Prothionamide
Protionamide (or prothionamide) is a drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.615 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
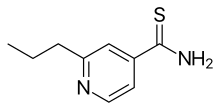
| Formula | C9H12N2S |
| Molar mass | 180.27 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
It has also been tested for use in the treatment of leprosy.[2]
References
- Wang F, Langley R, Gulten G, et al. (January 2007). "Mechanism of thioamide drug action against tuberculosis and leprosy". J. Exp. Med. 204 (1): 73–8. doi:10.1084/jem.20062100. PMC 2118422. PMID 17227913.
- Fajardo TT, Guinto RS, Cellona RV, Abalos RM, Dela Cruz EC, Gelber RH (March 2006). "A clinical trial of ethionamide and prothionamide for treatment of lepromatous leprosy". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 74 (3): 457–61. PMID 16525107.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.