Maralixibat chloride
Maralixibat chloride, sold under the brand name Livmarli, is a medication used to treat cholestatic pruritus in people with Alagille syndrome.[1] Maralixibat chloride is an ileal bile acid transporter (IBAT) inhibitor.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Livmarli |
| Other names | LUM001 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Ileal bile acid transporter (IBAT) inhibitor |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
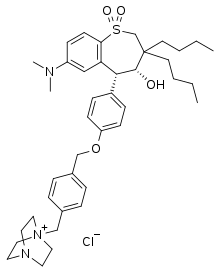
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C40H56ClN3O4S |
| Molar mass | 710.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Maralixibat was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2021.[1][2][3]
History
Maralixibat was granted orphan drug designations in 2013,[4][5] and in 2020.[6]
Society and culture
Legal status
On 13 October 2022, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances for the medicinal product Livmarli, intended for the treatment of cholestatic pruritus in patients with Alagille syndrome (ALGS).[7] The applicant for this medicinal product is Mirum Pharmaceuticals International B.V.[7]
Names
Maralixibat chloride is the international nonproprietary name (INN).[8]
References
- "Livmarli- maralixibat chloride solution". DailyMed. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- "Maralixibat: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- "U.S. FDA Approves Livmarli (maralixibat) as the First and Only Approved Medication for the Treatment of Cholestatic Pruritus in Patients with Alagille Syndrome One Year of Age and Older". Mirum Pharmaceuticals (Press release). 29 September 2021. Retrieved 29 September 2021 – via Business Wire.
- "Maralixibat Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 4 September 2013. Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- "Maralixibat Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 4 September 2013. Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- "Maralixibat Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 21 October 2020. Retrieved 29 September 2021.
- "Livmarli: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency. 14 October 2022. Retrieved 15 October 2022. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- World Health Organization (2016). "International nonproprietary names for pharmaceutical substances (INN): recommended INN: list 75". WHO Drug Information. 30 (1). hdl:10665/331046.
External links
- "Maralixibat". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Maralixibat chloride". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Clinical trial number NCT02160782 for "Safety and Efficacy Study of LUM001 (Maralixibat) With a Drug Withdrawal Period in Participants With Alagille Syndrome (ALGS) (ICONIC)" at ClinicalTrials.gov