Treponema
Treponema is a genus of spiral-shaped bacteria. The major treponeme species of human pathogens is Treponema pallidum, whose subspecies are responsible for diseases such as syphilis, bejel, and yaws. Treponema carateum is the cause of pinta.[2] Treponema paraluiscuniculi is associated with syphilis in rabbits.[3] Treponema succinifaciens has been found in the gut microbiome of traditional rural human populations.[4]
| Treponema | |
|---|---|
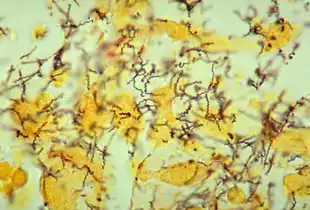 | |
| Treponema pallidum spirochaetes | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Spirochaetota |
| Class: | Spirochaetia |
| Order: | Spirochaetales |
| Family: | Treponemataceae |
| Genus: | Treponema Schaudinn 1905 emend. Abt, Göker & Klenk 2013 |
| Type species | |
| Treponema pallidum (Schaudinn & Hoffmann 1905) Schaudinn 1905 | |
| Species[1] | |
See text | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Phylogeny
The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)[5] and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).[6]
| 16S rRNA based LTP_12_2021[7][8][9] | GTDB 07-RS207 by Genome Taxonomy Database[10][11][12] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Unassigned species:
- Treponema calligyrum Noguchi 1913
- Treponema carateum Brumpt 1939 (pinta-causing Treponema)
- "Ca. Treponema faecavium" Gilroy et al. 2021
- Treponema paraluisleporis Lumeij et al. 1994
- Treponema paraluiscuniculi ♦ (Jacobsthal 1920) Smibert 1974
- Treponema pertenue ♦ (Castellani 1905) Castellani & Chalmers 1910
- "Ca. Treponema suis" Molbak et al. 2006
- Treponema refringens (Schaudinn and Hofmann 1905) Castellani and Chalmers
- "Treponema scoliodonta" (Hoffmann 1920) Noguchi 1928 ex Smibert 1984
- "Ca. Treponema teratonymphae" Noda et al. 2018
Notes:
♦ Type strain lost or not available
The species Treponema hyodysenteriae and Treponema innocens have been reclassified into Serpulina hyodysenteriae and Serpulina innocens.[13]
References
- "Treponema". NCBI taxonomy. Bethesda, MD: National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- Antal GM, Lukehart SA, Meheus AZ (January 2002). "The endemic treponematoses". Microbes Infect. 4 (1): 83–94. doi:10.1016/S1286-4579(01)01513-1. PMID 11825779.
- Harper KN, Liu H, Ocampo PS, et al. (August 2008). "The sequence of the acidic repeat protein (arp) gene differentiates venereal from nonvenereal Treponema pallidum subspecies, and the gene has evolved under strong positive selection in the subspecies that causes syphilis". FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 53 (3): 322–32. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00427.x. PMID 18554302.
- Angelakis E, Bachar D, Yasir M, Musso D, Djossou F, Gaborit B, et al. (January 2019). "Treponema species enrich the gut microbiota of traditional rural populations but are absent from urban individuals". New Microbes and New Infections. 27: 14–21. doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2018.10.009. PMC 6276622. PMID 30555706.
- J.P. Euzéby. "Treponema". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Retrieved 2016-03-20.
- Sayers; et al. "Treponema". National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy database. Retrieved 2016-03-20.
- "The LTP". Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- "LTP_all tree in newick format". Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- "LTP_12_2021 Release Notes" (PDF). Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- "GTDB release 07-RS207". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- "ar53_r207.sp_label". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- "Taxon History". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- Stanton TB, Jensen NS, Casey TA, Tordoff LA, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ (January 1991). "Reclassification of Treponema hyodysenteriae and Treponema innocens in a new genus, Serpula gen. nov., as Serpula hyodysenteriae comb. nov. and Serpula innocens comb. nov". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 41 (1): 50–8. doi:10.1099/00207713-41-1-50. PMID 1704792.