Cortes Generales
The Cortes Generales (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈkoɾtes xeneˈɾales]; English: Spanish Parliament, lit. 'General Courts') are the bicameral legislative chambers of Spain, consisting of the Congress of Deputies (the lower house) and the Senate (the upper house).
General Courts Cortes Generales | |
|---|---|
| 15th Cortes Generales | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Senate Congress of Deputies |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 615 265 senators 350 deputies |
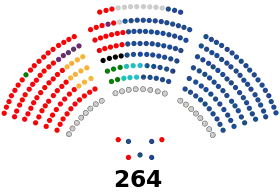 | |
Senate political groups | Government (91)
Supported by (20)
Opposition (153)
|
 | |
Congress of Deputies political groups | Caretaker Government (152)
Supported by (18) Opposition (180) |
| Elections | |
First Senate election | 15 June 1977 |
First Congress of Deputies election | January–September 1810 |
Last Senate election | 23 July 2023 |
Last Congress of Deputies election | 23 July 2023 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Senate Palacio del Senado Plaza de la Marina Española Centro, Madrid | |
_17.jpg.webp) | |
| Congress of Deputies Palacio de las Cortes Carrera de San Jerónimo Centro, Madrid | |
| Website | |
| cortesgenerales | |
The Congress of Deputies meets in the Palacio de las Cortes. The Senate meets in the Palacio del Senado. Both are in Madrid. The Cortes are elected through universal, free, equal, direct and secret suffrage,[1] with the exception of some senatorial seats, which are elected indirectly by the legislatures of the autonomous communities. The Cortes Generales are composed of 615 members: 350 Deputies and 265 Senators.
The members of the Cortes Generales serve four-year terms, and they are representatives of the Spanish people.[2] In both chambers, the seats are divided by constituencies that correspond with the fifty provinces of Spain, plus Ceuta and Melilla. However, the Canary and Balearic islands form different constituencies in the Senate.
As a parliamentary system, the Cortes confirm and dismiss the Prime Minister of Spain and their government; specifically, the candidate for Prime Minister has to be invested by the Congress with a majority of affirmative votes. The Congress can also dismiss the Prime Minister through a vote of no confidence. The Cortes also hold the power to enact a constitutional reform.
The modern Cortes Generales were created by the 1978 Constitution of Spain, but the institution has a long history.
History
Visigothic Kingdom
The tribal councils organized under Germanic law in the Visigothic Kingdom had the power of appointing and confirming kings, as well as passing laws and judgment. The Visigothic Code compiled under kings Chindasuinth and Recceswinth in the mid-7th century placed the kings, Visigoths, and native Spanish under a single law and formed the basis of Spanish law through the medieval period. The Visigothic councils, however, gradually came to be completely dominated by the clergy under the leadership of the archbishop of Toledo; with ecclesiastical prerogatives completely secure, they then tended to allow royal edicts to come into effect without further ratification.[3]
High Middle Ages (8th–12th centuries)

The royal councils (Latin: curia regis) of the Iberian peninsula's various kingdoms came to be known as cortes (Castilian Spanish) or corts (Valencian Spanish). They began as advisory councils made up of the most powerful nobles and the feudal lords closest to the king. General councils were convened in 873, 1020, 1050, and 1063. The 1188 Cortes of León convened by Alfonso IX is sometimes taken to mark the beginning of parliamentary bodies in Western Europe[4] because it provided was the first to provide formal national representation of the free urban citizens alongside the clergy and hereditary nobility. Subsequently, larger and more inclusive Cortes occurred in the Principality of Catalonia in 1192, the Kingdom of Portugal in 1211, the Kingdom of Castile in 1250, the Kingdom of Aragon in 1274, the Kingdom of Valencia in 1283, and Kingdom of Navarre in 1300. The Leonese and Castilian Corteses were merged in 1258, after which it provided representation to Burgos, Toledo, León, Seville, Córdoba, Murcia, Jaén, Zamora, Segovia, Ávila, Salamanca, Cuenca, Toro, Valladolid, Soria, Madrid, Guadalajara, and (after 1492) Granada.
Rise of the bourgeoisie (12th–15th centuries)

During the Reconquista, the growth of trade and an urbanized middle class (Spanish: burguesía) expanded their importance at the various corteses. The king retained the ability to call and dismiss the Cortes but tended to exchange fueros, further grants of privileges and autonomy, to the residents of certain cities in exchange for lump sum payments to meet military and other obligations. (Modern Navarre preserves certain rights and privileges in its current statute of autonomy directly derived from these fueros.) In some cases, the Cortes was able to independently select agents to act as permanent advisors to the king between its sessions.
Habsburg rule (16th–17th centuries)


Beginning with the Catholic Monarchs Isabella and Ferdinand, monarchs' control over Spain's various kingdoms in personal union allowed them to curtail the power of the grandees and burghers. Queen Isabella initially had difficulty in securing funding for the voyages of Christopher Columbus in the 1490s but her grandson the Habsburg emperor Charles V (Charles I of Spain) was able to easily provide for Ferdinand Magellan's 1519 expedition and then to pointedly sell away all of Spain's rights to the Spice Islands (now Indonesia's Malukus) without any consultation with the Toledo Cortes in 1529. The 1520 Revolt of the Comuneros had intended to reverse this trend and provide a stronger role for the Cortes but was crushed by the Constable's royalist forces at the 1521 Battle of Villalar and then brutally suppressed.
Reorganized, the corteses retained some power over the realm's finances—particularly in Aragon—but became limited to a consultative entity. By the reign of Philip II, the delegates of the Cortes of Castile were financially dependent on the Crown for their income.[5] The Imperial Cortes and its deputation (Spanish: Diputación General de Cortes) primarily concerned themselves with overseeing previous agreements and the collection of taxes in Castile and the larger empire; separate deputations oversaw similar work in Aragon and Navarre.[6]
The corteses were able to regain some of their previous powers and influence during the 17th century, as repeated sovereign defaults reduced the monarchy to financial dependency and a series of deputies including the Count-Duke of Olivares oversaw most day-to-day government. Under the young and chronically ill Charles II, the Cortes of Castile was responsible for naming his mother Mariana regent.
Bourbon rule (18th–19th centuries)
During the War of the Spanish Succession, the Bourbon king Philip V suppressed the corteses of Aragon and Valencia in 1707 and those of Catalonia and the Balearic Islands in 1714. Following the Peace of Utrecht, the 1716 Nueva Planta Decrees fully abolished the autonomy of the Crown of Aragon. Philip also acted to repeal or curtail most of the diverse grants of autonomy and privilege (fueros) throughout his kingdom. Navarre was finally merged during the 1833 territorial division of Spain.[7]
Napoleonic Spain and the Three Liberal Years

With both the Bourbon monarchs Charles IV and Ferdinand VII having abdicated their throne and Napoleon Bonaparte having appointed his brother Joseph as the new king, a "Cortes of Cádiz" was convened that claimed sovereignty over Spain and operated as a government-in-exile. The Cortes was the first to act as a single representative body for the entire country and empire, although substitutes had to be chosen from among the people of Cádiz for many regions occupied by the French and unable to send their own delegates. Extremely liberal, the Constitution of 1812 enacted by the Cortes was immediately set aside by Ferdinand upon his restoration in 1814. His conservative policies led to a series of military coups that culminated in Col. Rafael del Riego forcing him to accept a more liberal constitution from 1820–1823, the Trienio Liberal ("Three Liberal Years"). Ferdinand vetoed nearly every law passed during the period and repeatedly asked other nations to invade and restore him to his previous authority. Finally, a French invasion crushed the National Militia and restored absolutist rule in Spain. During the subsequent reaction, many liberals were forced into exile, many—ironically—ending up in France, but generally Ferdinand VII was less strident in his policies through the remainder of his reign.
First Spanish Republic (1873–1874)
When the monarchy was overthrown in 1873, the king was forced into exile. The Senate was abolished because of its royally appointed nature. A republic was proclaimed and the Congress of Deputies members started writing a Constitution, supposedly that of a federal republic, with the power of Parliament being nearly supreme (see parliamentary supremacy, although Spain did not use the Westminster system). However, due to numerous issues, Spain was not ready to become a republic; after several crises the government collapsed, and the monarchy was restored in 1874.
Restoration (1874–1930)
The regime just after the First Republic is called the Bourbon Restoration. It was formally a constitutional monarchy, with the monarch as a rubberstamp to the Cortes' acts but with some reserve powers, such as appointing and dismissing the Prime Minister and appointing senators for the new Senate, remade as an elected House. In practice there was an artificial two-party system called El Turno Pacífico (peaceful rotation) in which elections were informally fixed so the Conservatives and Liberals would have alternating periods as the majority in the Cortes, with other parties restricted to a smaller number of seats.
Soon after the Soviet revolution (1917), the Spanish political parties started polarizing, and the left-wing Communist Party (PCE) and Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) blamed the Government for supposed election fraud in small towns (caciquismo), which was incorrectly supposed to have been wiped out in the 1900s by the failed regenerationist movement. In the meantime, spiralling violence started with the murders of many leaders by both sides. Deprived of those leaders, the regime entered a general crisis, with extreme police measures which led to a dictatorship (1921–1930) during which the Senate was again abolished.
Second Spanish Republic (1931–1939)
The dictatorship, now ruled by Admiral Aznar-Cabañas, called for local elections. The results were overwhelmingly favorable to the monarchist cause nationally, but most provincial capitals and other sizable cities sided heavily with the republicans. This was interpreted as a victory, as the rural results were under the always-present suspicion of caciquismo and other irregularities while the urban results were harder to influence. The King left Spain, and a Republic was declared on April 14, 1931.
The Second Spanish Republic was established as a presidential republic, with a unicameral Parliament and a President of the Republic as the Head of State. Among his powers were the appointment and dismissal of the Prime Minister, either on the advice of Parliament or just having consulted it before, and a limited power to dissolve the Parliament and call for new elections.
The first term was the constituent term charged with creating the new Constitution, with the ex-monarchist leader Niceto Alcalá Zamora as President of the Republic and the left-wing leader Manuel Azaña as Prime Minister. The election gave a majority in the Cortes and thus, the Government, to a coalition between Azaña's party and the PSOE. A remarkable deed is universal suffrage, allowing women to vote, a provision highly criticized by Socialist leader Indalecio Prieto, who said the Republic had been backstabbed. Also, for the second time in Spanish history, some regions were granted autonomous governments within the unitary state. Many on the extreme right rose up with General José Sanjurjo in 1932 against the Government's social policies, but the coup was quickly defeated.
The elections for the second term were held in 1933 and won by the coalition between the Radical Party (center) and the Confederación Española de Derechas Autónomas (CEDA) (right). Initially, only the Radical Party entered the Government, with the parliamentary support of the CEDA. However, in the middle of the term, several corruption scandals (among them the Straperlo and the Nombela affairs) sank the Radical Party and the CEDA entered the Government in 1934. This led to uprisings by some leftist parties that were quickly suffocated. In one of them, the left wing government of Catalonia, which had been granted home rule, formally rebelled against the central government, denying its power. This provoked the dissolution of the Generalitat de Catalunya and the imprisonment of their leaders. The leftist minority in the Cortes then pressed Alcalá Zamora for a dissolution, arguing that the uprising were the consequence of social rejection of the right-wing government. The President, a former monarchist Minister wary of the authoritarianism of the right, dissolved Parliament.
The next election was held in 1936. It was hotly contested, with all parties converging into three coalitions: the leftist Popular Front, the right-winged National Front and a Centre coalition. In the end, the Popular Front won with a small edge in votes over the runner-up National Front, but achieved a solid majority due to the new electoral system introduced by the CEDA government hoping that they would get the edge in votes. The new Parliament then dismissed Alcalá-Zamora and installed Manuel Azaña in his place. During the third term, the extreme polarisation of the Spanish society was more evident than ever in Parliament, with confrontation reaching the level of death threats. The already bad political and social climate created by the long-term left-right confrontation worsened, and many right-wing rebellions were started. Then, in 1936, the Army's failed coup degenerated into the Spanish Civil War, putting an end to the Second Republic.
From November 1936 to October 1937, the Cortes were held at Valencia City Hall, which was still being used for its local purposes at the same time. The building was a target for the Italian Air Force in service of the Nationalist faction, resulting in a bombing in May 1937.[8]
Francoist Spain (1943–1977)
Francisco Franco did not prioritize the creation of a consultative or legislative type of assembly during his rule.[9] In 1942, following the first symptoms of change in the international panorama in favour of the Allied Powers, a law established the Cortes Españolas (Spanish Cortes), a non-democratic chamber made up of more than 400 procuradores (singular procurador). Both the Cortes' founding law and the subsequent regulations were based on the principles of rejection of parliamentarism and political pluralism.[10] Members of the Cortes were not elected and exercised only symbolic power. It had no power over government spending, and the cabinet, appointed and dismissed by Franco alone, retained real legislative authority. In 1967, with the enaction of the Organic Law of the State, the accommodation of "two family representatives per province, elected by those on the electoral roll of family heads and married women" (the so-called tercio familiar) ensued, opening a fraction of the Cortes' composition to some mechanisms of individual participation.[11]
Cortes Generales under the Constitution of 1978
.jpg.webp)

The Cortes are a bicameral parliament composed of a lower house (Congreso de los Diputados, congress of deputies) and an upper house (Senado, senate). Although they share legislative power, the Congress holds the power to ultimately override any decision of the Senate by a sufficient majority (usually an absolute majority or three-fifths majority).
The Congress is composed of 350 deputies (but that figure may change in the future as the constitution establishes a maximum of 400 and a minimum of 300) directly elected by universal suffrage approximately every four years.
The Senate is partly directly elected in that four senators per province are elected as a general rule and partly appointed by the legislative assemblies of the autonomous communities, one for each community and another one for every million inhabitants in their territory. Although the Senate was conceived as a territorial upper house, it has been argued by nationalist parties and the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party that it does not accomplish such a task because 208 out of 265 members of the Senate are elected by popular vote in each province, and only 58 are representatives appointed by the regional legislatures of autonomous communities. Proposals to reform the Senate have been discussed for at least ten years as of November 2007. One of the main themes of reform is to move towards a higher level of federalization and make the Senate a thorough representation of autonomous communities instead of the current system, which tries to incorporate the interests of province and autonomous communities at the same time.
Joint Committees
| Committee | Office | Chair(s) | Term | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relations with the Court of Auditors | deputy | Santos Cerdán León (PSOE) | 2020–present | [12] |
| European Union | deputy | Susana Sumelzo Jordán (PSOE) | 2020–present | [13] |
| Relations with the Ombudsman | deputy | Vicente Tirado Ochoa (PP) | 2020–present | [14] |
| Parliamentary Control of RTVE's Board and its Partnerships | senator | Antonio José Cosculluela Bergua (PSOE) | 2020–present | [15] |
| National Security | deputy | Carlos Aragonés Mendiguchía (PP) | 2020–present | [16] |
| Study of Addictions' Issues | deputy | Francesc Xavier Eritja Ciuró (ERC) | 2020–present | [17] |
| Coordination and Monitoring of the Spanish Strategy to accomplish the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) | deputy | Joan Mena Arca (ECP) | 2020 | [18] |
| deputy | Aina Vidal Saéz (ECP) | 2020–present |
See also
.svg.png.webp) |
|---|
Notes
References
- Article 68.1 and 69.1 of the Constitution of Spain (1978)
- Article 66 of the Constitution of Spain (1978)
- Scott, Samuel Parsons, ed. (1910), The Visigothic Code (Forum Judicum), Boston, MA: Boston Book Co., pp. ix–xxi
- Keane, John (2009), The Life and Death of Democracy, London: Simon & Schuster.
- Haliczer, Stephen (1981), The Comuneros of Castile: The Forging of a Revolution, 1475–1521, Madison, Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin Press, p. 227, ISBN 0-299-08500-7
- García de Cortázar, J.A. (1978), Historia de España (in Spanish), Alfaguara, p. 306, ISBN 8420620408.
- García de Cortázar y Ruiz de Aguirre, José Angel (1976). La época medieval (3 ed.). Madrid: Alfaguara. p. 250. ISBN 84-206-2040-8. OCLC 3315063.
- "Cuando el Ayuntamiento de Valencia fue bombardeado" [When Valencia City Hall was bombed]. El País (in Spanish). 30 May 2017. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- Giménez Martínez 2015, pp. 71–72.
- Giménez Martínez, Miguel Ángel (2015). "Las Cortes de Franco o el Parlamento imposible" (PDF). Trocadero: Revista de historia moderna y contemporánea (27): 73. ISSN 0214-4212.
- Giménez Martínez 2015, p. 75.
- "Current membership of Comisión Mixta para las Relaciones con el Tribunal de Cuentas". Congreso de los Diputados. Archived from the original on 11 September 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- "Current membership of Comisión Mixta para la Unión Europea". Congreso de los Diputados. Archived from the original on 11 September 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2019.
- "Current membership of Comisión Mixta de Relaciones con el Defensor del Pueblo". Congreso de los Diputados. Archived from the original on 11 September 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- "Current membership of Comisión Mixta de Control Parlamentario de la Corporación RTVE y sus Sociedades". Congreso de los Diputados. Archived from the original on 11 September 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- "Current membership of Comisión Mixta de Seguridad Nacional". Congreso de los Diputados. Archived from the original on 11 September 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- "Current membership of Comisión Mixta para el Estudio de los Problemas de las Adicciones". Congreso de los Diputados. Archived from the original on 11 September 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- "Current membership of Comisión Mixta para la Coordinación y Seguimiento de la Estrategia Española para alcanzar los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible (ODS)". Congreso de los Diputados. Archived from the original on 11 September 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
