Ventral posterior nucleus
The ventral posterior nucleus is the somato-sensory relay nucleus in thalamus of the brain.
| Ventral posterior nucleus | |
|---|---|
 Thalamic nuclei: MNG = Midline nuclear group AN = Anterior nuclear group MD = Medial dorsal nucleus VNG = Ventral nuclear group VA = Ventral anterior nucleus VL = Ventral lateral nucleus VPL = Ventral posterolateral nucleus VPM = Ventral posteromedial nucleus LNG = Lateral nuclear group PUL = Pulvinar MTh = Metathalamus LG = Lateral geniculate nucleus MG = Medial geniculate nucleus | |
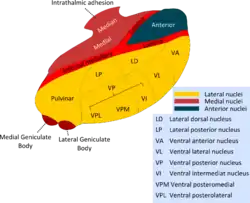 Thalamic nuclei | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Thalamus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nucleus ventralis posterior thalami |
| NeuroNames | 343 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1116 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Input and output
The ventral posterior nucleus receives neuronal input from the medial lemniscus, spinothalamic tracts, and trigeminothalamic tract. It projects to the somatosensory cortex and the ascending reticuloactivation system.
Subdivisions
The ventral posterior nucleus is divided into:
- Ventral posterolateral nucleus, which receives sensory information from the body.
- Ventral posteromedial nucleus, which receives sensory information from the head and face via the trigeminal nerve.
- Ventral intermediate nucleus, implicated in oscillatory tremor generation in Parkinson's disease and essential tremor.[1]
Function
Functions in touch, body position, pain, temperature, itch, taste, and arousal. Modulates tremor in certain pathology.
Additional images
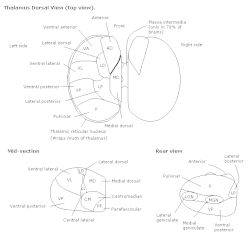 Thalamus
Thalamus Thalamus
Thalamus
References
- Deiber, MP (1993). "Thalamic stimulation and suppression of parkinsonian tremor". Brain. 116 (1): 267–79. doi:10.1093/brain/116.1.267. PMID 8453462.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.