Guanoclor
Guanoclor (INN), also known as guanochlor, is a sympatholytic drug. It is known to bind to non-adrenergic sites in pig kidney membranes.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.334 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H12Cl2N4O |
| Molar mass | 263.12 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Synthesis
When β-(2,6-dichlorophenoxy)ethyl bromide (1) is reacted with hydrazine to give 2, and this is reacted with S-methylthiourea, guanochlor (3) results.[2][3]
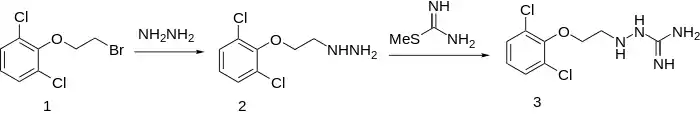
Guanoclor synthesis
References
- Vigne P, Lazdunski M, Frelin C (January 1989). "Guanabenz, guanochlor, guanoxan and idazoxan bind with high affinity to non-adrenergic sites in pig kidney membranes". European Journal of Pharmacology. 160 (2): 295–8. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(89)90503-7. PMID 2527160.
- Durant GJ, Smith GM, Spickett RG, Wright SH (January 1966). "Biologically active guanidines and related compounds. II. Some antiinflammatory aminoguanidines". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 9 (1): 22–7. doi:10.1021/jm00319a005. PMID 5958955.
- Prepn of free base and sulfate: BE 629613 (1963 to Pfizer), C.A. 60, 14437d (1964).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.