Transverse muscle of tongue
The transverse muscle of tongue (transversus linguae) is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue. It consists of fibers which arise from the median fibrous septum. It passes laterally to insert into the submucous fibrous tissue at the sides of the tongue. It is supplied by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII). It moves the tongue.
| Transverse muscle of tongue | |
|---|---|
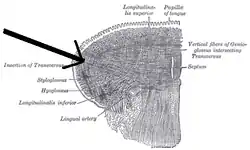 Coronal section of tongue, showing intrinsic muscles. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | median fibrous septum |
| Insertion | sides of the tongue |
| Nerve | hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) |
| Actions | makes the tongue narrow and elongated |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus transversus linguae |
| TA98 | A05.1.04.108 |
| TA2 | 2124 |
| FMA | 46695 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
Structure
The transverse muscle of the tongue is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue.[1] It consists of fibers which arise from the median fibrous septum. It passes laterally to insert into the submucous fibrous tissue at the sides of the tongue.
Nerve supply
The transverse lingual muscle is supplied by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII).[2]
Function
The transverse muscle of the tongue muscle moves the tongue.[1] It narrows and elongates it.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1130 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1130 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Aggarwal, Annu; Thompson, Philip D. (2011). "44 - Unusual focal dyskinesias". Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Elsevier. pp. 617–628. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-52014-2.00044-6. ISBN 978-0-444-52014-2. ISSN 0072-9752.
- Love, Russell J.; Webb, Wanda G. (1992). "7 - The Cranial Nerves". Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 112–136. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7506-9076-8.50013-7. ISBN 978-0-7506-9076-8.