Odevixibat
Odevixibat, sold under the trade name Bylvay, is a medication for the treatment of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC).[1][4] It is taken by mouth.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Bylvay |
| Other names | A4250 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
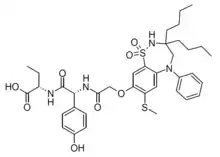
| Formula | C37H48N4O8S2 |
| Molar mass | 740.93 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
The most common side effects include diarrhea, abdominal pain, hemorrhagic diarrhea, soft feces, and hepatomegaly (enlarged liver).[4]
Odevixibat is a reversible, potent, selective inhibitor of the ileal bile acid transporter (IBAT).[4][5][6]
Odevixibat was approved for medical use in the United States and in the European Union in July 2021.[1][2][3][7][8]
Medical uses
In the United States, odevixibat is indicated for the treatment of pruritus in people three months of age and older with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC).[1] In the European Union it is indicated in people six months of age and older.[2][3]
Mechanism of action
Odevixibat is a reversible inhibitor of the ileal sodium/bile acid transporter which is the transporter responsible for reabsorption of the majority of bile acids in the distal ileum. [9] The reduced absorption of the bile acids in the distal ileum compounds and leads to a decrease in stimulation of FXR, decreasing the inhibition of bile acid synthesis.[10]
Pharmacokinetics
Odevixibat is majorly protein-bound in-vitro. [10] A dose of Odevixibat that is 7.2 mg reaches a Cmax concentration of 0.47 ng/mL with an AUC (0-24h) of 2.19 h*ng/mL. [11] Adult and pediatric patients given the therapeautic dose of Odevixibat did not display plasma concentrations of the drug. [8] Odevixibat is eliminated majorly unchanged. [11] Odevixibat has an average half-life of 2.36 hours.[10]
Adverse effects
Common side effects of Odevixibat include diarrhea, stomach pain, vomiting, abnormal liquid function tests, and a deficiency in vitamins A,D, E and K. [10]
Contraindications
Odevixibat cannot be given to a child on a liquid diet. [11]
Society and culture
Legal status
In May 2021, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) recommended granting a marketing authorization in the European Union for odevixibat for the treatment of PFIC in people aged six months or older.[4][12] It was approved for medical use in the European Union in July 2021.[2][3]
References
- "Bylvay- odevixibat capsule, coated pellets". DailyMed. Retrieved 28 July 2021.
- "Bylvay EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 20 April 2021. Retrieved 28 July 2021.
- "Bylvay". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 23 July 2021.
- "First treatment for rare liver disease". European Medicines Agency (EMA) (Press release). 21 May 2021. Retrieved 21 May 2021. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- "Odevixibat". Albireo Pharma. Retrieved 21 May 2021.
- Karpen SJ, Kelly D, Mack C, Stein P (September 2020). "Ileal bile acid transporter inhibition as an anticholestatic therapeutic target in biliary atresia and other cholestatic disorders". Hepatology International. 14 (5): 677–689. doi:10.1007/s12072-020-10070-w. PMID 32653991. S2CID 220481607.
- "Odevixibat: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 23 July 2021.
- "Albireo Announces FDA Approval of Bylvay (odevixibat), the First Drug Treatment for Patients With Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis (PFIC)". Albireo Pharma (Press release). 20 July 2021. Retrieved 23 July 2021 – via GlobeNewswire.
- "Odevixibat". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- "Odevixibat Uses, Side Effects & Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- "Odevixibat Uses, Side Effects & Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- "Bylvay: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 19 May 2021. Retrieved 21 May 2021.
External links
- "Odevixibat". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Clinical trial number NCT03566238 for "This Study Will Investigate the Efficacy and Safety of A4250 in Children With PFIC 1 or 2 (PEDFIC 1)" at ClinicalTrials.gov