syndrome pieds-mains-bouche
Français
Étymologie
Locution nominale
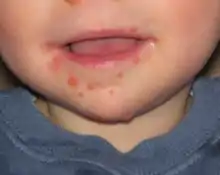
Des lésions typiques de la bouche du syndrome pieds-mains-bouche d’un enfant de 11 mois.
syndrome pieds-mains-bouche \sɛ̃.dʁom pje mɛ̃ buʃ\ masculin
- (Médecine) Maladie infectieuse virale se manifestant principalement chez les enfants, due à des entérovirus comme le virus Coxsackie A16 et l’entérovirus 71.
Synonymes
- maladie mains-pieds-bouche
Traductions
- Allemand : Hand-Fuß-Mund-Krankheit (de)
- Anglais : hand, foot and mouth disease (en)
- Arabe : مرض اليد، القدم والفم (ar)
- Catalan : febre aftosa (ca)
- Chinois : 手足口病 (zh)
- Coréen : 수족구병 (ko) sujokgubyeong
- Espagnol : fiebre aftosa humana (es)
- Finnois : enterorokko (fi)
- Hébreu : מחלת הפה, ידיים ורגליים (he)
- Indonésien : flu singapura (id)
- Italien : malattia mano-piede-bocca (it)
- Japonais : 手足口病 (ja) teashikuchibyō
- Néerlandais : hand-, voet- en mondziekte (nl)
- Norvégien : hånd-, fot- og munnsykdom (no)
- Persan : بیماری دست، پا و دهان (fa)
- Polonais : zespół dłoni, stóp i ust (pl)
- Suédois : vesikulös stomatit (sv)
- Tchèque : nemoc rukou, nohou a úst (cs)
- Thaï : โรคมือ เท้า และปาก (th)
- Vietnamien : bệnh tay, chân, miệng (vi)
Cet article est issu de Wiktionary. Le texte est sous licence Creative Commons - Attribution - Partage dans les Mêmes. Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s'appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.