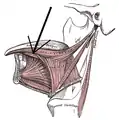
Inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue
The inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue. It is situated on the under surface of the tongue between the genioglossus and hyoglossus. It helps to move the tongue.
| Inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue | |
|---|---|
 Coronal section of tongue, showing intrinsic muscles. | |
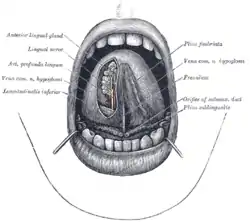 The mouth cavity. (Longitudinalis inferior labeled at bottom left.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | root of tongue |
| Insertion | apex of tongue |
| Nerve | hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) |
| Actions | retracts tongue with superior longitudinal muscle, making tongue short and thick |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus longitudinalis inferior linguae |
| TA98 | A05.1.04.107 |
| TA2 | 2123 |
| FMA | 46694 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
Structure
The inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue.[1] It extends from the root to the apex of the tongue. Behind, some of its fibers are connected with the body of the hyoid bone. In front, it blends with the fibers of styloglossus.
Nerve supply
The inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue is supplied by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII).[2]
Function
The inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue moves the tongue.[1] Movement of material through the pharynx is dependent upon the coordinated activity of the longitudinal and smooth muscle of the gut.
Additional images
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1130 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1130 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Aggarwal, Annu; Thompson, Philip D. (2011). "44 - Unusual focal dyskinesias". Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Elsevier. pp. 617–628. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-52014-2.00044-6. ISBN 978-0-444-52014-2. ISSN 0072-9752.
- Love, Russell J.; Webb, Wanda G. (1992). "7 - The Cranial Nerves". Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 112–136. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7506-9076-8.50013-7. ISBN 978-0-7506-9076-8.