Omenn syndrome
Omenn syndrome is an autosomal recessive severe combined immunodeficiency.[1] It is associated with hypomorphic missense mutations in immunologically relevant genes of T-cells (and B-cells) such as recombination activating genes (RAG1 and RAG2), Interleukin-7 receptor-α (IL7Rα), DCLRE1C-Artemis, RMRP-CHH, DNA-Ligase IV, common gamma chain, WHN-FOXN1, ZAP-70 and complete DiGeorge syndrome. It is fatal without treatment.
| Omenn syndrome | |
|---|---|
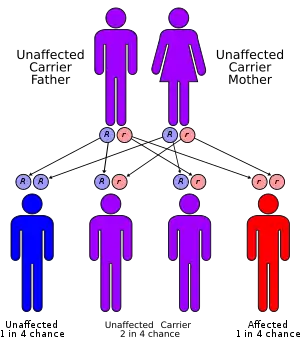 | |
| Omenn syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. | |
| Specialty | Hematology |
Symptoms and signs

The symptoms are very similar to graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). This is because the patients have some T cells with limited levels of recombination with the mutant RAG genes. These T cells are abnormal and have a very specific affinity for self antigens found in the thymus and in the periphery. Therefore, these T cells are auto-reactive and cause the GVHD phenotype.
A characteristic symptom is chronic inflammation of the skin, which appears as a red rash[2] (early onset erythroderma). Other symptoms include eosinophilia, failure to thrive, swollen lymph nodes, swollen spleen, diarrhea, enlarged liver, low immunoglobulin levels (except immunoglobulin E, which is elevated), low T cell levels, and no B cells.[3]
Genetics
Omenn syndrome is caused by a partial loss of RAG gene function and leads to symptoms similar to severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome, including opportunistic infections. The RAG genes are essential for gene recombination in the T-cell receptor and B-cell receptor, and loss of this ability means that the immune system has difficulty recognizing specific pathogens.[2] Omenn Syndrome is characterised by the loss of T-cell function, leading to engraftment of maternal lymphocytes in the foetus and the co-existence of clonally expanded autologous and transplacental-acquired maternal lymphocytes.[4] Omenn syndrome can occasionally be caused in other recombination genes, including IL-7Rα and RMRP.[3]
Diagnosis
In order to diagnose a patient specifically with Omenn Syndrome, an autosomal recessive form of SCID, a physician can order a genetic testing panel to look for 22q11 microdeletions or mutations of the RAG1/RAG2 genes.[5]
Treatment
The only treatment for Omenn syndrome is chemotherapy followed by a bone marrow transplantation.[3] Without treatment, it is rapidly fatal in infancy.[2]
References
- Santagata S, Villa A, Sobacchi C, Cortes P, Vezzoni P (2000). "The genetic and biochemical basis of Omenn syndrome". Immunol Rev. 178: 64–74. doi:10.1034/j.1600-065X.2000.17818.x. PMID 11213808. S2CID 32270945.
- Parham, Peter (2009). The Immune System (3rd ed.). Taylor & Francis Group. p. 128. ISBN 9781136977107.
- Geha, Raif; Notarangelo, Luigi (2012). Case Studies in Immunology: A Clinical Companion (6th ed.). Garland Science. ISBN 978-0-8153-4441-4.
- Lev A, Simon AJ, Ben-Ari J, Takagi D, Stauber T, Trakhtenbrot L, Rosenthal E, Rechavi G, Amariglio N, Somech R (2014). "Co-existence of clonal expanded autologous and transplacental-acquired maternal T cells in recombination activating gene-deficient severe combined immunodeficiency". Clin Exp Immunol. 176 (3): 380–6. doi:10.1111/cei.12273. PMC 4008982. PMID 24666246.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (last updated 2016). Omenn Syndrome. Retrieved from: https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/8198/omenn-syndrome