Bongo (antelope)
The bongo (Tragelaphus eurycerus) is a herbivorous, mostly nocturnal forest ungulate. Bongos are characterised by a striking reddish-brown coat, black and white markings, white-yellow stripes and long slightly spiralled horns. They are the only tragelaphid in which both sexes have horns. They have a complex social interaction and are found in African dense forest mosaics. Native to Africa, they are the third-largest antelope in the world.[3]
| Bongo | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Western/lowland bongo at the Marwell Zoo in Hampshire, England | |
 | |
| An eastern/mountain bongo at the Jacksonville Zoo, Jacksonville, Duval County | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Bovinae |
| Genus: | Tragelaphus |
| Species: | T. eurycerus |
| Binomial name | |
| Tragelaphus eurycerus (Ogilby, 1837) | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
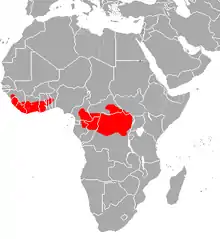 | |
| Lowland bongo range | |
 | |
| Mountain bongo range | |
The western or lowland bongo, T. e. eurycerus, faces an ongoing population decline, and the IUCN Antelope Specialist Group considers it to be Near Threatened on the conservation status scale.[2]
The eastern or mountain bongo, T. e. isaaci, of Kenya, has a coat even more vibrant than that of T. e. eurycerus. The mountain bongo is only found in the wild in a few mountain regions of central Kenya. This bongo is classified by the IUCN Antelope Specialist Group as Critically Endangered, with fewer individuals in the wild than in captivity (where it breeds readily).[4]
In 2000, the Association of Zoos and Aquariums in the USA (AZA) upgraded the bongo to a Species Survival Plan participant and in 2006 added the Bongo Restoration to Mount Kenya Project to its list of the Top Ten Wildlife Conservation Success Stories of the year. However, in 2013, it seems, these successes have been compromised by reports of possibly only 100 mountain bongos left in the wild due to logging and poaching.
Taxonomy
The scientific name of the bongo is Tragelaphus eurycerus, and it belongs to the genus Tragelaphus and family Bovidae. It was first described by Irish naturalist William Ogilby in 1837.[5] The generic name Tragelaphus is composed of two Greek words: trag-, meaning a goat; and elaphos, meaning deer.[6] The specific name eurycerus originated from the fusion of eurus (broad, widespread) and keras (an animal's horn).[7] The common name "bongo" originated probably from the Kele language of Gabon. The first known use of the name "bongo" in English dates to 1861.[8]
Bongos are further classified into two subspecies: T. e. eurycerus, the lowland or western bongo, and the far rarer T. e. isaaci, the mountain or eastern bongo, restricted to the mountains of Kenya only. The eastern bongo is larger and heavier than the western bongo. Two other subspecies are described from West and Central Africa, but taxonomic clarification is required. They have been observed to live up to 19 years.[9]
Appearance

Bongos are one of the largest of the forest antelopes. In addition to the deep chestnut colour of their coats, they have bright white stripes on their sides to help with camouflage.
Adults of both sexes are similar in size. Adult height is about 1.1 to 1.3 m (3.6 to 4.3 ft) at the shoulder and length is 2.15 to 3.15 m (7.1 to 10.3 ft), including a tail of 45–65 cm (18–26 in). Females weigh around 150–235 kg (331–518 lb), while males weigh about 220–405 kg (485–893 lb). Its large size puts it as the third-largest in the Bovidae tribe of Strepsicerotini, behind both the common and greater elands by about 300 kg (660 lb), and above the greater kudu by about 40 kg (88 lb).[10][11]
Both sexes have heavy spiral horns; those of the male are longer and more massive. All bongos in captivity are from the isolated Aberdare Mountains of central Kenya.
Coat and body

The bongo sports a bright auburn or chestnut coat, with the neck, chest, and legs generally darker than the rest of the body. Coats of male bongos become darker as they age until they reach a dark mahogany-brown colour. Coats of female bongos are usually more brightly coloured than those of males. The eastern bongo is darker in color than the western and this is especially pronounced in older males which tend to be chestnut brown, especially on the forepart of their bodies.
The pigmentation in the coat rubs off quite easily; anecdotal reports suggest rain running off a bongo may be tinted red with pigment. The smooth coat is marked with 10–15 vertical white-yellow stripes, spread along the back from the base of the neck to the rump. The number of stripes on each side is rarely the same. It also has a short, bristly, brown ridge of dorsal hair from the shoulder to the rump; the white stripes run into this ridge.
A white chevron appears between the eyes, and two large white spots grace each cheek. Another white chevron occurs where the neck meets the chest. The large ears are to sharpen hearing, and the distinctive coloration may help bongos identify one another in their dark forest habitats. Bongos have no special secretion glands, so rely less on scent to find one another than do other similar antelopes. The lips of a bongo are white, topped with a black muzzle.
Horns

Bongos have two heavy and slightly spiralled horns that slope over their backs, and like many other antelope species, both male and female bongos have horns. Bongos are the only tragelaphids in which both sexes have horns. The horns of bongos are in the form of a lyre and bear a resemblance to those of the related antelope species of nyalas, sitatungas, bushbucks, kudus and elands.
Unlike deer, which have branched antlers shed annually, bongos and other antelopes have pointed horns they keep throughout their lives. Males have massive backswept horns, while females have smaller, thinner, and more parallel horns. The size of the horns range between 75 and 99 cm (29.5 and 39 in). The horns twist once.
Like all other horns of antelopes, the core of a bongo's horn is hollow and the outer layer of the horn is made of keratin, the same material that makes up human fingernails, toenails and hair. The bongo runs gracefully and at full speed through even the thickest tangles of lianas, laying its heavy spiralled horns on its back so the brush cannot impede its flight. Bongos are hunted for their horns by humans.[12]
Social organization and behavior

Like other forest ungulates, bongos are seldom seen in large groups. Males, called bulls, tend to be solitary, while females with young live in groups of six to eight. Bongos have seldom been seen in herds of more than 20. Gestation is about 285 days (9.5 months), with one young per birth, and weaning occurs at six months. Sexual maturity is reached at 24–27 months. The preferred habitat of this species is so dense and difficult to operate in, that few Europeans or Americans observed this species until the 1960s. As young males mature and leave their maternal groups, they most often remain solitary, although rarely they join an older male. Adult males of similar size/age tend to avoid one another. Occasionally, they meet and spar with their horns in a ritualised manner and it is rare for serious fights to take place. However, such fights are usually discouraged by visual displays, in which the males bulge their necks, roll their eyes, and hold their horns in a vertical position while slowly pacing back and forth in front of the other male. They seek out females only during mating time.[13] When they are with a herd of females, males do not coerce them or try to restrict their movements as do some other antelopes.
Although mostly nocturnal, they are occasionally active during the day. However, like deer, bongos may exhibit crepuscular behaviour.[14] Bongos are both timid and easily frightened; after a scare, a bongo moves away at considerable speed, even through dense undergrowth. Once they find cover, they stay alert and face away from the disturbance, but peek every now and then to check the situation.[9] The bongo's hindquarters are less conspicuous than the forequarters, and from this position the animal can quickly flee.
When in distress, the bongo emits a bleat. It uses a limited number of vocalisations, mostly grunts and snorts; females have a weak mooing contact-call for their young. Females prefer to use traditional calving grounds restricted to certain areas, while newborn calves lie in hiding for a week or more, receiving short visits by the mother to suckle.[15]
The calves grow rapidly and can soon accompany their mothers in the nursery herds. Their horns grow rapidly and begin to show in 3.5 months. They are weaned after six months and reach sexual maturity at about 20 months.
Ecology
Distribution and habitat
Bongos are found in tropical jungles with dense undergrowth up to an altitude of 4,000 meters (13,000 feet) in Central Africa, with isolated populations in Kenya, and these West African countries: Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone, South Sudan.

Historically, bongos are found in three disjunct parts of Africa: East, Central and West. Today, all three populations' ranges have shrunk in size due to habitat loss for agriculture and uncontrolled timber cutting, as well as hunting for meat.
Bongos favour disturbed forest mosaics that provide fresh, low-level green vegetation. Such habitats may be promoted by heavy browsing by elephants, fires, flooding, tree-felling (natural or by logging), and fallowing. Mass bamboo die-off provides ideal habitat in East Africa. They can live in bamboo forests.
Diet

Like many forest ungulates, bongos are herbivorous browsers and feed on leaves, bushes, vines, bark and pith of rotting trees, grasses/herbs, roots, cereals, and fruits.
Bongos require salt in their diets, and are known to regularly visit natural salt licks. Bongos are also known to eat burnt wood after a storm, as a rich source of salt and minerals.[16][17] This behavior is believed to be a means of getting salts and minerals into their diets. This behavior has also been reported in the okapi. Another similarity to the okapi, though the bongo is unrelated, is that the bongo has a long prehensile tongue which it uses to grasp grasses and leaves.
Suitable habitats for bongos must have permanent water available.[18] As a large animal, the bongo requires an ample amount of food, and is restricted to areas with abundant year-round growth of herbs and low shrubs.
Population and conservation
Few estimates of population density are available. Assuming average population densities of 0.25 animals per km2 in regions where it is known to be common or abundant, and 0.02 per km2 elsewhere, and with a total area of occupancy of 327,000 km2, a total population estimate of around 28,000 is suggested. Only about 60% are in protected areas, suggesting the actual numbers of the lowland subspecies may only be in the low tens of thousands. In Kenya, their numbers have declined significantly and on Mount Kenya, they were extirpated within the last decade due to illegal hunting with dogs. Although information on their status in the wild is lacking, lowland bongos are not presently considered endangered.
Bongos are susceptible to diseases such as rinderpest, which almost exterminated the species during the 1890s. Tragelaphus eurycerus may suffer from goitre. Over the course of the disease, the thyroid glands greatly enlarge (up to 10 x 20 cm) and may become polycystic. Pathogenesis of goiter in the bongo may reflect a mixture of genetic predisposition coupled with environmental factors, including a period of exposure to a goitrogen.[19] Leopards and spotted hyenas are the primary natural predators (lions are seldom encountered due to differing habitat preferences); pythons sometimes eat bongo calves. Humans prey on them for their pelts, horns, and meat, with the species being a common local source for "bush meat".[5] Bongo populations have been greatly reduced by hunting, poaching, and animal trapping, although some bongo refuges exist.
Although bongos are quite easy for humans to catch using snares, many people native to the bongos' habitat believed that if they ate or touched bongo, they would have spasms similar to epileptic seizures. Because of this superstition, bongos were less harmed in their native ranges than expected. However, these taboos are said no longer to exist, which may account for increased hunting by humans in recent times.
Zoo programmes

An international studbook is maintained to help manage animals held in captivity. Because of its bright colour, it is very popular in zoos and private collections. In North America, over 400 individuals are thought to be held, a population that probably exceeds that of the mountain bongo in the wild.
In 2000, the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) upgraded the bongo to a Species Survival Plan participant, which works to improve the genetic diversity of managed animal populations. The target population for participating zoos and private collections in North America is 250 animals. Through the efforts of zoos in North America, a reintroduction to the population in Kenya is being developed.
At least one collaborative effort for reintroduction between North American wildlife facilities has already been carried out. In 2004, 18 eastern bongos born in North American zoos gathered at White Oak Conservation in Yulee, Florida for release in Kenya. White Oak staff members traveled with the bongos to a Mount Kenya holding facility, where they stayed until being reintroduced.[20]
Conservation
In the last few decades, a rapid decline in the numbers of wild mountain bongo has occurred due to poaching and human pressure on their habitat, with local extinctions reported in Cherangani and Chepalungu hills, Kenya.
The Bongo Surveillance Programme, working alongside the Kenya Wildlife Service, have recorded photos of bongos at remote salt licks in the Aberdare Forests using camera traps, and, by analyzing DNA extracted from dung, have confirmed the presence of bongo in Mount Kenya, Eburru and Mau forests. The programme estimate as few as 140 animals left in the wild – spread across four isolated populations. Whilst captive breeding programmes can be viewed as having been successful in ensuring survival of this species in Europe and North America, the situation in the wild has been less promising. Evidence exists of bongo surviving in Kenya. However, these populations are believed to be small, fragmented, and vulnerable to extinction.
Animal populations with impoverished genetic diversity are inherently less able to adapt to changes in their environments (such as climate change, disease outbreaks, habitat change, etc.). The isolation of the four remaining small bongo populations, which themselves would appear to be in decline, means a substantial amount of genetic material is lost each generation. Whilst the population remains small, the impact of transfers will be greater, so the establishment of a "metapopulation management plan" occurs concurrently with conservation initiatives to enhance in situ population growth, and this initiative is both urgent and fundamental to the future survival of mountain bongo in the wild.
The western/lowland bongo faces an ongoing population decline as habitat destruction and hunting pressures increase with the relentless expansion of human settlement. Its long-term survival will only be assured in areas which receive active protection and management. At present, such areas comprise about 30,000 km2, and several are in countries where political stability is fragile. So, a realistic possibility exists whereby its status could decline to Threatened in the near future.
As the largest and most spectacular forest antelope, the western/lowland bongo is both an important flagship species for protected areas such as national parks, and a major trophy species which has been taken in increasing numbers in Central Africa by sport hunters during the 1990s.[21] Both of these factors are strong incentives to provide effective protection and management of populations.[22]

Trophy hunting has the potential to provide economic justification for the preservation of larger areas of bongo habitat than national parks, especially in remote regions of Central Africa, where possibilities for commercially successful tourism are very limited.[21]
The eastern/mountain bongo's survival in the wild is dependent on more effective protection of the surviving remnant populations in Kenya. If this does not occur, it will eventually become extinct in the wild. The existence of a healthy captive population of this subspecies offers the potential for its reintroduction.[23]
Groups supporting bongo conservation in Kenya
In 2004, Dr. Jake Veasey, the head of the Department of Animal Management and Conservation at Woburn Safari Park and a member of the European Association of Zoos and Aquariums Population Management Advisory Group, with the assistance of Lindsay Banks, took over responsibility for the management and coordination of the European Endangered Species Programme for the eastern bongo. This includes some 250 animals across Europe and the Middle East.
Along with the Rothschild giraffe, the eastern bongo is arguably one of the most threatened large mammals in Africa, with recent estimates numbering less than 140 animals, below a minimum sustainable viable population. The situation is exacerbated because these animals are spread across four isolated populations. Whilst the bongo endangered species program can be viewed as having been successful in ensuring survival of this species in Europe, it has not yet become actively involved in the conservation of this species in the wild in a coordinated fashion. The plan is to engage in conservation activities in Kenya to assist in reversing the decline of the eastern bongo populations and genetic diversity in Africa, and in particular, applying population management expertise to help ensure the persistence of genetic diversity in the free ranging wild populations.


To illustrate significance of genetic diversity loss, assume the average metapopulation size is 35 animals based on 140 animals spread across four populations (140/4=35). Assuming stable populations, these populations will lose 8% of their genetic diversity every decade. By managing all four populations as one, through strategic transfers, gene loss is reduced from 8% to 2% per decade, without any increase in bongo numbers in Kenya. By managing the European and African populations as one – by strategic exports from Europe combined with in situ transfers, gene loss is reduced to 0.72% every 100 years, with both populations remaining stable. If populations in Kenya are allowed to grow through the implementation of effective conservation, including strategic transfers, gene loss can be effectively halted in this species and its future secured in the wild.
The initial aims of the project are:
- Through faecal DNA analysis, estimate the genetic diversity of the remaining wild bongos and calculate the relatedness of the isolated wild populations.
- More accurately estimate the total population of wild bongos through faecal DNA analysis, camera trapping, and transect surveying.
- Through direct sampling, estimate the genetic diversity of the captive bongo population and calculate its relatedness with the remaining isolated wild populations.
- Collect DNA samples from western bongos to calculate the relatedness of the two subspecies.
- Fund rangers to collect the above data in Kenya, enhance the degree of protection afforded to and level of understanding of the eastern bongos' ecological needs.
- To realise such a metapopulation management plan, work with local communities is essential to reverse the decline and allow for the implementation of a transfer strategy. A substantial proportion of wild genetic diversity likely will have already been lost.
If effective protection were implemented immediately and bongo populations allowed to expand without transfers, then this would create a bigger population of genetically impoverished bongos. These animals would be less able to adapt to a dynamic environment. Whilst the population remains small, the impact of transfers will be greater. For this reason, the 'metapopulation management plan' must occur concurrently with conservation strategies to enhance in situ population growth. This initiative is both urgent and fundamental to the future survival of the mountain bongo in the wild.
In 2013, SafariCom telecommunications donated money to the Bongo Surveillance Programme[24] to try to keep tabs on what are thought to be the last 100 eastern bongos left in the wild in the Mau Eburu Forest in central Kenya, whose numbers are still declining due to logging of their habitat and illegal poaching.[25]
Mount Kenya Wildlife Conservancy runs a bongo rehabilitation program in collaboration with the Kenya Wildlife Service.[26] The Conservancy aims to prevent extinction of the bongo through breeding and release back into the wild.[27][28]
Status
The IUCN Antelope Specialist Group considers the western or lowland bongo, T. e. eurycerus, to be Lower Risk (Near Threatened)[2] and the eastern or mountain bongo, T. e. isaaci, of Kenya, to be Critically Endangered.[4] These bongos may be endangered due to human environmental interaction, as well as hunting and illegal actions towards wildlife.
CITES lists bongos as an Appendix III species, only regulating their exportation from a single country, Ghana. It is not protected by the US Endangered Species Act and is not listed by the USFWS.
References
- IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group. (2017) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Tragelaphus eurycerus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22047A115164600. Retrieved 24 October 2020.
- IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group. (2017). "Tragelaphus eurycerus ssp. eurycerus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T22058A50197275. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T22058A50197275.en. Retrieved 24 October 2020.
- Estes, Richard. "Bongo". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 11 March 2021.
- IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group. (2017). "Tragelaphus eurycerus ssp. isaaci". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T22057A50197212. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T22057A50197212.en. Retrieved 24 October 2020.
- Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M., eds. (2005). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 698. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- "Tragelaphus". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- Huffman, B. "Bongo". Ultimate Ungulate. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- "Bongo". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 7 February 2016.
- Spinage, C.A. (1986) The Natural History of Antelopes. New York: Facts on File Publications.
- Ralls, Katherine (1978). "Tragelaphus eurycerus" (PDF). Mammalian Species (111): 1–4. doi:10.2307/3503808. JSTOR 3503808. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 April 2012. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- Kingdon, Jonathan (1993). Kingdon Guide to African Mammals. ISBN 978-0-85112-235-9.
- Walther, F. R. (1990) "Spiral-horned antelopes". In Grzimek's Encyclopedia of Mammals. S. P. Parker (ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. Volume 5, pp. 344–359.
- Estes, Richard D. (1991) The Behavior Guide to African Mammals: Including Hoofed Mammals, Carnivores, Primates. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press.
- "Eastern bongo". www.zoobarcelona.cat. Retrieved 2 September 2020.
- Estes, Richard (1993) The Safari Companion. Vermont: Chelsea Green Publishing Co..
- "Bongo Antelope Facts and Information | SeaWorld Parks & Entertainment".
- van Lill, Dawid (17 February 2015). African Wildlife Trivia. Penguin Random House South Africa. p. 153. ISBN 978-1-920544-34-8.
- Nowak, Ronald (1991) M. Walker's Mammals of the World 5th ed. Vol. II. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press
- Schiller, C. A.; Montali, R. J.; Doi, S.; Grollman, E. F. (1995). "Clinical and Morphologic Findings of Familial Goiter in Bongo Antelope (Tragelaphus eurycerus)". Veterinary Pathology. 32 (3): 242–9. doi:10.1177/030098589503200305. PMID 7604491. S2CID 26590186.
- "Eastern Bongo". Retrieved 21 June 2013.
- Wilkie, D. S.; Carpenter, J. (1999). "The potential role of safari hunting as a source of revenue for protected areas in the Congo Basin". Oryx. 33 (4): 340. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3008.1999.00079.x.
- Institute of Applied Ecology (1998). "Tragelaphus eurycerus". In African Mammals Databank – A Databank for the Conservation and Management of the African Mammals Vol 1 and 2. Bruxelles: European Commission Directorate
- IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources). 2002. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
- Bongo Surveillance Programme monitoring and surveillance continues in Aberdare, Mt. kenya, Eburru and South West Mau. mountainbongo.org
- Kenya's Mountain Bongo antelope under threat. BBC News. 18 April 2013
- "Mount Kenya Wildlife Conservancy - Magical Kenya". Magical Kenya. Archived from the original on 13 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- "Wildlife Rehabilitation | Mt. Kenya Wildlife Conservancy". www.animalorphanagekenya.org. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- Mulli, Thorn. "Date with the mountain bongo". The Standard. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
