Oxymorphol
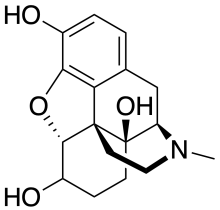
Oxymorphol is oxymorphone which has been hydrogenated at the 6-position and consists of a mixture of 4,5α-Epoxy-17-methylmorphinan-3,6β,14-triol and 4,5α-Epoxy-17-methylmorphinan-3,6α,14-triol (hydromorphinol).[1] It is produced by the human body as an active metabolite of oxymorphone and some bacteria as an intermediate in turning morphine into hydromorphone.[2] It can also be manufactured and is the subject of patents by drug companies looking for new semi-synthetic analgesics and cough suppressants.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 4,5α-Epoxy-17-methylmorphinan-3,6,14-triol |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 303.358 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
A derivative of oxymorphol, 8-hydroxy-6-α-oxymorphol, was discovered in the first decade of the 21st century and the subject of a patent application by Endo Pharmaceuticals for an analgesic and antitussive.[3]
References
- α-Oxymorphol as "Hydromorphinol"
- Cone EJ, Darwin WD, Buchwald WF, Gorodetzky CW (1983). "Oxymorphone metabolism and urinary excretion in human, rat, guinea pig, rabbit, and dog". Drug Metabolism and Disposition: The Biological Fate of Chemicals. 11 (5): 446–50. PMID 6194952.
- "OPIOID AND METHODS OF MAKING AND USING THE SAME - Patent application". www.faqs.org. Archived from the original on 2014-05-02.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.