RAD140
RAD140 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) that is developed by Radius Health, Inc. for use in androgen replacement therapy. It was licensed to Ellipses Pharmaceuticals in 2020.[1][2][3][4] Some of the potential benefits under investigation are for the treatment of conditions such as muscle wasting and bone loss.
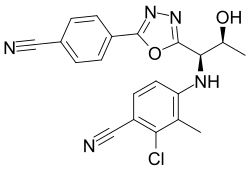 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H16ClN5O2 |
| Molar mass | 393.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Clinical trials
The first-in-human study was initiated in October of 2017 and completed in September 2020 in postmenopausal women with breast cancer. The study investigated oral doses of 50mg or higher. "No clinically significant androgenic effects were observed."[5][6]
In early 2020 a single case report of drug-induced liver injury following use of RAD 140 was published.[7][8]
Animal studies
RAD 140 appears to be safer than testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) in rats.[9]
RAD 140 slightly increased lean muscle mass when used in primates, by targeting androgen receptors in skeletal tissue.[10]
References
- Jayaraman A, Christensen A, Moser VA, Vest RS, Miller CP, Hattersley G, Pike CJ (April 2014). "Selective androgen receptor modulator RAD140 is neuroprotective in cultured neurons and kainate-lesioned male rats". Endocrinology. 155 (4): 1398–406. doi:10.1210/en.2013-1725. PMC 3959610. PMID 24428527.
- Hamson DK, Wainwright SR, Taylor JR, Jones BA, Watson NV, Galea LA (September 2013). "Androgens increase survival of adult-born neurons in the dentate gyrus by an androgen receptor-dependent mechanism in male rats". Endocrinology. 154 (9): 3294–304. doi:10.1210/en.2013-1129. PMID 23782943.
- Miller CP, Shomali M, Lyttle CR, O'Dea LS, Herendeen H, Gallacher K, et al. (February 2011). "Design, Synthesis, and Preclinical Characterization of the Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator (SARM) RAD140". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2 (2): 124–9. doi:10.1021/ml1002508. PMC 4018048. PMID 24900290.
- Yu Z, He S, Wang D, Patel HK, Miller CP, Brown JL, et al. (December 2017). "Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator RAD140 Inhibits the Growth of Androgen/Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Models with a Distinct Mechanism of Action". Clinical Cancer Research. 23 (24): 7608–7620. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0670. PMID 28974548.
- Hamilton E, LoRusso P, Ma C, Vidula N, Bagley RG, Troy S, et al. (2020-02-15). "Abstract P5-11-01 : Phase 1 dose escalation study of a novel selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), RAD140, in estrogen receptor positive (ER ), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative (HER2-), metastatic breast cancer". Cancer Research. 80 (4 Supplement): P5–11–01. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.sabcs19-p5-11-01. S2CID 216326672.
- Clinical trial number NCT03088527 for "Phase 1, First-in-Human Study of RAD140 in Postmenopausal Women With Breast Cancer" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Flores JE, Chitturi S, Walker S (March 2020). "Drug-Induced Liver Injury by Selective Androgenic Receptor Modulators". Hepatology Communications. 4 (3): 450–452. doi:10.1002/hep4.1456. PMC 7049679. PMID 32140660.
- RAD 140 Testolone
- Jayaraman A, Christensen A, Moser VA, Vest RS, Miller CP, Hattersley G, Pike CJ (April 2014). "Selective androgen receptor modulator RAD140 is neuroprotective in cultured neurons and kainate-lesioned male rats". Endocrinology. 155 (4): 1398–406. doi:10.1210/en.2013-1725. PMC 3959610. PMID 24428527.
- Miller CP, Shomali M, Lyttle CR, O'Dea LS, Herendeen H, Gallacher K, et al. (February 2011). "Design, Synthesis, and Preclinical Characterization of the Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator (SARM) RAD140". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2 (2): 124–9. doi:10.1021/ml1002508. PMC 4018048. PMID 24900290.