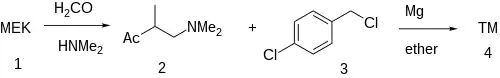Clobutinol
Clobutinol is a cough suppressant formerly distributed by Boehringer Ingelheim and its licensees under the names Lomisat and Silomat, by Bioter as Biotussin, and by Violani-Farmavigor as Pertoxil. It has been withdrawn from the market worldwide.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Biotussin, Lomisat, Pertoxil, Silomat |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.373 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H22ClNO |
| Molar mass | 255.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Side effects and withdrawal
Side effects include drozwsiness, dizziness, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort.[1] Studies in 2004 had indicated that clobutinol has the potential to prolong the QT interval.[2] Clobutinol was in 2007 determined to cause cardiac arrhythmia in some patients.[3]
Boehringer Ingelheim products containing clobutinol were voluntarily withdrawn from sale in Germany, and the rest of the world, on August 31, 2007.[4]
The approval for Germany and the EU was revoked in 2008.[5]
Prior to withdrawal, it was available throughout Europe and Central America, as well as in South Africa. Trade names include Biotussin, Lomisat (Spain), Pertoxil (Italy), and in most of the world, Silomat.[6]
Synthesis
The Mannich reaction of 2-butanone (1) with formaldehyde and dimethylamine gives 4-Dimethylamino-3-methyl-2-butanone [22104-62-7] (2). Grignard reaction with 4-chlorobenzylchloride [104-83-6] (3) afforded clobutinol (4).
See also
References
- Schlesser JL (1991). Drugs Available Abroad, 1st Edition. Derwent Publications Ltd. p. 29. ISBN 0-8103-7177-4.
- Bellocq C, Wilders R, Schott JJ, Louérat-Oriou B, Boisseau P, Le Marec H, et al. (November 2004). "A common antitussive drug, clobutinol, precipitates the long QT syndrome 2". Molecular Pharmacology. 66 (5): 1093–102. doi:10.1124/mol.104.001065. PMID 15280442.
-
"Clobutinol-haltige Arzneimittel: BfArM ordnet Widerruf der Zulassung an". BfArM (German Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices). 2007-08-31. Archived from the original on 2012-04-01.
Clobutinol: BfArM orders cancellation of approval
- "Boehringer Ingelheim voluntarily withdraws its clobutinol containing medications". Boehringer Ingelheim. 2007-08-31. Archived from the original on 2012-01-27.
-
"Cancellation of approval" (PDF). BfArM (German Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices). 2008-06-06. Archived from the original (pdf) on 2012-04-01.
Die Zulassungen für die o.g. Arzneimittel werden mit sofortiger Wirkung widerrufen.
- Schlesser JL (1991). Drugs Available Abroad, 1st Edition. Derwent Publications Ltd. p. 29. ISBN 0-8103-7177-4.
- GB898010 idem Alex Berg, U.S. Patent 3,121,087 (1962, 1964 both to Thomae).
- Dipl-Chem Dr Alex Berg, DE 1153380 (1963 to Thomae GmbH Dr K).