STD Risk and Oral Sex - CDC Fact Sheet
On This Page
- Fast Facts
- What is Oral Sex?
- How Common is Oral Sex?
- Can STDs Be Spread During Oral Sex?
- Which STDs Can Be Passed On from Oral Sex?
- Is Oral Sex Safer than Vaginal or Anal Sex?
- What May Increase the Chances of Giving or Getting an STD through Oral Sex?
- What Can You Do to Prevent STD Transmission During Oral Sex?
Fast Facts
- Many sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can be spread through oral sex.
- Using a condom, dental dam or other barrier method each and every time you have oral sex can reduce the risk of giving or getting an STD.
- Although oral sex may carry a lower risk for spreading HIV than other forms of sex, repeated unprotected exposures may increase risk of transmission.
What is Oral Sex?
Oral sex involves using the mouth, lips, or tongue to stimulate the penis (fellatio), vagina (cunnilingus), or anus (anilingus) of a sex partner. The penis and testicles and the vagina and area around the vagina are also called the genitals or genital area.
How Common is Oral Sex?
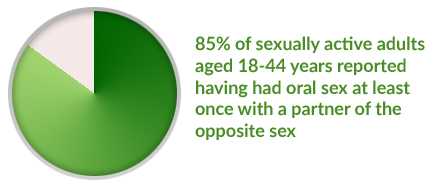
Oral sex is commonly practiced by sexually active adults. Oral sex can happen between heterosexual (straight) and same-sex (gay or lesbian) couples. More than 85% of sexually active adults aged 18-44 years reported having had oral sex at least once with a partner of the opposite sex. A separate survey conducted during 2007-2010 found that 33% of teenage girls and boys aged 15-17 years reported having had oral sex with a partner of the opposite sex.
Can STDs Be Spread During Oral Sex?

Many STDs, as well as other infections, can be spread through oral sex. Anyone exposed to an infected partner can get an STD in the mouth, throat, genitals, or rectum. The risk of getting an STD from oral sex, or spreading an STD to others through oral sex, depends on a number of things, including
- The particular STD.
- The sex acts practiced.
- How common the STD is in the population to which the sex partners belong.
- The number of specific sex acts performed.
In general:
- It may be possible to get some STDs in the mouth or throat from giving oral sex to a partner with a genital or anal/rectal infection, particularly from giving oral sex to a partner with an infected penis.
- It also may be possible to get certain STDs on the penis (and possibly the vagina, anus or rectum) from getting oral sex from a partner with a mouth or throat infection.
- It’s possible to have an STD in more than one area at the same time, for example in the throat and the genitals.
- Several STDs that may be transmitted by oral sex can then spread throughout the body of an infected person.
- STDs can be spread to a sex partner even when the infected partner has no signs or symptoms. If you are infected with an STD, you might not know it because many STDs may have no symptoms.
Which STDs Can Be Passed On from Oral Sex?
 Chlamydia
Chlamydia
(Chlamydia trachomatis)
Risk of infection from oral sex:
- Giving oral sex to a man with an infected penis can result in getting chlamydia in the throat.
- Giving oral sex to a woman with an infected vagina or urinary tract may result in getting chlamydia in the throat.*
- Giving oral sex to a man or woman with an infected rectum might result in getting chlamydia in the throat.*
- Getting oral sex on the penis from a partner with chlamydia in the throat can result in getting chlamydia of the penis.
- Getting oral sex on the vagina from a partner with chlamydia in the throat might result in getting chlamydia of the vagina or urinary tract.*
- Getting oral sex on the anus from a partner with chlamydia in the throat might result in getting chlamydia in the rectum.*
* Statements followed by an asterisk (*) have not been well studied.
Areas of initial infection:
- Throat
- Genitals
- Urinary tract
- Rectum
Initial signs and symptoms of infection:
- Most chlamydia infections in the throat have no symptoms. When symptoms are present, they can include a sore throat.
- Many genital, urinary tract, or rectal chlamydia infections have no symptoms. When symptoms are present, they can include:
- Discharge from vagina or penis (discharge from the vagina may be bloody).
- Burning feeling when urinating.
- Painful or swollen testicles.
- Rectal pain or discharge
Treatment:
- Chlamydia can be cured with the right medicine.
- The sex partners of a person with chlamydia should also be tested for infection. Those who are diagnosed with chlamydia should not have sex until they and their sex partners have completed treatment.
If left untreated, throat infections:
- Can be spread to uninfected sex partners, particularly by performing oral sex on a male partner’s penis.
If left untreated, genital, urinary and/or rectal infections:
- Can be spread to uninfected sex partners.
- In women:
- Can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can lead to chronic pelvic pain, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy (a pregnancy in the fallopian tube or elsewhere outside of the womb).
- In pregnant women:
- Might result in premature birth or low birth weight in babies.
- Can be spread to the baby during delivery, and can cause chlamydia infection in the eyes or infection of the respiratory tract that can develop into pneumonia.
- In men:
- Can cause epididymitis, a painful condition of the ducts attached to the testicles that may lead to ductal scarring.
- In both men and women:
- May increase risk of getting HIV infection.
- Might increase risk of spreading HIV to sex partners.
- May cause a reaction (reactive arthritis) throughout the body that can lead to arthritis (joint pain), conjunctivitis (pink eye), and/or a rash on the soles of the feet or elsewhere.
 Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea
(Neisseria gonorrhoeae)
Risk of infection from oral sex:
- Giving oral sex to a man with an infected penis can result in getting gonorrhea in the throat.
- Giving oral sex to a woman with an infected vagina or urinary tract might result in getting gonorrhea in the throat.*
- Giving oral sex to a man or woman with an infected rectum might result in getting gonorrhea in the throat.*
- Getting oral sex on the penis from a partner with gonorrhea in the throat may result in getting gonorrhea of the penis.
- Getting oral sex on the vagina from a partner with gonorrhea in the throat might result in getting gonorrhea of the vagina or urinary tract.*
- Getting oral sex on the anus from a partner with gonorrhea in the throat might result in getting gonorrhea in the rectum.*
* Statements followed by an asterisk (*) have not been well studied.
Areas of initial infection:
- Throat
- Genitals
- Urinary tract
- Rectum
Initial signs and symptoms of infection:
- Most gonorrhea infections in the throat have no symptoms. When symptoms are present, they can include a sore throat.
- Symptoms of genital, urinary tract, or rectal infection may include:
- Discharge from vagina or penis (discharge from the vagina may be bloody).
- Burning feeling when urinating.
- Painful or swollen testicles.
- Rectal pain or discharge.
Treatment:
- Infections in the throat are harder to cure than genital or rectal infections but can be treated with recommended antibiotics.
- Genital and rectal infections can also be cured with the right medicine.
- The sex partners of a person with gonorrhea should also be tested for infection. Those who are diagnosed with gonorrhea should not have sex until they and their sex partners have completed treatment.
If left untreated, throat infections:
- Can be spread to uninfected sex partners.
- Might spread through the body causing skin sores and joint pain. This condition is called disseminated gonococcal infection. The heart can also be infected. This is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition.
If left untreated, genital, urinary and/or rectal infections:
- Can be spread to other sex partners.
- In women:
- Can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can lead to chronic pelvic pain, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy (a pregnancy in the fallopian tube or elsewhere outside of the womb).
- In pregnant women:
- Can be spread to the baby during delivery, and can cause blindness, joint infection, or a life-threatening blood infection in the baby.
- In men:
- Can cause epididymitis, a painful condition of the ducts attached to the testicles that may lead to ductal scarring.
- In both men and women:
- May increase risk of getting HIV infection.
- Might increase risk of spreading HIV to sex partners.
- May spread through the body causing skin sores and joint pain. This condition is called disseminated gonococcal infection. The heart can also be infected, which is a serious and potentially life threatening condition.
 Syphilis
Syphilis
(Treponema pallidum)
Risk of infection from oral sex:
- Giving oral sex to a partner with a syphilis sore or rash on the genitals or anus can result in getting syphilis.
- Getting oral sex from a partner with a syphilis sore or rash on the lips or mouth, or in the throat, can result in getting syphilis.
- Another important factor that affects risk of spreading syphilis is how long an infected partner has had syphilis.
Areas of initial infection:
- Lips
- Mouth
- Throat
- Genitals
- Anus
- Rectum
Initial signs and symptoms of infection:
- May not have symptoms.
- One or more painless ulcers or sores on the lips, mouth, or throat; on the skin; or on or near the genitals or anus.
- Rash on trunk, palms of hands, and/or soles of feet.
- Flu-like symptoms.
Treatment:
- Syphilis can be cured with the right medicine.
- Sex partners of a person with syphilis should also be tested for infection, including some of the infected person’s past sex partners. Some of these partners should be treated even if their syphilis test results are negative.
If left untreated, syphilis:
- Can be spread to others through contact with syphilis sores or rash.
- In pregnant women:
- Can be spread to the baby during pregnancy.
- Can cause stillbirth (a baby born dead).
- Babies with untreated syphilis may become developmentally delayed, have seizures, or die.
- In both men and women:
- Can increase risk of getting HIV infection.
- Can increase risk of spreading HIV to sex partners.
- May cause damage to internal organs, blindness, muscle weakness, dementia, and even death.
 Herpes
Herpes
(herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2)
Risk of infection from oral sex:
- Giving oral sex to a partner with herpes on the genital area, anus, buttocks, or in the rectum may result in getting herpes on the lips, mouth, or in the throat.
- Getting oral sex from a partner with herpes on the lips, mouth, or in the throat can result in getting herpes on the genital area, anus, buttocks, or in the rectum.
Areas of infection:
- Lips
- Mouth
- Throat
- Genital area
- Anus
- Rectum
- Buttocks
Signs and symptoms of infection:
- May not have symptoms.
- Headache or fever (during initial infection).
- Painful or itching sores at or near the area of infection.
Treatment:
- There is no cure for a herpes, but antiviral medicine can shorten and help decrease symptoms of herpes outbreaks.
- Daily antiviral medication can prevent or shorten herpes outbreaks.
Even with treatment, oral (lip, mouth and throat) infections:
- Can be spread to others, including sex partners.
Even with treatment, genital area, buttock, anal, and/or rectal infections:
- Can be spread to uninfected sex partners.
- In pregnant women:
- May be spread to the baby during delivery, and can cause brain damage, damage to internal organs, or even death of the baby.
- In both men and women:
- Can increase risk of getting HIV infection.
- Can increase risk of giving HIV to sex partners.
 HPV
HPV
(human papillomavirus)
Risk of infection from oral sex:
- Giving oral sex to a man with an HPV-infected penis or genital area can result in getting HPV in the throat.
- Giving oral sex to a woman with an HPV-infected vagina or genital area can result in getting HPV in the throat.
- Giving oral sex to a man or woman with HPV on the anus or in the rectum may result in getting HPV in the throat.*
- Getting oral sex from a partner with HPV in the throat might result in getting HPV on the genital area, anus, or rectum.*
* Statements followed by an asterisk (*) have not been well studied.
Areas of infection:
- Mouth
- Throat
- Genital area
- Vagina
- Cervix
- Anus
- Rectum
Signs and symptoms of infection:
- May have no symptoms.
- Warts in the throat (laryngeal or respiratory papillomatosis):
- May cause changes in the voice, difficulty speaking, or shortness of breath.
- Genital or anal warts.
- Abnormal changes in cells of vagina, cervix, or anus that can be found by clinical examination and tests (Pap and/or HPV tests).
- Some types of HPV can lead to vaginal or cervical cancer, anal, penile, head, and neck cancers.
Vaccine:
-
HPV vaccine protects against transmission of certain types of HPV.
- HPV vaccine is is recommended for 11- or 12-year-old girls, and for girls and women ages 13 through 26 years who have not yet been vaccinated with all recommended doses. Girls as young as age 9 years may be vaccinated.
- HPV vaccine is also recommended for 11- or 12-year-old boys, and for boys and men ages 13 through 21 years who have not yet been vaccinated with all recommended doses. Boys as young as age 9 years and men through age 26 years may also be vaccinated.
- Vaccination through age 26 years is recommended for men who have sex with men and for immunocompromised persons (including those who are living with HIV) who have not yet been vaccinated with all recommended doses.
Treatment:
- Warts in the mouth and throat:
- May disappear, remain unchanged, or grow in size or number.
- Surgery may be used to remove warts in the throat.
- Treatment may reduce warts but does not cure HPV infection.
- Genital and anal warts:
- May go away on their own, remain unchanged, or grow in size or number.
- Treatments include medicines applied to the warts, freezing the warts (cryotherapy), or surgery to remove the warts.
- Treatment may reduce warts but does not cure HPV infection.
- Abnormal changes in cells of vagina, cervix, or anus:
- May need more clinical examination and testing (Pap and/or HPV tests).
- Other procedures may be used, such as biopsy (taking a small sample of tissue) and/or removal of abnormal tissue, depending on age, pregnancy status, and test results.
Even with treatment, warts in the throat:
- Might be spread to uninfected sex partners.
- May have recurrences (recurrent respiratory papillomatosis).
Even with treatment, genital and anal warts:
- Can be spread to uninfected sex partners.
- May return but will not develop into cancer.
Mouth and throat infections by several types of HPV that do not cause warts may develop into head or neck cancer.
Abnormal changes in cells of vagina or anus:
- Might develop into cancer. Although some women have abnormal Pap and/or HPV test results, few women get cervical cancer if they get the appropriate follow-up and treatment.
 HIV
HIV
(human immunodeficiency virus)
Risk of infection from oral sex:
- Giving oral sex on the penis of a man with HIV can result in getting HIV. The risk of infection is lower than the risks from vaginal or anal sex.
- Giving oral sex on the vagina of a woman with HIV may result in getting HIV. The risk of infection is thought to be very low.
- Giving oral sex on the anus of a partner with HIV may result in getting HIV. There are few reports of transmission from this type of oral sex.
- Getting oral sex on the penis from a partner with HIV may result in getting HIV. This risk is thought to be very low, but has not been well studied.
- Getting oral sex on the vagina from a partner with HIV might result in getting HIV. This risk is thought to be extremely low, but has not been well studied.
- Getting oral sex on the anus from a partner with HIV might result in getting HIV. There are few reports of transmission from this type of oral sex.
- Another important factor that affects risk of HIV spread is the virus level (i.e., viral load) in an infected partner’s blood and other body fluids at the time of the sexual encounter. A low HIV viral load in an infected partner does not completely eliminate the risk of spreading HIV from oral sex.
Areas of infection:
- Iinfection of the immune system throughout the body.
Initial signs and symptoms of infection:
- May have no symptoms for many years.
- Flu-like symptoms.
Treatment
- There is no cure for HIV, but antiviral and other medicines can help people with HIV live longer with a better quality of life.
Even with treatment, HIV infection:
- Can be spread to uninfected sex partners.
- Can increase the risk of getting certain infections and cancers.
 Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis
(infection with T. vaginalis)
Risk of infection from oral sex:
- Giving oral sex to a woman with an infected vagina or a man with an infected penis might result in getting trichomoniasis of the throat. There are few reports of potential spread from oral sex.
- Spread of trichomoniasis by other oral sex practices has not been reported.
Areas of initial infection
- Vagina
- Penis
- Mouth/throat (possibly)
Initial signs and symptoms of infection
- Infections of the genitals or urinary tract may have no symptoms, especially in men
- Symptoms of genital or urinary tract infection can include:
- Discharge from vagina or penis.
- Vaginal area redness.
- Vaginal itching.
- Burning feeling when urinating.
Treatment
- Can be cured with right medicine.
- The sex partners of people with trichomoniasis should also be tested for infection. Those who are diagnosed with trichomoniasis should not have sex until they and their sex partners have completed treatment.
If left untreated, genital or urinary infections:
- Can be spread to uninfected sex partners.
In addition to the STDs above, other infections such as hepatitis A virus, Shigella and intestinal parasites (amebiasis) can be spread through giving oral sex on the anus.
Is Oral Sex Safer than Vaginal or Anal Sex?

- Many STDs can be spread through oral sex. However, it is difficult to compare the exact risks of getting specific STDs from specific types of sexual activity. This is partly because most people who have oral sex also have vaginal or anal sex. Also, few studies have looked at the risks of getting STDs other than HIV from giving oral sex on the vagina or anus, compared to giving oral sex on the penis.
- Studies have shown that the risk of getting HIV from having oral sex with an infected partner (either giving or getting oral sex) is much lower than the risk of getting HIV from anal or vaginal sex with an infected partner. This may not be true for other STDs – in one study of gay men with syphilis, 1 out of 5 reported having only oral sex.
- Getting HIV from oral sex may be less likely than vaginal or anal sex, but it still carries risk. If you are having oral sex you should still protect yourself. Repeated unprotected oral sex exposure to HIV may represent a considerable risk for spread of HIV, as well as other STDs for which the risk of spread through oral sex has not been as well studied.
- It is possible that getting certain STDs, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, in the throat may not pose as great a threat to an infected person’s health as getting an STD in the genital area or rectum. Having these infections in the throat might increase the risk of getting HIV. Having gonorrhea in the throat also may lead to spread of the disease throughout the body. In addition:
- Having infections of chlamydia and gonorrhea in the throat may make it easier to spread these infections to others through oral sex. This is especially important for gonorrhea, since throat infections are harder to treat than urinary, genital or rectal infections.
- Infections from certain STDs, such as syphilis and HIV, spread throughout the body. Therefore, infections that are acquired in the throat may lead to the same health problems as infections acquired in the genitals or rectum.
- Mouth and throat infections by certain types of HPV may develop into oral or neck cancer.
What May Increase the Chances of Giving or Getting an STD through Oral Sex?
It is possible that certain factors may increase a person’s chances of getting HIV or other STDs during oral sex if exposed to an infected partner, such as:
- Having poor oral health which can include tooth decay, gum disease or bleeding gums, and oral cancer.
- Having sores in the mouth or on the genitals.
- Being exposed to the “pre-cum” or “cum” (also known as pre-ejaculate or ejaculate) of an infected partner.
However, no scientific studies have been done to show whether or not these factors actually do increase the risk of getting HIV or STDs from oral sex.
What Can You Do to Prevent STD Transmission During Oral Sex?
You can lower your chances of giving or getting STDs during oral sex by using a condom, dental dam or other barrier method each and every time you have oral sex.
- For oral sex on the penis:
- Cover the penis with a non-lubricated latex condom.
- Use plastic (polyurethane) condoms if you or your partner is allergic to latex.
- For oral sex on the vagina or anus:
- Use a dental dam.
- Cut open a condom to make a square, and put it between the mouth and the partner’s vagina or anus.
The only way to avoid STDs is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting an STD:
- Being in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who is not infected with an STD (e.g., a partner who has been tested and has negative STD test results).
- Using latex condoms the right way every time you have sex.
It’s important to remember that many infected individuals may be unaware of their infection because STDs often have no symptoms and are unrecognized.
If you are sexually active, you should get tested regularly for STDs and HIV and talk to your partner(s) about STDs. If you think you might have an STD, stop having sex and visit your doctor or clinic to get tested. There are free and low-cost options for testing in your area. It is important that you talk openly with your health care provider about any activities that might put you at risk for an STD, including oral sex.
Additional Resources:
For more information on all the STDs discussed in this fact sheet visit: https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/fact_sheets.htm
FOR MORE INFORMATION:
STD information and referrals to STD Clinics
CDC-INFO
1-800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636)
TTY: 1-888-232-6348
In English, en Español
American Sexual Health Association (ASHA)
1-800-783-9877
www.ashastd.org
References
Chandra A, Mosher WD, Copen C, Sionean C. Sexual behavior, sexual attraction, and sexual identity in the United States: data from the 2006-2008 National Survey of Family Growth. 36, 1-36. 2011. Hyattsville, MD, National Center for Health Statistics. National health statistics reports.
Copen CE, Chandra A, Febo-Vazquez I. Sexual behavior, sexual attraction, and sexual orientation among adults aged 18-44 in the United States: data from the 2011-2013 National Survey of Family Growth. 88, 1-13. 2016. Hyattsville, MD, National Center for Health Statistics. National health statistics reports.
Sparling PF, Swartz MN, Musher DM, Healy BP. Clinical Manifestations of Syphilis. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;662-684.
Dooley SW, Thrun M. HIV Transmission Prevention in the Context of Care. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1362-1392.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Questions and answers on the use of HIV medications to help prevent the transmission of HIV. 4-13-2010. 2-7-2012.
Jones RB, Rabinovitch RA, Katz BP et al. Chlamydia trachomatis in the pharynx and rectum of heterosexual patients at risk for genital infection. Annals of Internal Medicine 1985;102:757-762.
Templeton DJ, Jin F, Imrie J et al. Prevalence, incidence and risk factors for pharyngeal chlamydia in the community based Health in Men (HIM) cohort of homosexual men in Sydney, Australia. Sexually Transmitted Infections 2008;84:361-363.
Wikstrom A, Rotzen-Ostlund M, Markowitz E. Occurrence of pharyngeal Chlamydia trachomatis is uncommon in patients with a suspected or confirmed genital infection. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica 2010;89:78-81.
Benn PD, Rooney G, Carder C et al. Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection and the sexual behaviour of men who have sex with men. Sexually Transmitted Infections 2007;83:106-112.
Bradshaw CS, Tabrizi SN, Read TRH et al. Etiologies of nongonococcal urethritis: bacteria, viruses and the association with orogenital exposure. Journal of Infectious Diseases 6 A.D.;193:336-345.
Jin F, Prestage GP, Mao L et al. Incidence and risk factors for urethral and anal gonorrhoea and chlamydia in a cohort of HIV-negative homosexual men: the Health in Men Study. Sexually Transmitted Infections 2007;83:113-119.
Bernstein KT, Stephens SC, Barry PM et al. Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae transmission from the oropharynx to the urethra among men who have sex with men. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2009;49:1793-1797.
Lafferty WE, Hughes JP, Handsfield HH. Sexually transmitted diseases in men who have sex with men. Acquisition of gonorrhea and nongonococcal urethritis by fellatio and implications for STD/HIV prevention. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 1997;24:272-278.
Stamm WE. Chlamydia trachomatis Infections of the Adult. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;575-593.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transimitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2010. Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report 2010;59:1-110.
Paavonen J, Westrom L, Eschenbach D. Pelivc Inflammatory Disease. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1017-1050.
Hitti J, Watts DH. Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections in Pregnancy. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1529-1561.
Kohlhoff SA, Hammerschlag MR. Gonoccal and Chlamydial Infections in Infants and Children. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1613-1627.
Geisler WM, Krieger JN. Epididymitis. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1127-1145.
Berman SM, Cohen MS. STD Treatment: How Can It Improve HIV Prevention in the South? Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2006;33:850-857.
Rottingen JA, Cameron DW, Garnett GP. A systematic review of the epidemiologic interactions between classic sexually transmitted diseases and HIV: how much really is known?. [Review] [147 refs]. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2001;28:579-597.
Fleming DT, Wasserheit JN. From epidemiological synergy to public health policy and practice: the contribution of other sexually transmitted diseases to sexual transmission of HIV infection. [Review] [81 refs]. Sexually Transmitted Infections 1999;75:3-17.
World Health Organization. Consultation on STD interventions for preventing HIV: what is the evidence? 1-54. 2000. UNAIDS/00.06E, WHO/HIS/2000.02. 2-19-2010.
Colven R. Generalized Cutaneous Manifestations of STD and HIV Infection: Typical Presentations, Differential Diagnosis, and Management. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1177-1197.
Murray AB, Greenhouse PR, Nelson WL, Norman JE, Jeffries DJ, Anderson J. Coincident acquisition of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and HIV from fellatio. Lancet 1991;338:830.
Wong ML, Chan RK. A prospective study of pharyngeal gonorrhoea and inconsistent condom use for oral sex among female brothel-based sex workers in Singapore. International Journal of STD & AIDS 1999;10:595-599.
Morris SR, Klausner JD, Buchbinder SP et al. Prevalence and incidence of pharyngeal gonorrhea in a longitudinal sample of men who have sex with men: the EXPLORE study. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2006;43:1284-1289.
Sackel SG, Alpert S, Fiumara NJ, Donner A, Laughlin CA, McCormack WM. Orogenital Contact and the Isolation of Neisserioa gonorrhoeae, Mycoplasma hominis, and Ureaplasma urealyticum from the Pharynx. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 1979;6:64-68.
Wong ML, Chan RK, Koh D. Promoting condoms for oral sex: impact on pharyngeal gonorrhea among female brothel-based sex workers. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2002;29:311-318.
Castor D, Jolly PE, Furlonge C et al. Determinants of gonorrhoea infection among STD clinic attenders in Trinidad – II: Sexual behavioural factors. International Journal of STD & AIDS 2002;13:46-51.
Hook EW, III, Handsfield HH. Gonococcal Infections in the Adult. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;627-645.
Jin F, Prestage GP, Imrie J et al. Anal Sexually Transmitted Infections and Risk of HIV Infection in Homosexual Men. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes: JAIDS 2010;53:144-149.
Weir SS, Feldblum PJ, Roddy RE, Zekeng L. Gonorrhea as a risk factor for HIV acquisition. AIDS 1994;8:1605-1608.
Peterman TA, Furness BW. The resurgence of syphilis among men who have sex with men. [Review] [65 refs]. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases 2007;20:54-59.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Transmission of primary and secondary syphilis by oral sex–Chicago, Illinois, 1998-2002. MMWR – Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report 2004;53:966-968.
Hourihan M, Wheeler H, Houghton R, Goh BT. Lessons from the syphilis outbreak in homosexual men in east London. Sexually Transmitted Infections 2004;80:509-511.
Imrie J, Lambert N, Mercer CH et al. Refocusing health promotion for syphilis prevention: results of a case-control study of men who have sex with men on England’s south coast. Sexually Transmitted Infections 2006;82:80-83.
Simms I, Fenton KA, Ashton M et al. The re-emergence of syphilis in the United Kingdom: the new epidemic phases. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2005;32:220-226.
Campos-Outcalt D, Hurwitz S. Female-to-female transmission of syphilis: a case report. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2002;29:119-120.
Ditzen AK, Braker K, Zoellner KH, Teichmann D. The syphilis-HIV interdependency. International Journal of STD & AIDS 2005;16:642-643.
McCall MB, van Lith-Verhoeven JJ, van CR et al. Ocular syphilis acquired through oral sex in two HIV-infected patients. Netherlands Journal of Medicine 2004;62:206-208.
Jin F, Prestage GP, Kippax SC et al. Epidemic syphilis among homosexually active men in Sydney.[see comment]. Medical Journal of Australia 2005;183:179-183.
Shafii T, Radolf JD, Sanchez PJ, Schulz KF, Murphy KF. Congenital Syphilis. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1577-1612.
Jin F, Prestage GP, Mao L et al. Transmission of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in a prospective cohort of HIV-negative gay men: the health in men study. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2006;194:561-570.
Lafferty WE, Coombs RW, Benedetti J, Critchlow C, Corey L. Recurrences after oral and genital herpes simplex virus infection. Influence of site of infection and viral type. New England Journal of Medicine 1987;316:1444-1449.
Lafferty WE, Downey L, Celum C, Wald A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 as a cause of genital herpes: impact on surveillance and prevention. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2000;181:1454-1457.
Lowhagen GB, Tunback P, Andersson K, Bergstrom T, Johannisson G. First episodes of genital herpes in a Swedish STD population: a study of epidemiology and transmission by the use of herpes simplex virus (HSV) typing and specific serology. Sexually Transmitted Infections 2000;76:179-182.
Corey L, Wald A. Genital Herpes. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;399-437.
Whitley RJ. Herpes Simplex Virus. In: Wallace RB, ed. Public Health and Preventive Medicine. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.; 2008.
Coyle PV, O’Neill HJ, Wyatt DE, McCaughey C, Quah S, McBride MO. Emergence of herpes simplex type 1 as the main cause of recurrent genital ulcerative disease in women in Northern Ireland. Journal of Clinical Virology 2003;27:22-29.
Lowhagen GB, Tunback P, Bergstrom T. Proportion of herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 and type 2 among genital and extragenital HSV isolates. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2002;82:118-120.
Bradford RD, Whitley RL, Stagno S. Herpesvirus Infections in Neonates and Children: Cytomegalovirus and Herpes Simplex Virus. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1629-1658.
Smith EM, Ritchie JM, Summersgill KF et al. Age, sexual behavior and human papillomavirus infection in oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers. International Journal of Cancer 2004;108:766-772.
Kashima HK, Shah F, Lyles A et al. A comparison of risk factors in juvenile-onset and adult-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 1992;102:9-13.
D’Souza G, Kreimer AR, Viscidi R et al. Case-control study of human papillomavirus and oropharyngeal cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;356:1944-1956.
Coutlee F, Trottier AM, Ghattas G et al. Risk factors for oral human papillomavirus in adults infected and not infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 1997;24:23-31.
Dahlstrom KR, Li G, Tortolero-Luna G, Wei Q, Sturgis EM. Differences in history of sexual behavior between patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma and patients with squamous cell carcinoma at other head and neck sites. Head & Neck 2010;33:847-855.
D’Souza G, Agrawal Y, Halpern J, Bodison S, Gillison ML. Oral sexual behaviors associated with prevalent oral human papillomavirus infection. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2009;199:1263-1269.
Kreimer AR, Alberg AJ, Daniel R et al. Oral human papillomavirus infection in adults is associated with sexual behavior and HIV serostatus. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2004;189:686-698.
Kreimer AR, Alberg AJ, Viscidi R, Gillison ML. Gender differences in sexual biomarkers and behaviors associated with human papillomavirus-16, -18, and -33 seroprevalence. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2004;31:247-256.
Rintala M, Grenman S, Puranen M, Syrjanen S. Natural history of oral papillomavirus infections in spouses: a prospective Finnish HPV Family Study. Journal of Clinical Virology 2006;35:89-94.
Clarke J, Terry RM, Lacey CJ. A study to estimate the prevalence of upper respiratory tract papillomatosis in patients with genital warts. International Journal of STD & AIDS 1991;2:114-115.
Aaltonen LM, Cajanus S, Back L, Nieminen P, Paavonen J, Ranki A. Extralaryngeal HPV infections in male patients with adult-onset laryngeal papillomatosis. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 2005;262:708-712.
Gillison ML, Broutian T, Pickard RKL et al. Prevalence of oral HPV infection in the United States, 2009-2010. JAMA 2012;307:E1-E11.
Winer RL, Koutsky LA. Genital Human Papillomavirus Infection. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;489-508.
Castro TP, Bussoloti F, I. Prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) in oral cavity and oropharynx. [Review] [82 refs]. Revista Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia 2006;72:272-282.
Miller CS, White DK. Human papillomavirus expression in oral mucosa, premalignant conditions, and squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective review of the literature. [Review] [99 refs]. Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology Oral Radiology & Endodontics 1996;82:57-68.
Terai M, Hashimoto K, Yoda K, Sata T. High prevalence of human papillomaviruses in the normal oral cavity of adults. Oral Microbiology & Immunology 1999;14:201-205.
Derkay CS, Darrow DH. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. [Review] [63 refs]. Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology 2006;115:1-11.
Derkay CS. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. [Review] [39 refs]. Laryngoscope 2001;111:57-69.
Hawes SE, Kiviat NB. Screening for Cervical Cancer. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1075-1104.
Balasubramanian A, Palefsky JM, Koutsky LA. Cervical Neoplasia and Other STD-Related Genital Tract Neoplasias. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1051-1074.
Datta DS, Dunne E, Saraiya M, Unger E, Markowitz L. Human Papillomavirus. In: Roush SW, McIntyre L, Baldy LM, eds. Manual for the Surveillance of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases. Fourth ed. Atlanta, GA: Centers of Disease Control and Prevention; 2008;1-10.
Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al. Use of 9-valent human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination: updated HPV vaccination recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR – Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report. Recommendations and Reports. 2014;63(RR05):1-30.
Petrosky E, Bocchini Jr JA, Hariri S, et al. Human papillomavirus vaccination: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR – Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report. 2015;64(11):300-304
Derkay CS, Wiatrak B. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: a review. [Review] [106 refs]. Laryngoscope 2008;118:1236-1247.
Ragin CC, Modugno F, Gollin SM. The epidemiology and risk factors of head and neck cancer: a focus on human papillomavirus. [Review] [152 refs]. Journal of Dental Research 2007;86:104-114.
Kreimer AR, Clifford GM, Boyle P, Franceschi S. Human papillomavirus types in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas worldwide: a systematic review. [Review] [31 refs]. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 2005;14:467-475.
Gillison ML. Human papillomavirus-related diseases: oropharynx cancers and potential implications for adolescent HPV vaccination. [Review] [99 refs]. Journal of Adolescent Health 2008;43:Suppl-60.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Making Sense of Your Pap and HIV Test Results. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [serial online] 2008; Available from: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed February 25, 2010.
National Cancer Institute. Pap Test Fact Sheet. National Cancer Institute [serial online] 2009; Available from: National Cancer Institute. Accessed February 25, 2010.
Keet IP, brecht van LN, Sandfort TG, Coutinho RA, van Griensven GJ. Orogenital sex and the transmission of HIV among homosexual men. AIDS 1992;6:223-226.
del Romero J., Marincovich B, Castilla J et al. Evaluating the risk of HIV transmission through unprotected orogenital sex. AIDS 2002;16:1296-1297.
de Vincenzi I. A longitudinal study of human immunodeficiency virus transmission by heterosexual partners. European Study Group on Heterosexual Transmission of HIV. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;331:341-346.
Page-Shafer K, Shiboski CH, Osmond DH et al. Risk of HIV infection attributable to oral sex among men who have sex with men and in the population of men who have sex with men. AIDS 2002;16:2350-2352.
Samuel MC, Hessol N, Shiboski S, Engel RR, Speed TP, Winkelstein W, Jr. Factors associated with human immunodeficiency virus seroconversion in homosexual men in three San Francisco cohort studies, 1984-1989. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 1993;6:303-312.
Vittinghoff E, Douglas J, Judson F, McKirnan D, MacQueen K, Buchbinder SP. Per-contact risk of human immunodeficiency virus transmission between male sexual partners. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;150:306-311.
Lavoie E, Alary M, Remis RS et al. Determinants of HIV seroconversion among men who have sex with men living in a low HIV incidence population in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapies. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2008;35:25-29.
Schacker T. The role of HSV in the transmission and progression of HIV. [Review] [45 refs]. Herpes 2001;8:46-49.
van Griensven GJ, Tielman RA, Goudsmit J et al. Risk factors and prevalence of HIV antibodies in homosexual men in the Netherlands. American Journal of Epidemiology 1987;125:1048-1057.
Raiteri R, Fora R, Sinicco A. No HIV-1 transmission through lesbian sex. Lancet 1994;344:270.
Darrow WW, Echenberg DF, Jaffe HW et al. Risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections in homosexual men. American Journal of Public Health 1987;77:479-483.
Moir S, Chun T-W, Fauci AS. Immunology and Pathogenesis of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;341-358.
Coombs RW. Clinical Laboratory Diagnosis of HIV-1 and Use of Viral RNA to Monitor Infection. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1329-1347.
Eron JJ, Hirsch MS. Antiviral Therapy of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1393-1421.
Kaplan JE, Masur H. Preventing Opportunistic Infections Among HIV-Infected Persons. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1423-1440.
Decker CF, Masur H. Clinical Management of HIV Infection: Management of Opportunistic Infections. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1441-1467.
Cornett PA, Volberding P. AIDS-Related Malignancies. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1470-1421.
Press N, Chavez VM, Ticona E et al. Screening for sexually transmitted diseases in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients in Peru reveals an absence of Chlamydia trachomatis and identifies Trichomonas vaginalis in pharyngeal specimens. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2001;32:808-814.
Hobbs MM, Sena AC, Swygard H, Schwebke JR. Trichomas vaginalis and Trichomoniasis. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;771-793.
Lemon SM, Lok A, Alter MJ. Viral Hepatitis. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;509-543.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Shigella sonnei Outbreak Among Men Who Have Sex with Men — San Francisco, California, 2000–2001. MMWR – Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report 2001;50:922-926.
Aragon TJ, Vugia DJ, Shallow S et al. Case-control study of shigellosis in San Francisco: the role of sexual transmission and HIV infection. Clin Infect Dis 2007;44:327-334.
Rompalo AM, Quinn TC. Sexually Transmitted Intestinal Syndromes. In: Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE et al., eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008;1277-1308.
Salit IE, Khairnar K, Gough K, Pillai DR. A possible cluster of sexually transmitted Entamoeba histolytica: genetic analysis of a highly virulent strain. Clin Infect Dis 2009;49:346-353.
Stark D, van Hal SJ, Matthews G, Harkness J, Marriott D. Invasive amebiasis in men who have sex with men, Australia. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2008;14:1141-1143.
Baggaley RF, White RG, Boily MC. Systematic review of orogenital HIV-1 transmission probabilities. [Review] [29 refs]. International Journal of Epidemiology 2008;37:1255-1265.
Bratt GA, Berglund T, Glantzberg BL, Albert J, Sandstrom E. Two cases of oral-to-genital HIV-1 transmission. International Journal of STD & AIDS 1997;8:522-525.
Edwards S, Carne C. Oral sex and the transmission of viral STIs. [Review] [99 refs]. Sexually Transmitted Infections 1998;74:6-10.
Edwards SK, White C. HIV seroconversion illness after orogenital contact with successful contact tracing. International Journal of STD & AIDS 1995;6:50-51.
Lifson AR, O’Malley PM, Hessol NA, Buchbinder SP, Cannon L, Rutherford GW. HIV seroconversion in two homosexual men after receptive oral intercourse with ejaculation: implications for counseling concerning safe sexual practices. American Journal of Public Health 1990;80:1509-1511.
Varghese B, Maher JE, Peterman TA, Branson BM, Steketee RW. Reducing the risk of sexual HIV transmission: quantifying the per-act risk for HIV on the basis of choice of partner, sex act, and condom use. Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2002;29:38-43.
Weinstock H, Workowski KA. Pharyngeal gonorrhea: an important reservoir of infection? Clinical Infectious Diseases 2009;49:1798-1800.
Robinson EK, Evans BG. Oral sex and HIV transmission. [Review] [16 refs]. AIDS 1999;13:737-738.
Rothenberg RB, Scarlett M, del RC, Reznik D, O’Daniels C. Oral transmission of HIV. [Review] [126 refs]. AIDS 1998;12:2095-2105.
Hawkins DA. Oral sex and HIV transmission. Sexually Transmitted Infections 2001;77:307-308.
- Page last reviewed: December 1, 2016
- Page last updated: January 4, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir