Panthenol
Panthenol (also called pantothenol) is the alcohol analog of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), and is thus a provitamin of B5. In organisms, it is quickly oxidized to pantothenic acid. It is a viscous transparent liquid at room temperature. Panthenol is used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic products as a moisturizer and to improve wound healing.
 D-panthenol | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4-Dihydroxy-N-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutanamide[1] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1724945, 1724947 R | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.839 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | dexpanthenol |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H19NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 205.254 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Highly viscous, colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.2 g mL−1 (at 20 °C) |
| Melting point | 66 to 69 °C (151 to 156 °F; 339 to 342 K) |
| Boiling point | 118 to 120 °C (244 to 248 °F; 391 to 393 K) at 2.7 Pa |
| log P | −0.989 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.033 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 0.964 |
Chiral rotation ([α]D) |
+29° to +30° |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.499 |
| Pharmacology | |
| A11HA30 (WHO) D03AX03 (WHO), S01XA12 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
10,100 mg kg−1 (intraperitoneal, mouse); 15,000 mg kg−1 (oral, mouse) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Uses
_mit_Verpackung_und_Beipackzettel_%E2%80%94_Deutschland.jpg.webp)
In pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and personal-care products, panthenol is a moisturizer and humectant, used in ointments, lotions, shampoos, nasal sprays, eye drops, lozenges, and cleaning solutions for contact lenses.
In ointments it is used for the treatment of sunburns, mild burns, minor skin injuries, and disorders (in concentrations of up to 2–5%).[2] It improves hydration, reduces itching and inflammation of the skin, improves skin elasticity, and accelerates epidermal wounds' rate of healing.[3] For this purpose, it is sometimes combined with allantoin.
It binds to the hair shaft readily, so, it is a common component of commercial shampoos and hair conditioners (in concentrations of 0.1–1%). It coats the hair and seals its surface, lubricating the hair shaft and giving it a shiny appearance.
It is also recommended by tattoo artists as a post-tattooing moisturising cream.
Adverse effects
Panthenol is generally well tolerated. In rare cases, skin irritation and contact allergies have been reported.[2][3]
Pharmacology
Panthenol readily penetrates into the skin and mucous membranes (including the intestinal mucosa), where it is quickly oxidized to pantothenic acid. Pantothenic acid is extremely hygroscopic.[4] It is also used in the biosynthesis of coenzyme A, which plays a role in a wide range of enzymatic reactions and in cell growth.[2][3]
Physical and chemical properties

Panthenol is an odourless, slightly bitter, highly viscous, transparent, and colourless liquid at room temperature,[5] but salts of pantothenic acid (for example sodium pantothenate) are powders that are typically white. It is easily soluble in water and alcohol, moderately soluble in diethyl ether, soluble in chloroform (1:100),[5] in propylene glycol, and slightly soluble in glycerin.
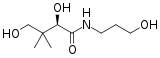
Panthenol's expanded chemical formula is HO–CH2–C(CH3)2–CH(OH)–CONH–CH2CH2CH2–OH.
Stereochemistry
Panthenol comes in two enantiomers: D, and L. Only D-panthenol (dexpanthenol) is biologically active, however both forms have moisturizing properties. For cosmetic use, panthenol comes either in D form, or as a racemic mixture of D and L (DL-panthenol).
References
- "Dexpanthenol – Compound summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 25 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 29 June 2012.
- Haberfeld H, ed. (2015). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. Bepanthen Creme.
- Ebner F, Heller A, Rippke F, Tausch I (2002). "Topical use of dexpanthenol in skin disorders". American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 3 (6): 427–33. doi:10.2165/00128071-200203060-00005. PMID 12113650. S2CID 35836478.
- Dinnendahl V, Fricke U, eds. (1991). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Vol. 7 (8 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. Pantothensäure. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
- List PH, Hörhammer L, eds. (1969). Hagers Handbuch der pharmazeutischen Praxis (in German). Vol. 2. Springer. p. 699.
