Synovial bursa
A synovial bursa (plural bursae or bursas) is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of viscous synovial fluid (similar in consistency to that of a raw egg white). It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement. Bursae are found around most major joints of the body.
| Synovial bursa | |
|---|---|
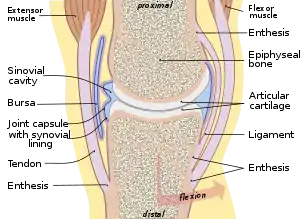 Typical joint | |
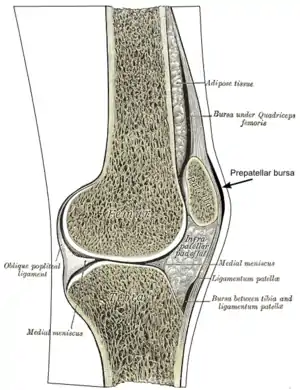 Within the knee joint: bursae visible top right, middle right and bottom right | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | bursa synovialis |
| MeSH | D002061 |
| TA98 | A03.0.00.039 A04.8.01.004 |
| TA2 | 2028 |
| TH | H3.03.00.0.00039 |
| FMA | 9692 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
There are four types of bursa: adventitious, subcutaneous, synovial, and sub-muscular. Among these, only adventitious is non-native. When any surface of the body is subjected to repeated stress, an adventitious bursa develops under it. Examples are Students' elbow and bunion.
Clinical significance
Infection or irritation of a bursa leads to bursitis (inflammation of a bursa). The general term for disease of bursae is "bursopathy."
History
Etymology
Bursa is Medieval Latin for "purse", so named for the resemblance of an anatomical bursa to a purse. Bursae or bursas is its plural form.
See also
- Bursa of Fabricius (a lymphatic organ in birds)
- Bursectomy
- Knee bursae
- Shoulder joint#Bursae
External links
- Hirji, Zameer; Hunjun, Jaspal S; Choudur, Hema N (2 May 2011). "Imaging of the Bursae". Journal of Clinical Imaging Science. 1: 22. doi:10.4103/2156-7514.80374. PMC 3177464. PMID 21966619.
- Bursa
- Diagram of elbow with olecranon bursa