Racemoramide
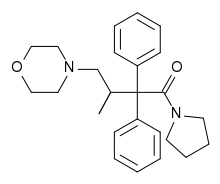
Racemoramide (INN, BAN), or simply moramide, is an opioid analgesic and a racemic mixture of the substances dextromoramide (the active component) and levomoramide (which is inactive), two enantiomers of a chiral molecule.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.085 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H32N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 392.543 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Racemoramide is itself controlled; in the United States it is under Schedule I as a Narcotic with an ACSCN of 9645 and a zero annual aggregate manufacturing quota as of 2014.[3] Its salts are the bitartrate (free base conversion ratio 0.723) and dihydrochloride (0.843)
Moramide intermediate is listed separately as a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance (ACSCN 9802), also with a zero quota.[3]
References
- Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ, Macdonald F (1997). Dictionary of pharmacological agents. CRC Press. p. 1375. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 29 November 2011.
- "Conversion Factors for Controlled Substances". Diversion Control Division. Drug Enforcement Agency, U.S. Department of Justice.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.