, H280, H310, H310+H330, H314, H330 | |
| P220, P244, P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P330+P331, P302+P350, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P320, P321, P322, P361, P363, P370+P376, P403, P403+P233, P405, P410+P403, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dinitrogen trioxide is only isolable at low temperatures, i.e. in the liquid and solid phases. In liquid and solid states, it has a deep blue color.[2] At higher temperatures the equilibrium favors the constituent gases, with KD = 193 kPa (25 °C).[5]
This compound is sometimes called "nitrogen trioxide", but this name properly refers to another compound, the (uncharged) nitrate radical •NO3.
Structure and bonding
Dinitrogen trioxide molecule contains an N–N bond. One of the numerous resonant structures of the molecule of dinitrogen trioxide is O=N−NO2, which can be described as a nitroso group −N=O attached to a nitro group −NO2 by a single bond between the two nitrogen atoms. All atoms and bonds of dinitrogen trioxide molecule contribute to the resonancy. The oxidation state of the nitrogen atom of the nitroso group is +3, while the oxidation state of the nitrogen atom of the nitro group is +5. This isomer is considered as the "anhydride" of the unstable nitrous acid (HNO2), and produces it when mixed with water, although an alternative structure might be anticipated for the true anhydride of nitrous acid, i.e. O=N−O−N=O, but this isomer is not observed.
Typically, N–N bonds are similar in length to that in hydrazine (145 pm). Dinitrogen trioxide, however, has an unusually long N–N bond at 186 pm. Some other nitrogen oxides also possess long N–N bonds, including dinitrogen tetroxide (175 pm). The N2O3 molecule is planar and exhibits Cs symmetry. The dimensions displayed on the picture below come from microwave spectroscopy of low-temperature, gaseous N2O3:[4]
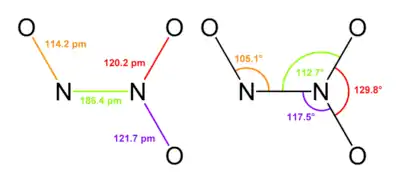
If the nitrous acid is not then used up quickly, it decomposes into nitric oxide and nitric acid. Nitrite salts are sometimes produced by adding N2O3 to water solutions of bases:
- N2O3 + 2 NaOH → 2 NaNO2 + H2O
References
- "Dinitrogen trioxide".
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 444. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- "Dinitrogen trioxide". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1984). Chemistry of the Elements. Oxford: Pergamon Press. pp. 521–22. ISBN 978-0-08-022057-4.
- Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
