Orteronel
Orteronel (TAK-700) is a nonsteroidal CYP17A1 inhibitor that was being developed for the treatment of cancer by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company in conjunction with Millennium Pharmaceuticals.[1] It completed two phase III clinical trials for metastatic, hormone-refractory prostate cancer but failed to extend overall survival rates, and development was voluntarily terminated as a result.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
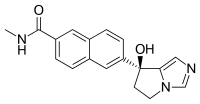
| IUPAC name
6-(7-Hydroxy-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[1,2-c]imidazol-7-yl)-N-methylnaphthalene-2-carboxamide | |
| Other names
TAK-700 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H17N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 307.353 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Orteronel is an androgen biosynthesis inhibitor. It selectively inhibits the enzyme CYP17A1[3] which is expressed in testicular, adrenal, and prostatic tumor tissues. CYP17 catalyzes two sequential reactions: (a) the conversion of pregnenolone and progesterone to their 17α-hydroxy derivatives by its 17α-hydroxylase activity, and (b) the subsequent formation of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and androstenedione, respectively, by its 17,20-lyase activity.[4] DHEA and androstenedione are androgens and precursors of testosterone. Inhibition of CYP17 activity thus decreases circulating levels of testosterone.
References
- Millennium and Takeda Announce Advancement of Prostate Cancer Program, Millennium Pharmaceuticals
- MarketWatch (2014). "Takeda Announces Termination of Orteronel (TAK-700) Development for Prostate Cancer in Japan, U.S.A. and Europe".
- Yamaoka, M; Hara, T; Hitaka, T; Kaku, T; Takeuchi, T; Takahashi, J; Asahi, S; Miki, H; et al. (2012). "Orteronel (TAK-700), a novel non-steroidal 17,20-lyase inhibitor: Effects on steroid synthesis in human and monkey adrenal cells and serum steroid levels in cynomolgus monkeys". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 129 (3–5): 115–28. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.01.001. PMID 22249003. S2CID 20204862.
- Attard G, Belldegrun AS, de Bono JS (December 2005). "Selective blockade of androgenic steroid synthesis by novel lyase inhibitors as a therapeutic strategy for treating metastatic prostate cancer". BJU Int. 96 (9): 1241–6. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05821.x. PMID 16287438.