Testing Health Care Workers
 Tuberculosis (TB) transmission has been documented in health care settings where workers and patients come in contact with people who have TB disease. Periodic testing of health care workers is recommended as part of a TB Infection Control Plan and may be required by state regulations.
Tuberculosis (TB) transmission has been documented in health care settings where workers and patients come in contact with people who have TB disease. Periodic testing of health care workers is recommended as part of a TB Infection Control Plan and may be required by state regulations.
TB testing programs should include anyone working or volunteering in health-care settings. Persons (health care workers and non- health care workers) who have face to face contact or potential exposure to TB through shared air or space with infectious patient(s) should be part of a TB testing program.
There are two types of testing for TB in health care workers.
- Initial baseline testing upon hire: Two-step testing with a TB skin test or a TB blood test
- Annual or serial screening: determined by state regulations or risk assessment outcomes.
Health care facilities have different TB testing requirements. Facilities should conduct staff TB testing based on risk classification.
|
Risk classification |
Frequency of testing |
|
Low |
Baseline; then test if TB exposure occurs |
|
Medium |
Baseline, then annually |
|
Potential ongoing transmission |
Baseline, then every 8–10 weeks until evidence of transmission has ceased |
To determine the risk classification for your facility, review the infection control guidelines and complete the Appendix B. Tuberculosis (TB) Risk Assessment Worksheet (PDF - 195k).
Contact your State TB Control Program for information about health care worker TB testing requirements in your state.
Baseline Testing
A baseline test should be given prior to employment. The result of this test can be compared with later tests (due to potential exposure or as part of annual testing) to help determine if recent TB transmission has occurred in the facility.
Annual or Serial Testing
You may need to test for TB on a regular basis. To standardize the interpretation of results, the same test should be used for the baseline and the later tests.
Baseline Testing: Two-Step Test
Two-step testing with the Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST) should be used for baseline or initial testing. Some people with latent TB infection have a negative reaction when tested years after being infected. The first TST may stimulate or boost a reaction. Positive reactions to subsequent TSTs could be misinterpreted as a recent infection.
Step 1
- Administer first TST following proper protocol
- Review result
- Positive — consider TB infected, no second TST needed; evaluate for TB disease.
- Negative — a second TST is needed. Retest in 1–3 weeks after first TST result is read.
- Document result
Step 2
- Administer second TST 1-3 weeks after first test
- Review results
- Positive — consider TB infected and evaluate for TB disease.
- Negative — consider person not infected.
- Document result
Two-Step TST Testing
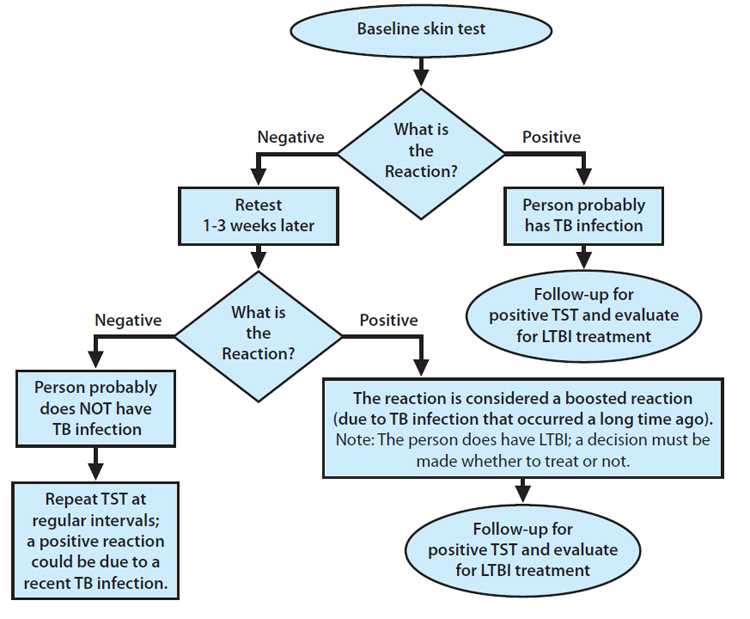
Annual or Serial Testing
Once everyone in your facility has a baseline TB test, you may need to test on a regular basis. To standardize the interpretation of results, the same test should be used for the baseline and the later tests. There is no need for a two-step TST test process for annual TB testing. The process for annual testing with a TB skin test is as follows:
- Administer the TB skin test following proper protocol
- Review result — a change from a prior negative test result to a positive test result is evidence of recent TB infection
- Document result
Baseline Testing
Using a TB blood test for initial or baseline testing does not require two-step testing and is not affected by BCG vaccination. The process for baseline testing using a TB blood test is as follows:
- Administer TB blood test following usual protocol
- Review result
- Negative — consider not infected
- Positive — consider TB infected and evaluate for TB disease
- Document result
Annual or Serial Testing
Once everyone your facility has an initial TB test result, you may need to test on a regular basis. To standardize the interpretation of results, the same test should be used for the baseline and the later tests. The process for annual testing for TB with a TB blood test is as follows:
- Administer the TB blood test following proper protocol
- Review result — a change from a prior negative test result to a positive test result is evidence of recent TB infection
- Document result
Related Links
- State TB Control Offices
- Guidelines for preventing the transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in health-care settings, 2005
- Testing and Diagnosis Fact sheets
- Testing and Diagnosis Guidelines
- Mantoux Tuberculin Skin Test Training Products
- What You Need to Know About the TB Skin Test (Pamphlet – PDF 202k)
- General information about TB blood tests
- Questions and Answers About TB
- Page last reviewed: April 15, 2016
- Page last updated: April 15, 2016
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir